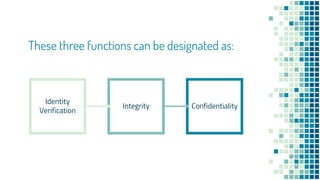
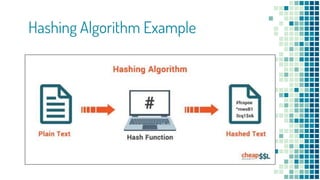
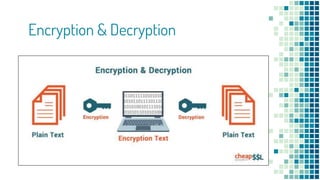
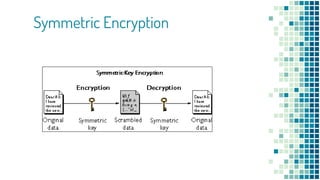
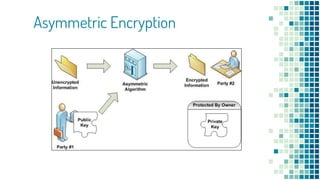
The document clarifies the differences between hashing, encryption, and encoding in the context of internet security. Hashing ensures data integrity by generating unique hash values that change with any alteration in input, while encryption transforms data into an unreadable format for confidentiality, utilizing cryptographic keys. Encoding, on the other hand, alters data format without security measures, allowing for compatibility among different systems.