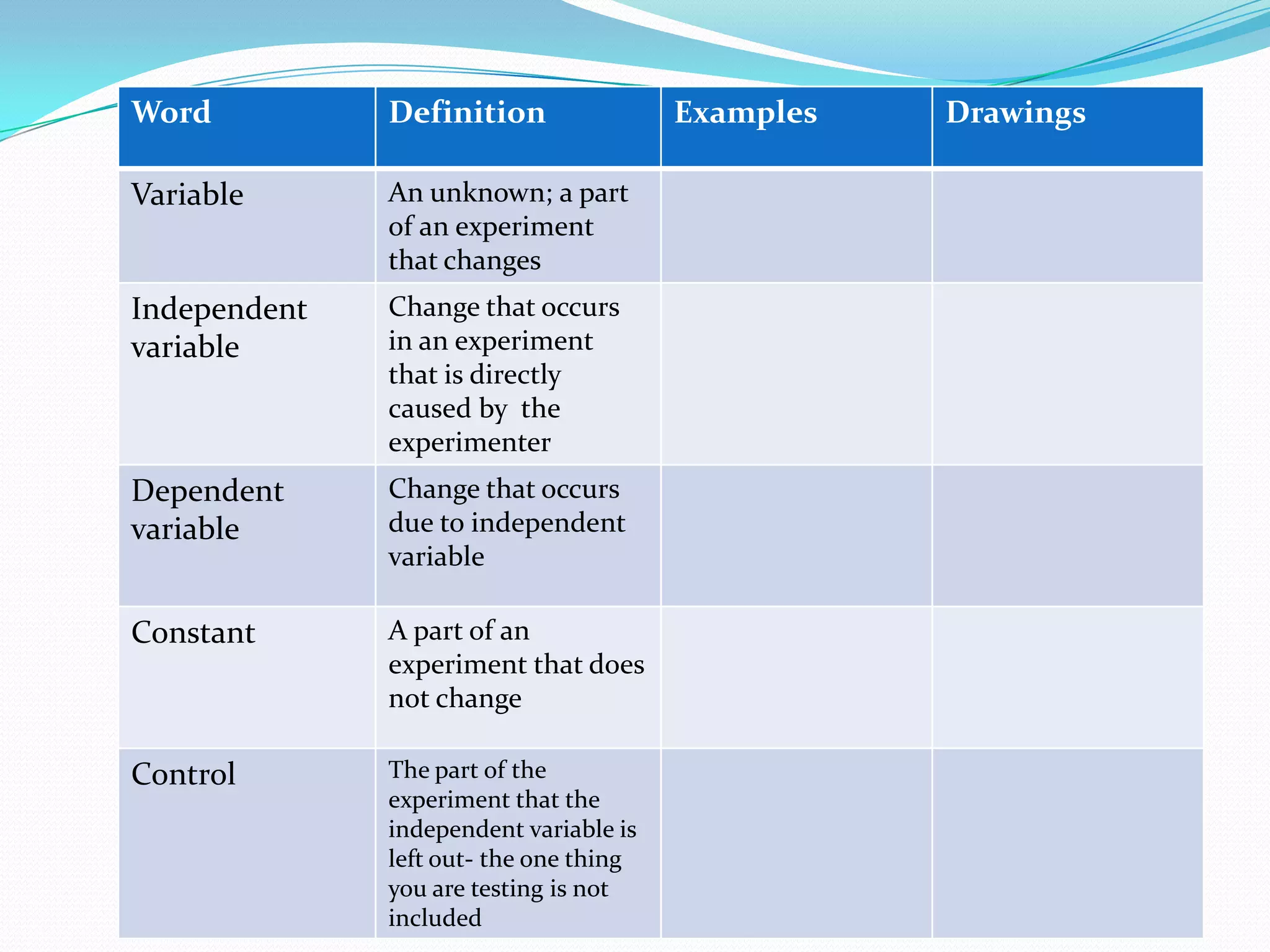
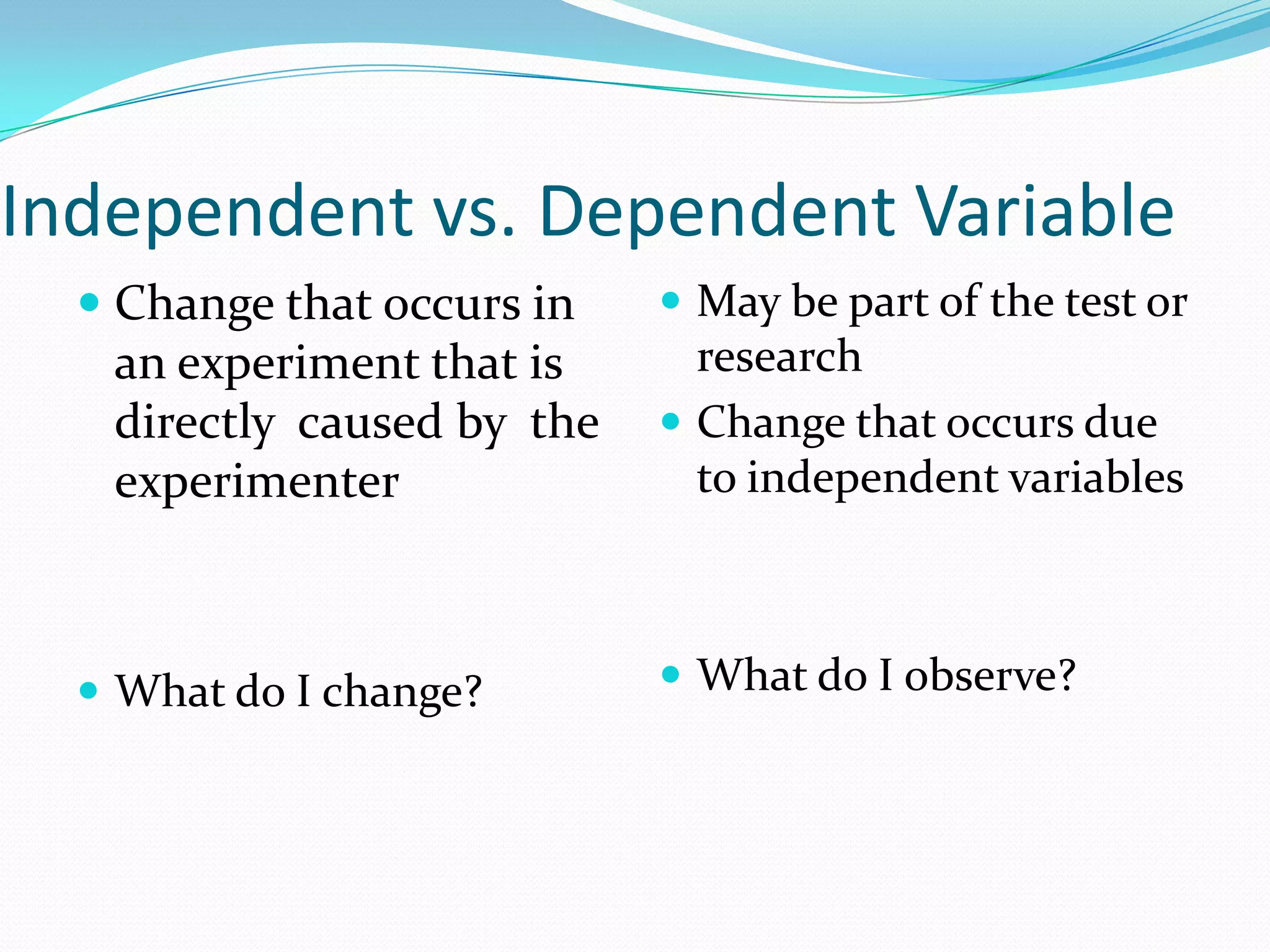
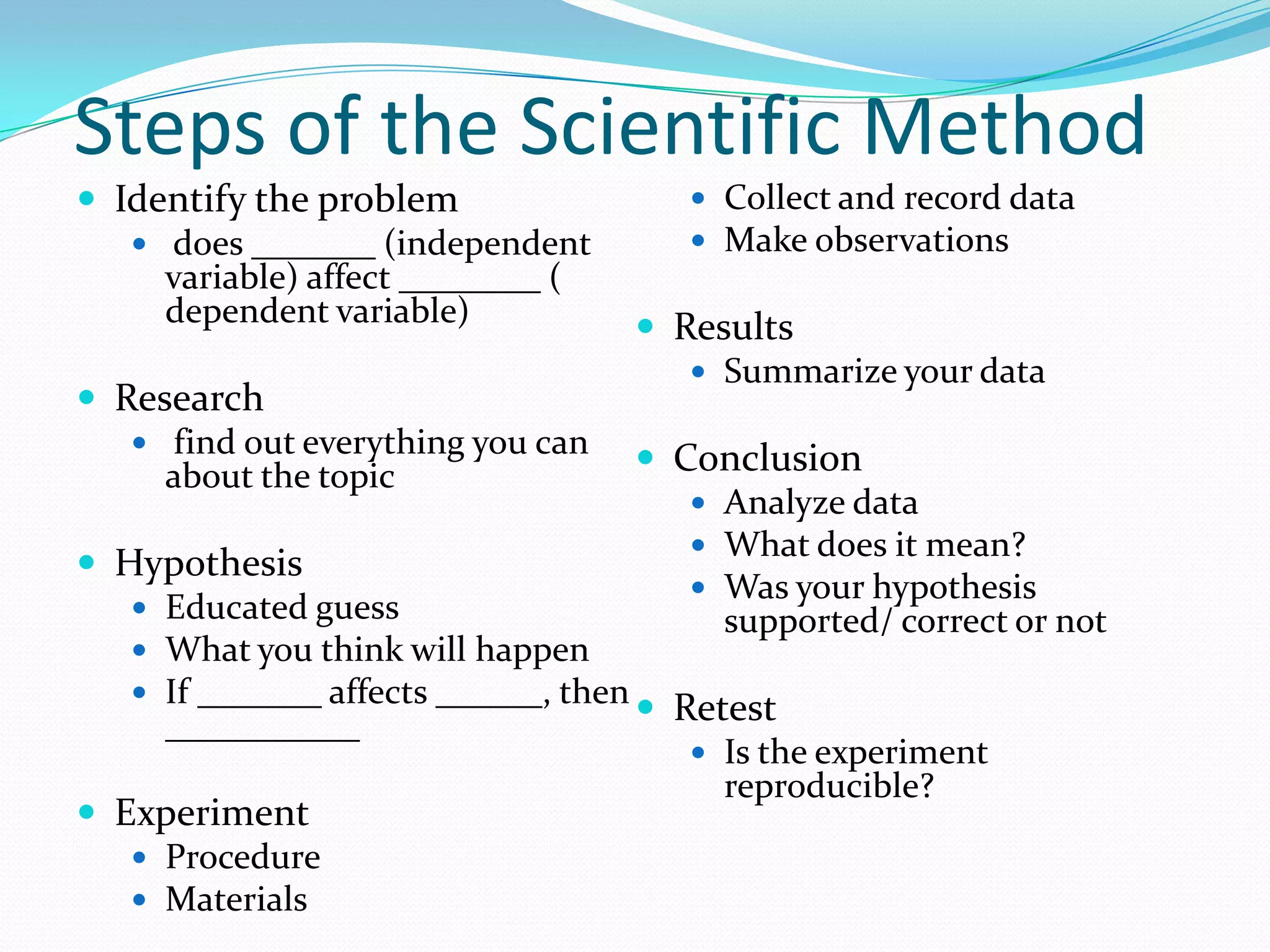
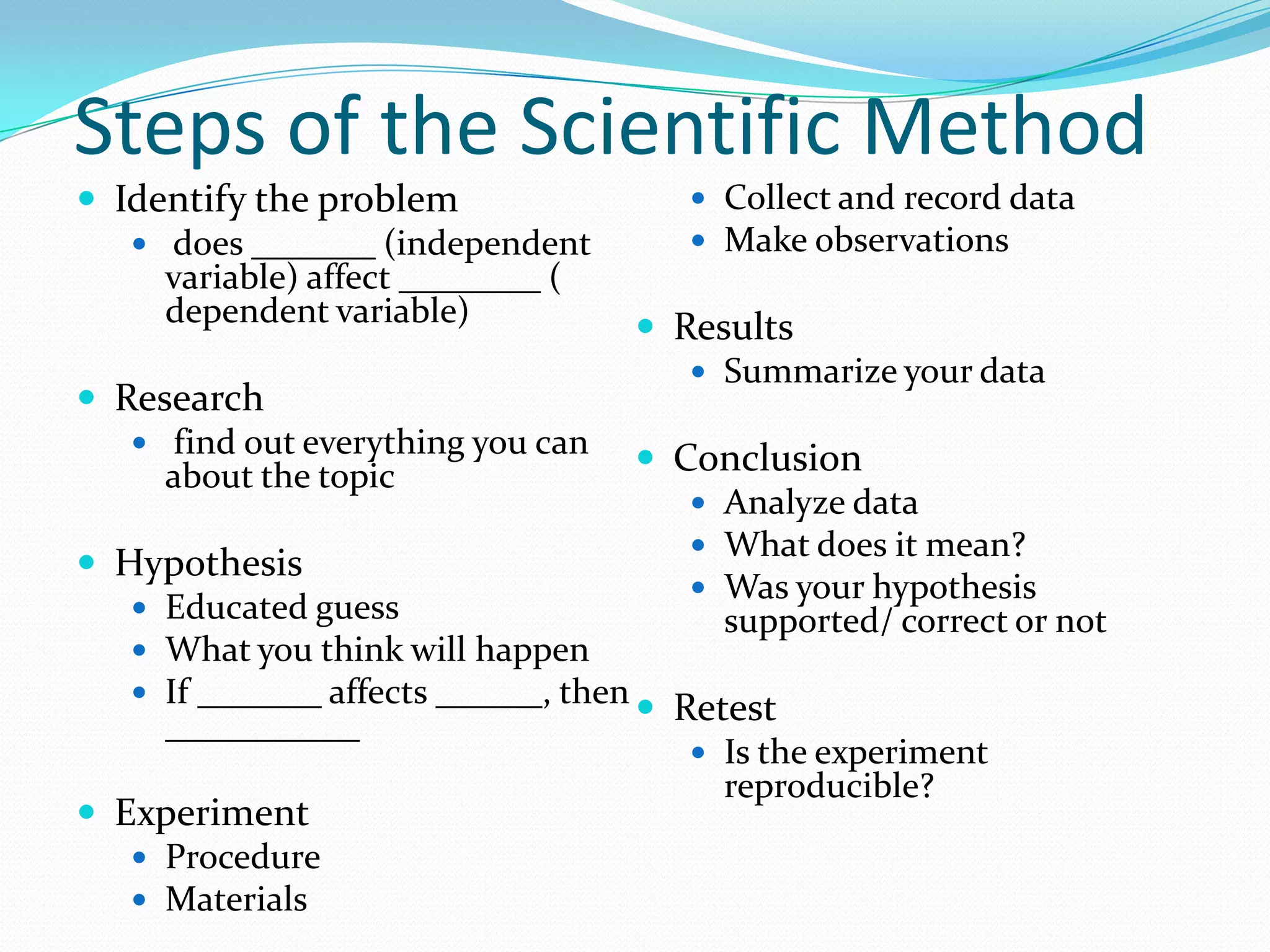
This document provides instruction and review of the scientific method. It begins with a warm up asking students to list what they remember about the scientific method. It then reviews the key steps of the scientific method including developing a title, problem, hypothesis, procedure, materials, performing the experiment, collecting data/results, and reaching a conclusion. The document also defines key scientific vocabulary words and has students practice applying these terms. It provides examples of experiments and homework problems for students to practice the scientific method.