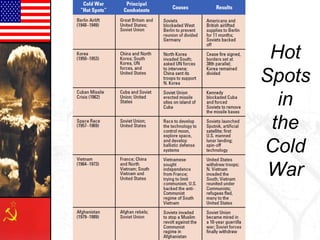
The Cold War (1947-1991) was marked by political and military tensions between the U.S. and the USSR, characterized by ideological discord without direct conflict. Key events included the Korean War, Cuban Missile Crisis, and Vietnam War, alongside strategies such as proxy wars, brinkmanship, and détente. The era ended with the collapse of the Soviet Union, driven by mutual distrust, competition for global influence, and internal reforms.







![• "From Stettin on the
Baltic to Trieste on
the Adriatic, an iron
curtain has
descended across
the continent [of
Europe]. Behind that
line lie all the
capitals of the
ancient states of
central and eastern
Europe.... All these
famous cities and
populations lie in
what I must call the
Soviet sphere."
--Winston Churchill , 1946](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-9-320.jpg)
![Soviet &
Eastern Bloc
Nations
[“Iron Curtain”]
US & the
Western
Democracies
GOAL spread world-
wide Communism
GOAL “Containment”
of Communism & the
eventual collapse of the
Communist world.
[George Kennan]METHODOLOGIES:
Espionage [KGB vs. CIA]
Arms Race [nuclear escalation]
Ideological Competition for the minds and hearts
of Third World peoples [Communist govt. &
command economy vs. democratic govt. & capitalist
economy] “proxy wars”
Bi-Polarization of Europe [NATO vs. Warsaw Pact]
The Ideological Struggle](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-10-320.jpg)
![1.1. Civil War in Greece.Civil War in Greece.
2.2. Turkey under pressure from theTurkey under pressure from the
USSR for concessions in theUSSR for concessions in the
Dardanelles.Dardanelles.
3.3. The U. S. should support freeThe U. S. should support free
peoples throughout the world whopeoples throughout the world who
were resisting takeovers by armedwere resisting takeovers by armed
minorities or outside pressures…Weminorities or outside pressures…We
must assist free peoples to work outmust assist free peoples to work out
their own destinies in their own way.their own destinies in their own way.
4.4. The U.S. gave Greece & TurkeyThe U.S. gave Greece & Turkey
$400 million in aid.$400 million in aid.
Truman Doctrine [1947]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-11-320.jpg)
![1.1. ““European RecoveryEuropean Recovery
Program.”Program.”
2.2. Secretary of State,Secretary of State,
George MarshallGeorge Marshall
3.3. The U. S. should provideThe U. S. should provide
aid toaid to allall European nationsEuropean nations
that need it. This movethat need it. This move
is not against any country or doctrine,is not against any country or doctrine,
but against hunger, poverty, desperation,but against hunger, poverty, desperation,
and chaos.and chaos.
4.4. $12.5 billion of US aid to Western$12.5 billion of US aid to Western
Europe extended to Eastern Europe &Europe extended to Eastern Europe &
USSR, [but this was rejected].USSR, [but this was rejected].
Marshall Plan [1948]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-12-320.jpg)

![• Blockade of Berlin
began on June 24, ’48
• From June 1948 to
May 1949, U.S. and
British planes airlift
1.5 million tons of
supplies to the
residents of West
Berlin.
• After 200,000
flights, the Soviet
Union lifts the
blockade.
Berlin Airlift
[1948-49]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-14-320.jpg)
![• The airlift marked a rise in tensions between the West and the
Soviets, but it also helped heal divisions left by World War II.
• Almost immediately, The United States, Great Britain, and
France shifted from Germany's conquerors to its protectors.
• "The airlift was the starting point for Germany's inclusion in the
West and for the reconciliation with the Western powers,"
Berlin Mayor Eberhard Diepgen says.
• Allied cooperation paved way for formation of new military
alliance, North Atlantic Treaty Organization, NATO
• Soviets formed their own alliance called Warsaw Pact in 1955
Berlin Airlift
[1948-49]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-15-320.jpg)
![} The Soviet UnionThe Soviet Union
exploded its firstexploded its first
A-bomb in 1949.A-bomb in 1949.
} Now there wereNow there were
two nucleartwo nuclear
superpowers!superpowers!
Arms Race Explodes[1949]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-16-320.jpg)
![ United StatesUnited States
BelgiumBelgium
BritainBritain
CanadaCanada
DenmarkDenmark
FranceFrance
IcelandIceland
ItalyItaly
LuxemburgLuxemburg
NetherlandsNetherlands
NorwayNorway
PortugalPortugal
1952: Greece &1952: Greece &
TurkeyTurkey
1955: West Germany1955: West Germany
1983: Spain1983: Spain
North Atlantic Treaty Organization [1949]
NATO](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-17-320.jpg)
![} U. S. S. R.U. S. S. R.
} AlbaniaAlbania
} BulgariaBulgaria
} CzechoslovakiaCzechoslovakia
} East GermanyEast Germany
} HungaryHungary
} PolandPoland
} Romania (ForRomania (For
Pheeeoooo)Pheeeoooo)
Warsaw Pact [1955]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-18-320.jpg)
![• In June, Jiang Jieshi
defeated by Mao
– Flee to island of Taiwan
• Oct 1, Mao proclaims
People’s Republic of
China (PRC)
• Two months later, Mao
travels to Moscow,
– negotiates the Sino-
Soviet Treaty of
Friendship, Alliance and
Mutual Assistance.
Communists Take Power in China
[1949]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-19-320.jpg)






![• On June 25, North Korean
communist forces cross
the 38th parallel and
invade South Korea.
• On June 27, Truman
orders U.S. forces to
assist the South Koreans
• The U.N. Security Council
condemns the invasion and
est’d a 15-nation fighting
force.
• Chinese troops enter the
conflict by year's end.
• Cease fire eventually
brings war to close by
1953
Korean War [1950-53]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-26-320.jpg)
![• After a long siege,
Vietnamese communists
under Ho Chi Minh defeat
French colonial forces at
Dien Bien Phu on May 7,
1954.
• In July, the Geneva
Accords divide the
country at the 17th
parallel, creating a North
and South Vietnam.
• The United States
assumes the chief
responsibility of providing
anti-communist aid to
South Vietnam.
Dein Bein Phu [1954]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-27-320.jpg)
![• On January 12, 1954 U.S.
Secretary of State John
Foster Dulles first
announces the doctrine of
Massive Retaliation.
• It threatens full-scale
nuclear attack on the
Soviet Union in response
to communist aggression
anywhere in the world.
John Foster Dulles and MacArthur in Korea, 1950
Massive Retaliation [1954]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-28-320.jpg)
![• On October 4, the Soviet
Union launches Sputnik, the
first man-made satellite to
orbit the Earth.
• In 1958, the U.S. creates the
National Aeronautics and
Space Administration, and
the space race is in full gear.
Sputnik I [1957]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-29-320.jpg)

![• On May 1, an American high-
altitude U-2 spy plane is shot
down on a mission over the Soviet
Union.
• After the Soviets announce the
capture of pilot Francis Gary
Powers, the United States
recants earlier assertions that
the plane was on a weather
research mission.
•Suffering major embarrassment,
Eisenhower was forced to admit
the truth, although he refused to
publicly apologize to Khrushchev.
•This refusal caused the Paris
Summit to collapse when
Khrushchev stormed out of
negotiations.
• Powers was sentenced to ten years in
prison, including seven years of hard
labor, following an infamous show-
trial. He served less than two years,
however, and was released in 1962 in
exchange for Soviet spy Rudolf Abel.
The U2 Affair [1960]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-32-320.jpg)
![• On August 15,
communist
authorities begin
construction on
the Berlin Wall to
prevent East
Germans from
fleeing to West
Berlin.
Berlin Wall [1961]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-33-320.jpg)
![Ich bin einIch bin ein
Berliner!Berliner!
President KennedyPresident Kennedy
tells Berlinerstells Berliners
that the West isthat the West is
with them!with them!
President Kennedy Speaks in Berlin
[1963]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-34-320.jpg)
![• January 1, 1959
leftist forces under
Fidel Castro
overthrow Fulgencio
Batista
• Castro nationalizes
the sugar industry
and signs trade
agreements with the
Soviet Union.
• The next year,
Castro seizes U.S.
assets on the island.
Castro Takes Power in Cuba [1959]
Khrushchev Embraces Castro [1961]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-35-320.jpg)
![• U.S.-organized invasion
force of 1,400 Cuban
exiles is defeated by
Castro's government
forces on Cuba's south
coast at the Bay of Pigs.
• Launched from Guatemala
in ships and planes
provided by the United
States, the invaders
surrender on April 20
after three days of
fighting.
• Kennedy takes full
responsibility for the
disaster.
Captured Cubans
Bay of Pigs [1961]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-36-320.jpg)
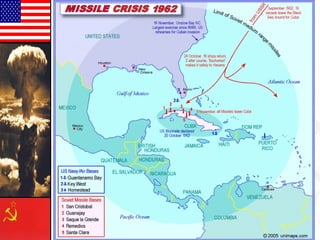
![• After Bay of Pigs invasion,
the Soviet Union installed
nuclear missiles in Cuba.
• After U-2 flights Kennedy
ordered a naval blockade
of Cuba on October 22
until the Soviet Union
removed its missiles.
• On October 28, the
Soviets agreed to remove
the missiles, defusing one
of the most dangerous
confrontations of the Cold
War.
Cuban Missile Crisis [1962]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-37-320.jpg)
![Vietnam War [1965-73]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-39-320.jpg)
![• North Vietnamese
patrol boats fired on
the USS Mattox in
the Gulf of Tonkin on
August 2.
• On August 7, the U.S.
Congress approves the
Gulf of Tonkin
Resolution, granting
President Johnson
authority to send U.S.
troops to South
Vietnam.
Gulf of Tonkin Resolution [1964]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-40-320.jpg)
![• Viet Cong guerrillas
and North Vietnamese
Army troops launched
attacks across South
Vietnam on January
30, the start of the
lunar new year Tet.
• In Saigon, guerrillas
battle Marines at the
U.S. Embassy.
• In March, Johnson
orders a halt to the
U.S. bombing of
North Vietnam and
offers peace talks.
Tet Offensive [1968]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-41-320.jpg)
![• 1968, Richard Nixon elected
President, defeating Hubert
Humphrey
• On June 8, 1969 U.S. President
Nixon announced his
"Vietnamization" plan, designed to
withdraw U.S ground forces from
Vietnam and turn control of the war
over to South Vietnamese forces.
Vietnamization [1968]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-42-320.jpg)

![• Nixon becomes the first U.S. president to
visit China, meeting with Mao Tse-tung on
February 21.
• The two countries issue a communique
recognizing their "essential differences"
while making it clear that "normalization
of relations" was in all nations' best
interests.
• The rapprochement changes the balance
of power with the Soviets.
President Nixon
Visits China [1972]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-44-320.jpg)

![• January 27, 1973, the United States,
South Vietnam, North Vietnam and the
Viet Cong sign the Paris Peace Treaty,
establishing a cease-fire.
• The United States is allowed to
continue providing aid to South Vietnam.
• Saigon falls in April 1975.
Paris Peace Treaty [1973]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-46-320.jpg)
![• 1975, Helsinki, Finland
• Attempt to reduce tensions
between Western Nations and
Communist Bloc
• Thirty-five states, including the USA,
Canada, and all European states
except Albania and Andorra
• Main result: Brought Europeans
together outside of the US vs USSR
power arrangements of the Cold
War
Erich Honecker (DDR,
left) and Helmut
Schmidt (FRG) in
Conference on
Security and Co-
operation in Europe
held in Helsinki 1975.
Helsinki Accords
[1975]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-47-320.jpg)

![• Soviets invade Afghanistan, help Communist
government against rebels
• Muslim rebels fight guerilla war against Soviets
with U.S. weapons for nearly a decade
– Osama Bin Laden helps organize defense of
Muslim lands
– Taliban emerge
• Afghanistan = the U.S.S.R.’s “Vietnam”
• U.S. stops grain shipments to Soviet Union; U.S.
also boycotts 1980 Summer Olympics held in
Moscow as protest
Afghanistan
[1979-1988]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-49-320.jpg)

![• March 23, Reagan outlinrd his Strategic
Defense Initiative, or "Star Wars," a
space-based defensive shield that would
use lasers and other advanced technology
to destroy attacking missiles far above
the Earth's surface.
• Soviets accuse the U.S of violating the
1972 Antiballistic Missile Treaty.
• Soviets forced to spend heavily to match
the program causing near economic
collapse.
Star Wars [1983]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-51-320.jpg)
![• On March 11, Mikhail Gorbachev
came to power in the Soviet
Union.
• Gorbachev ushered in an era of
reform.
– perestroika
• Economic reform- restructuring
– glasnost
– means openness, allowed greater
free expression and criticism of
Soviet policies
Gorbachev Comes to Power
in U.S.S.R. [1985]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-52-320.jpg)
![• On December 8, 1987,
Reagan and
Gorbachev signed the
Intermediate Range
Nuclear Forces Treaty
• It mandated the
removal of more than
2,600 medium-range
nuclear missiles from
Europe, & eliminated
the entire class of
Soviet SS-20 and U.S.
Cruise and Pershing II
missiles.
INF Treaty [1987]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-53-320.jpg)
![• Gorbachev renounced the
Brezhnev Doctrine, which
pledged to use Soviet force
to protect its interests in
Eastern Europe.
• On September 10, Hungary
opened its border with
Austria, allowing East
Germans to flee to the West.
• After massive public
demonstrations in East
Germany and Eastern Europe,
the Berlin Wall fell on
November 9.
Berlin Wall Falls [1989]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-54-320.jpg)
![• At a September 12 meeting in
Moscow, the United States, Soviet
Union, Great Britain, France and the
two Germanys agreed to end Allied
occupation rights in Germany.
• On October 3, East and West
Germany united as the Federal
Republic of Germany.
German Unification [1990]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-55-320.jpg)
![· As a result, fifteen
Soviet republics
gained their
independence.
· Eventually,
however, Gorbachev
was forced to resign
in 1991, and the
Soviet Union ceased
to exist.
Post-Soviet states in alphabetical order: 1. Armenia; 2. Azerbaijan; 3.
Belarus; 4. Estonia; 5. Georgia; 6. Kazakhstan; 7. Kyrgyzstan;
8. Latvia; 9. Lithuania; 10. Moldova; 11. Russia; 12. Tajikistan;
13. Turkmenistan; 14. Ukraine; 15. Uzbekistan
End of Soviet Union [1991]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycoldwarv2-150711132636-lva1-app6891/85/The-Cold-War-56-320.jpg)