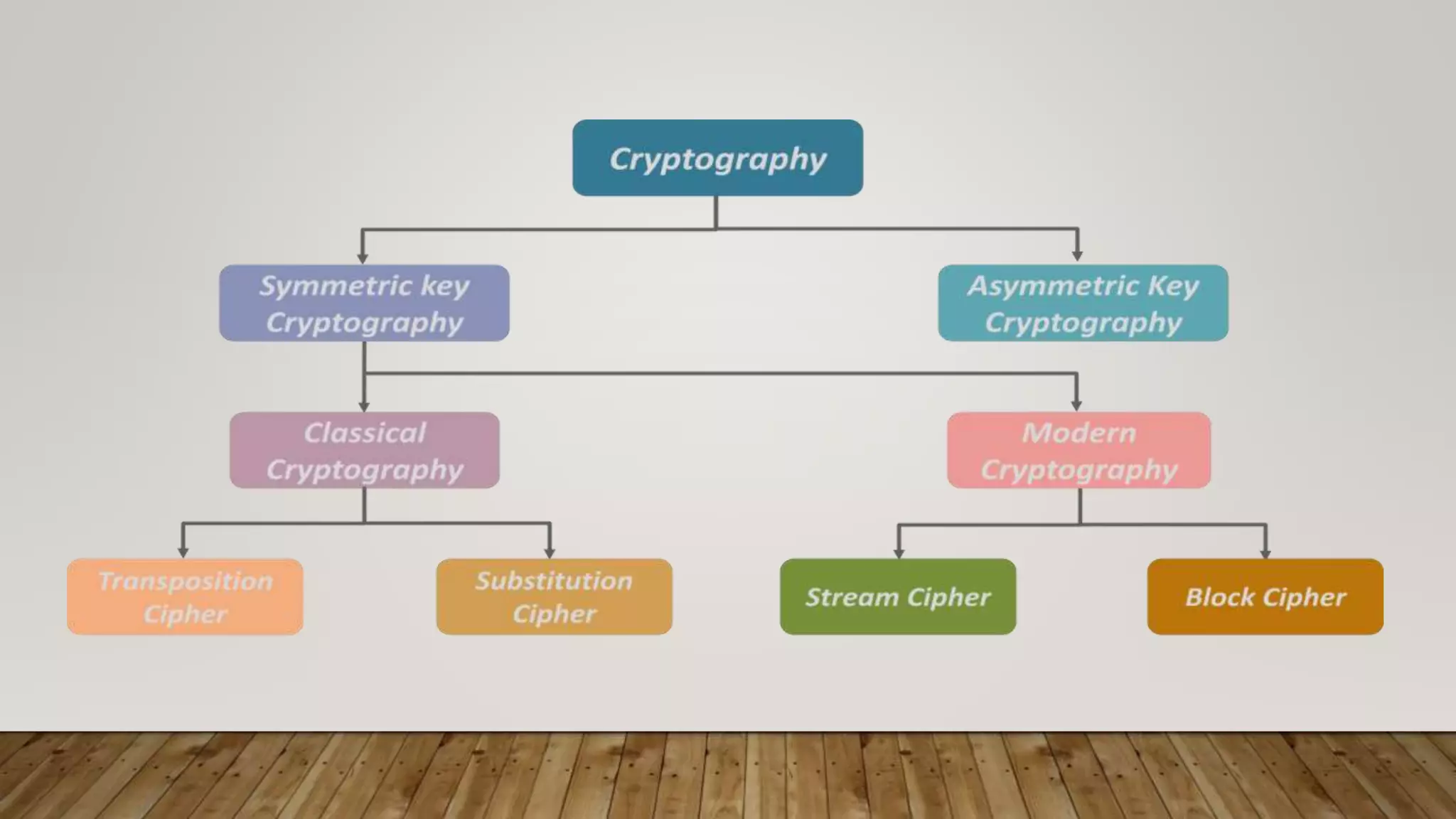
Symmetric and asymmetric encryption are two types of encryption algorithms. Symmetric encryption uses a single secret key that is shared between parties to encrypt and decrypt data. It is faster than asymmetric encryption but key distribution is an issue. Asymmetric encryption uses a public/private key pair, where the public key encrypts data and the private key decrypts it. It does not require key exchange but is slower than symmetric encryption due to longer key lengths. Both algorithms have advantages and disadvantages around speed, security, and key management.