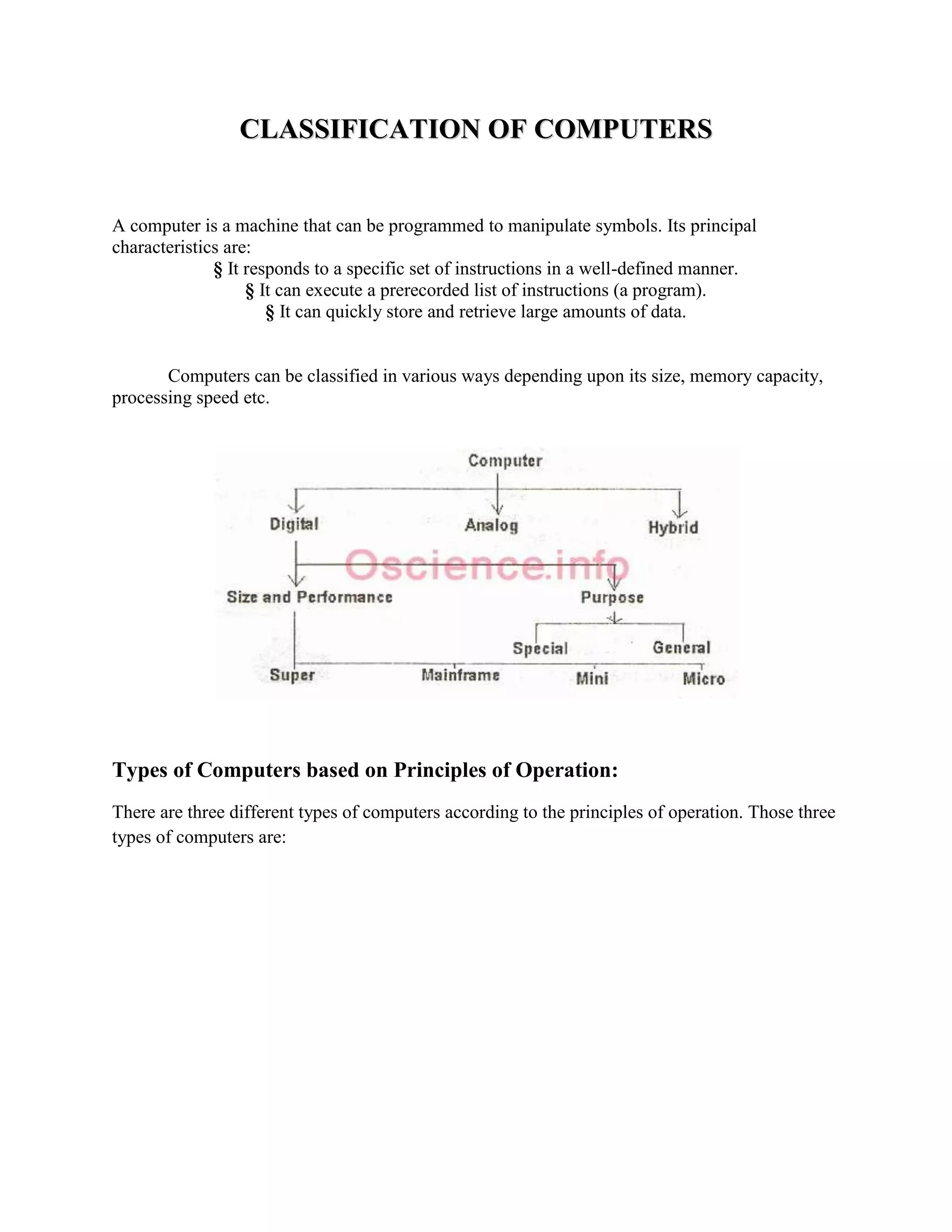
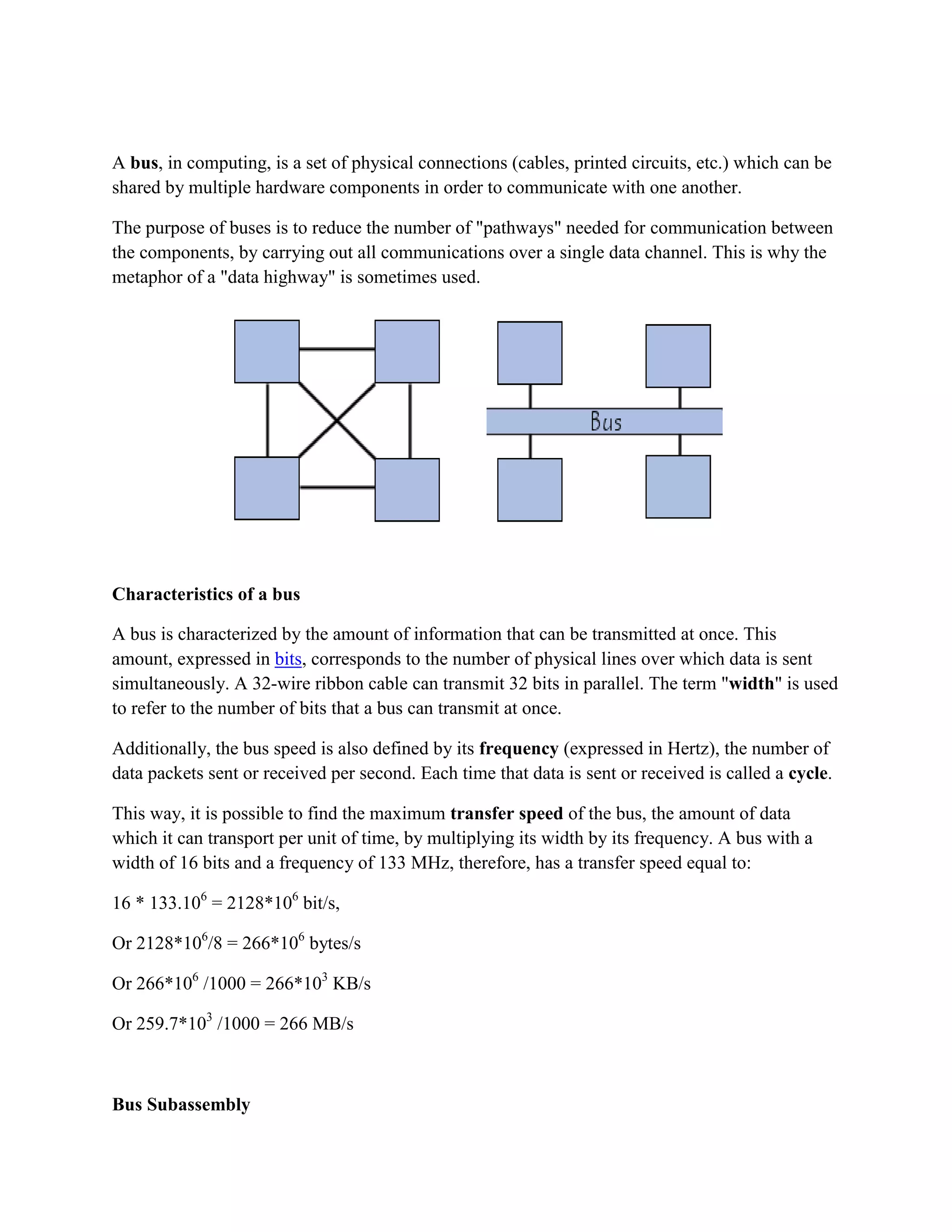
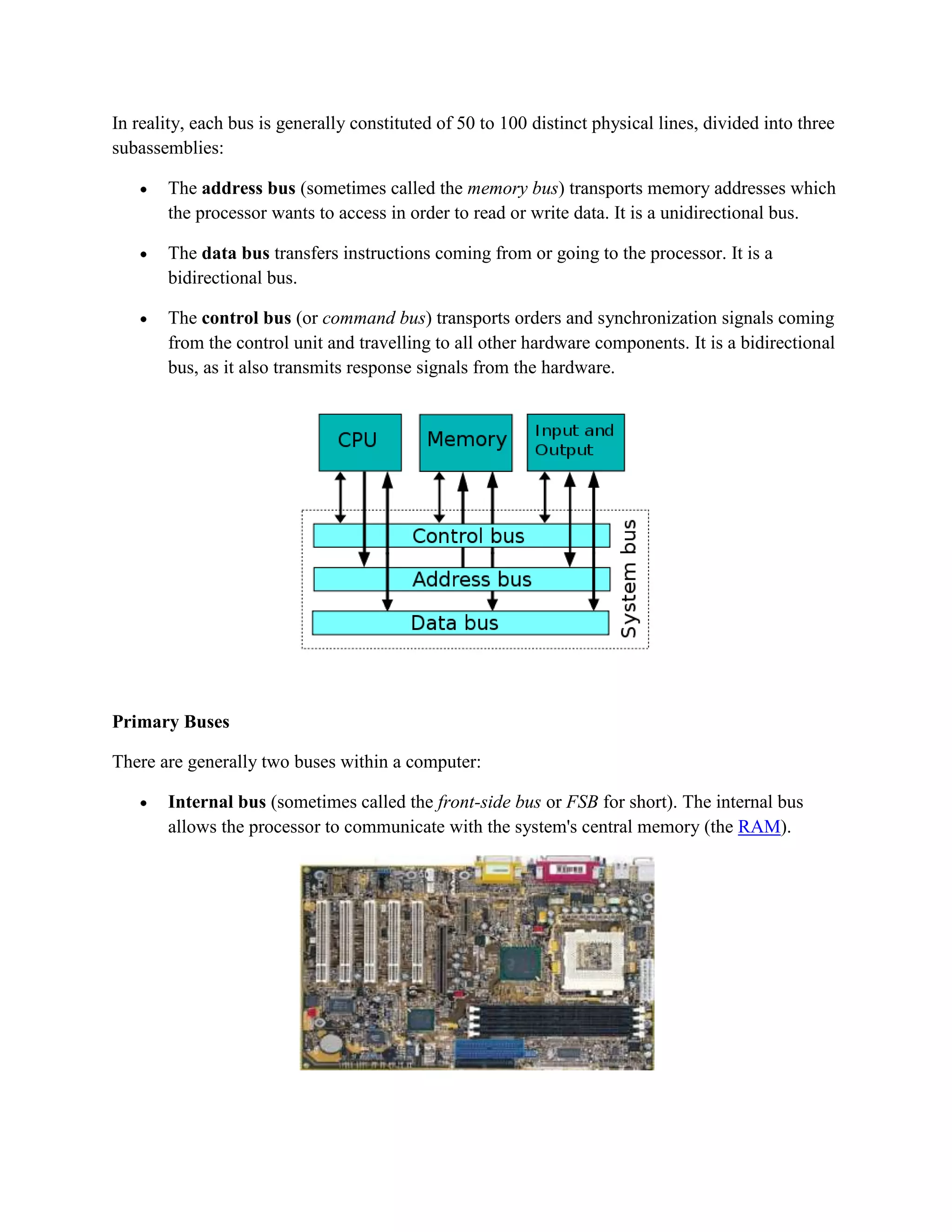
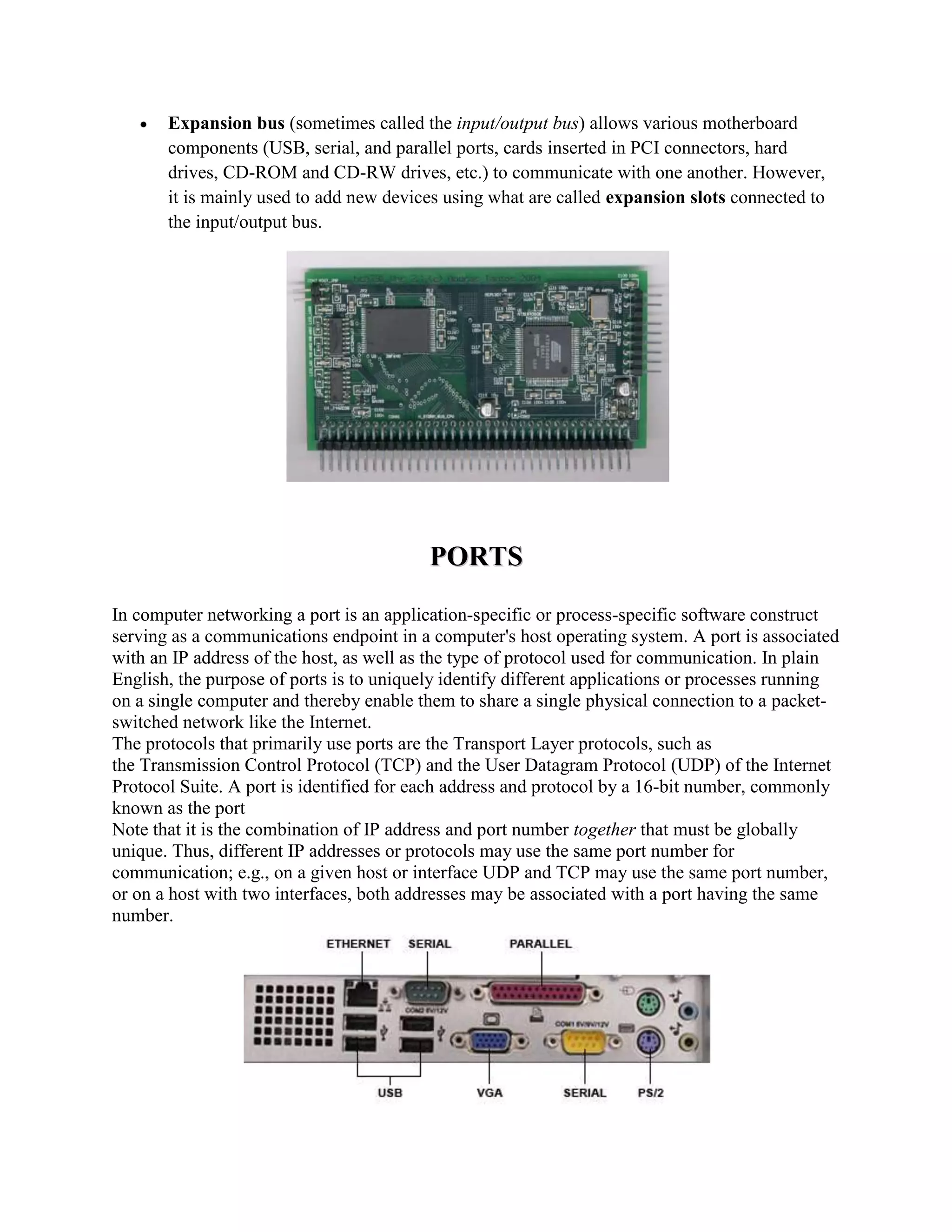
There are three main types of computers based on their principles of operation: analog computers, digital computers, and hybrid computers. Digital computers are the most common today and operate using binary numbers. Computers can also be classified based on their size, memory capacity, and processing speed into supercomputers, mainframe computers, mini computers, and microcomputers (personal computers). Microcomputers are the most ubiquitous. Computers also have different functions and configurations including servers, workstations, information appliances, and embedded systems. Buses and ports allow for communication between different computer components. A modem facilitates data transmission over telephone or cable lines by converting between digital and analog formats.