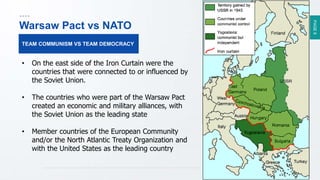
The document summarizes the escalation of tensions between the Western allies (US, UK, France) and the Soviet Union following World War 2. It describes how the Soviets set up communist governments across Eastern Europe and divided Germany, leading the Western powers to implement the policies of containment and the Truman Doctrine to provide military and economic assistance to countries resisting Soviet influence. It also discusses the formation of NATO in response to the Berlin Blockade, as the Western powers sought to counter the Soviet military threat through a defensive alliance.