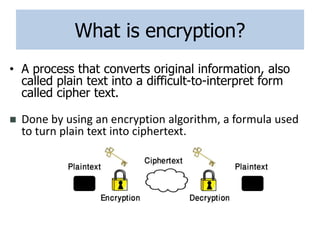
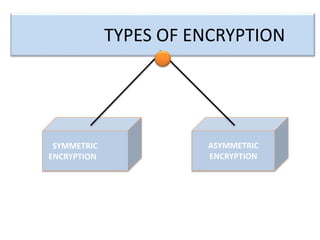
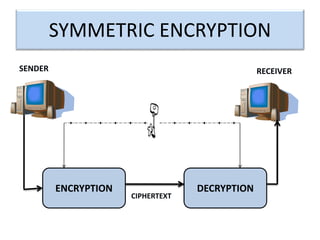
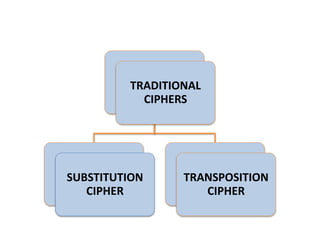
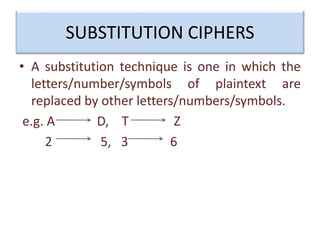
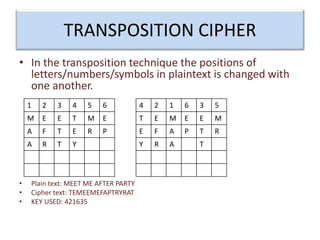
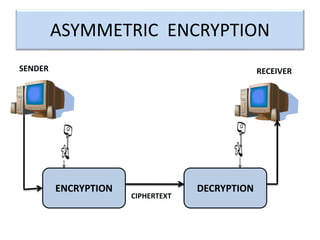
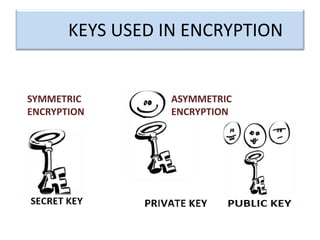
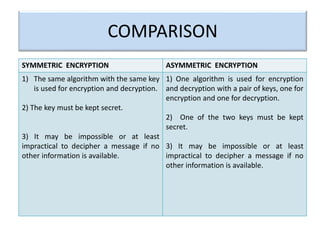
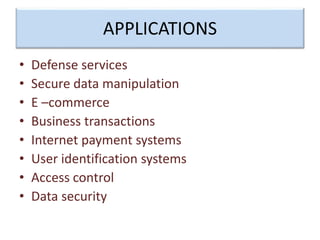
Encryption is a process that converts plain text into cipher text using an encryption algorithm. There are two main types: symmetric encryption which uses a shared secret key for encryption and decryption, and asymmetric encryption which uses a public/private key pair. While symmetric encryption is faster, asymmetric encryption is more secure as the private key is never shared. Encryption is used to provide authentication, privacy, accountability, integrity and security for data across various applications such as e-commerce, banking, defense services and more.