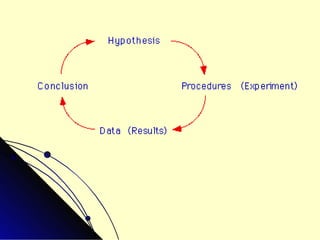
Scientific investigations follow a standard process:
1) Ask a question and form a hypothesis to make a prediction about the outcome.
2) Design an experiment to test the hypothesis by manipulating variables and collecting data through observation and measurement.
3) Analyze the results to determine whether the data supports or refutes the original hypothesis.