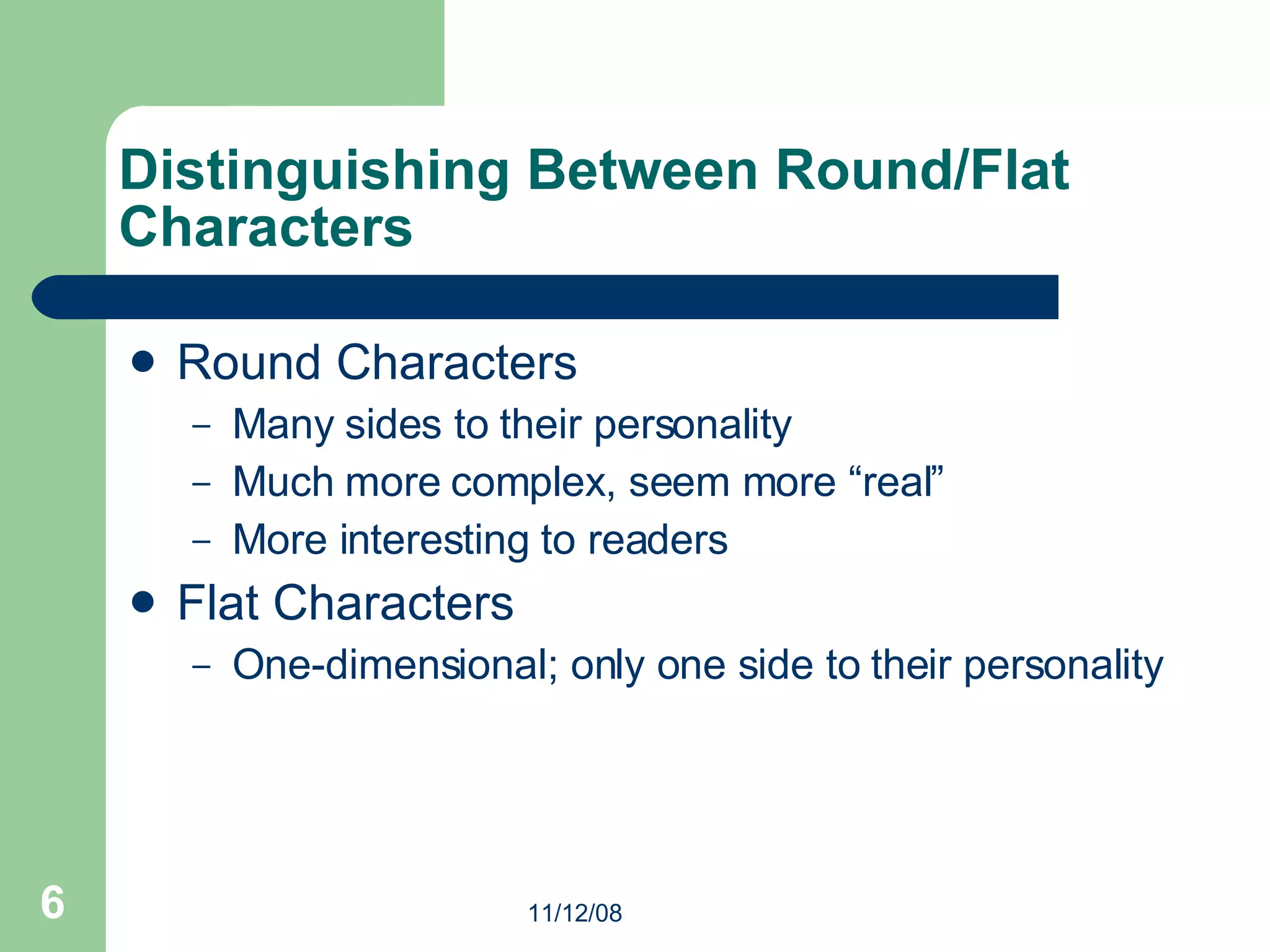
This document provides an overview of how to analyze characters in a story. It discusses determining whether a character is main or minor, dynamic or static, round or flat, and the protagonist or antagonist. It also provides guidance on interpreting characters by stating an opinion and backing it up with evidence from the story through paraphrasing, summarizing, or quoting. The document gives an example outline for analyzing specific characters like Mama, Dee, or Maggie and identifying what elements and evidence support that characterization.