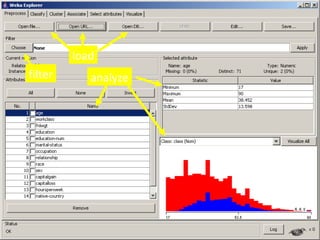
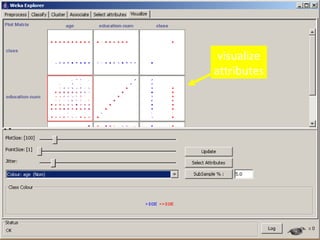
Weka is a collection of machine learning algorithms and data pre-processing tools developed at the University of Waikato. It contains tools for data pre-processing, classification, regression, clustering, association rule mining, and visualization. Weka is open source, free to use, and popular for research and applications. It has a graphical user interface and supports a variety of data formats including ARFF files.