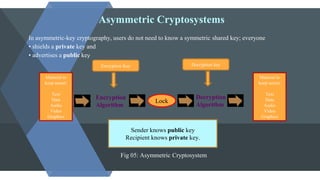
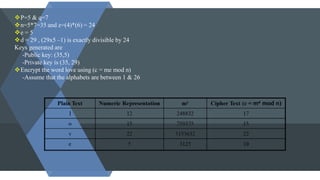
The document discusses symmetric and asymmetric key cryptography. It begins with an introduction to cryptography and its objectives of confidentiality, integrity, authentication and non-repudiation. It then explains the differences between symmetric and asymmetric cryptosystems. Symmetric cryptosystems involve a shared key between sender and receiver, while asymmetric cryptosystems use public and private key pairs. Examples of traditional symmetric ciphers like simple substitution and transposition ciphers are provided. The document also outlines the RSA algorithm as an example of asymmetric cryptography and discusses some limitations of both symmetric and asymmetric approaches.
















![References
[1] Thomas H. Cormen, Charles E. Leiserson, Ronald L. Rivest, and Clifford Stein. Introduction to Algorithms. MIT Press
and McGraw-Hill, 2001. ISBN 0-262-03293-7. Section 31.7: The RSA public-key cryptosystem, pp.881–887
[2] Bruce Schneier. Applied Cryptography. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1996. (ISBN: 0471128457)
[3] Bob Thibadeau http://dollar.ecom.cmu.edu/sec/lec02.ppt.
[4] [2]Data Communications and Networking By Behrouz A.Forouzan.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/symmetricandassymetriccryptography-201012141944/85/Symmetric-and-asymmetric-key-cryptography-23-320.jpg)
