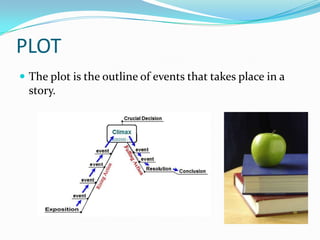
This document defines key literary elements used in fiction stories, including characters (protagonist, antagonist), setting, plot, conflict, climax, resolution, theme, point of view, foreshadowing, author's purpose, dialogue, tone, symbolism, and different genres (realistic fiction, science fiction, historical fiction, fantasy). It provides descriptions and examples for each element to explain how they are used in fictional stories.