Embed presentation
Downloaded 175 times





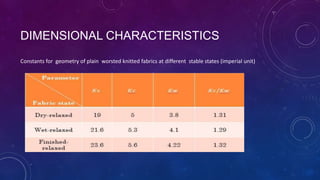










This document provides information about dimensional stability and geometry in weft knit fabric. It was presented by 7 students from the Textile department of Bangladesh University of Business & Technology. The key points discussed include how knitted fabrics are prone to changes in size and shape from wear and washing. It also discusses dimensional stability states, loop length, areal density, fabric cover, tightness factor, and spirality - defined as dimensional distortion where wale rows are not perpendicular to courses. Formulas are presented for factors that influence the angle of spirality, such as the number of feeders, loop shape, and number of active needles.














