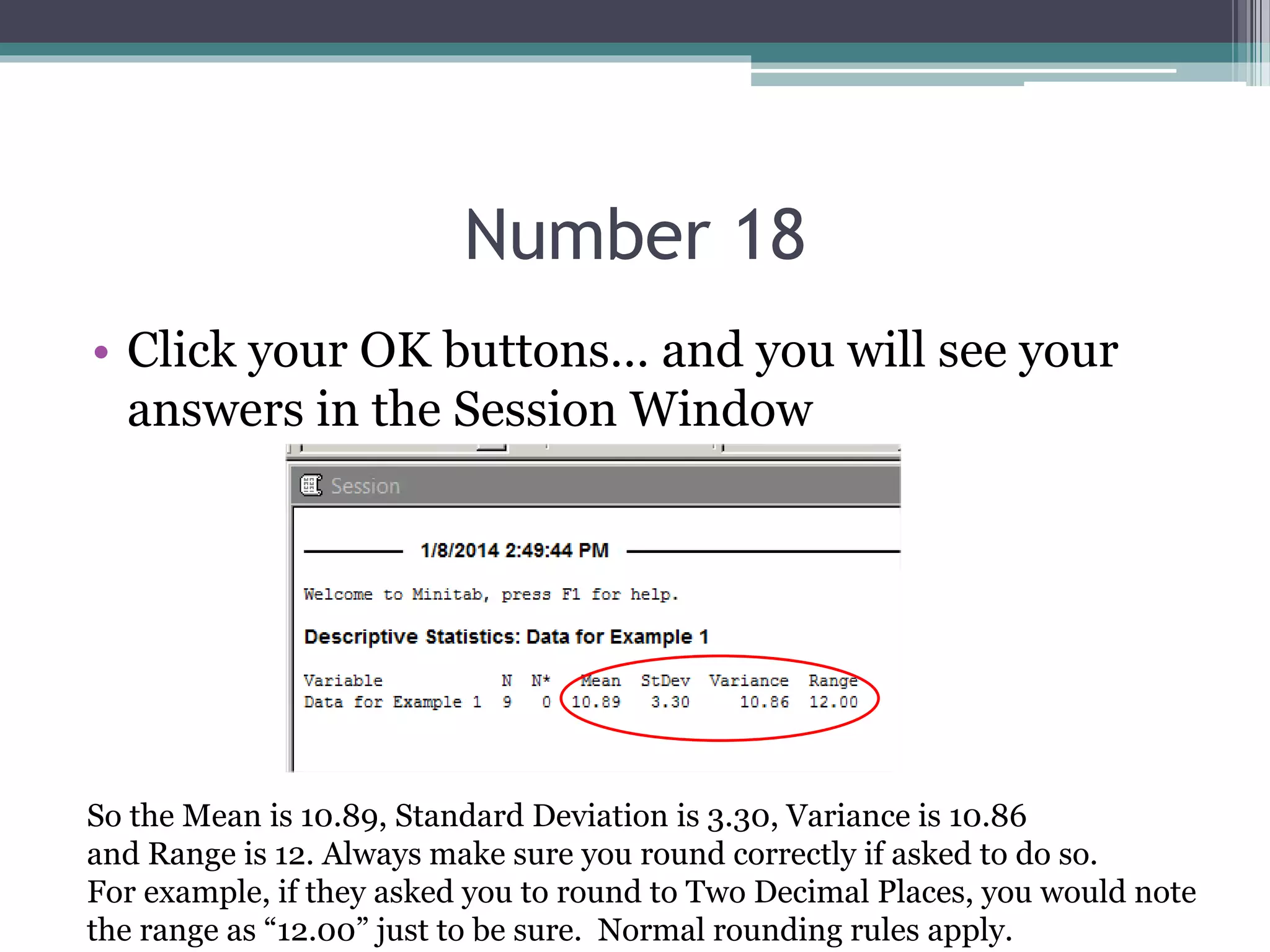
This document provides examples for 3 homework problems from a statistics class. Problem 18 demonstrates how to calculate the range, mean, variance, and standard deviation of a data set using Minitab software. Problem 22 shows how to identify the minimum, maximum, quartiles, and interquartile range from a box and whisker plot. Problem 24 matches z-scores to a histogram by considering their relationship to the mean and standard deviation.