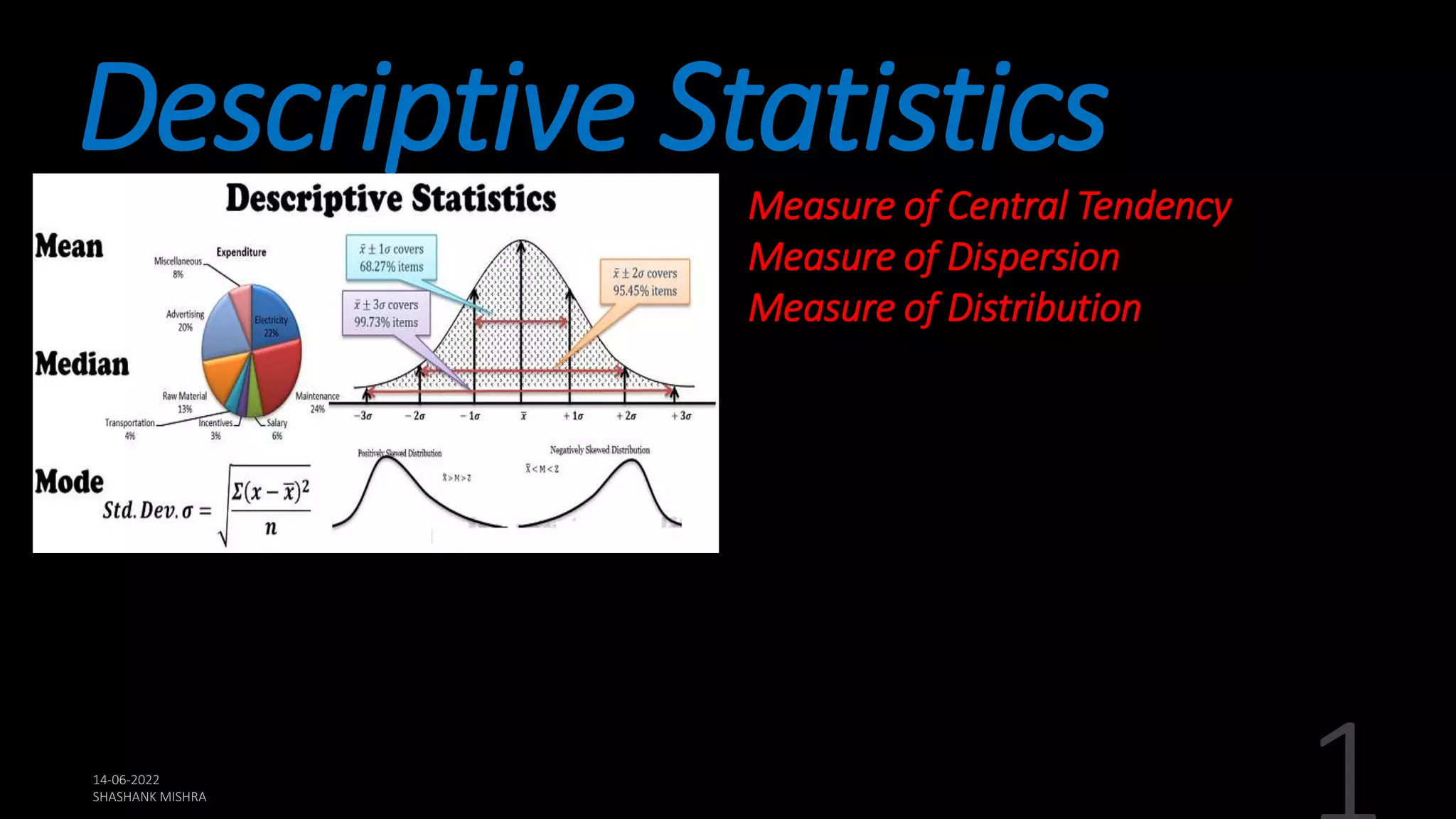
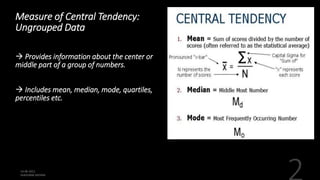
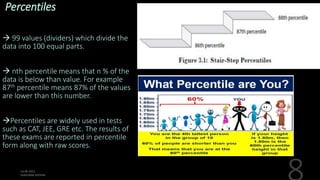
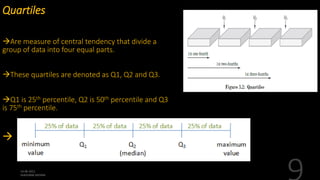
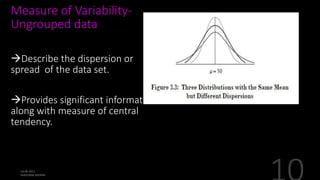
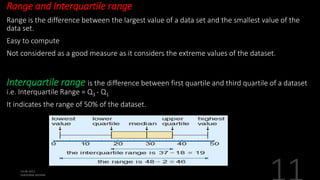
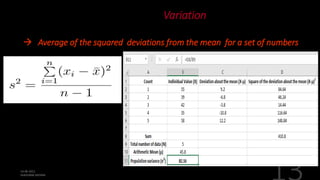
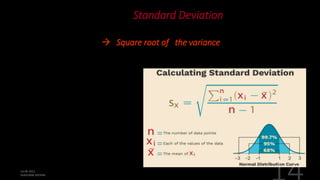
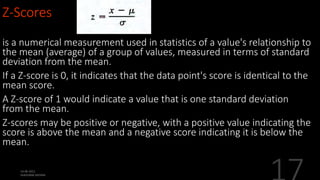
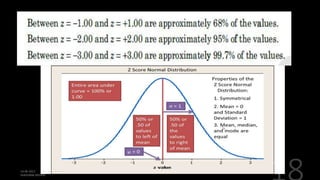
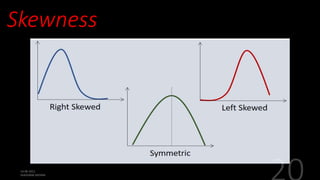
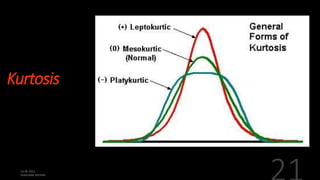
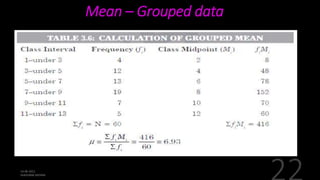
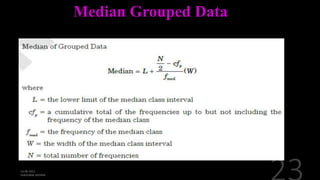
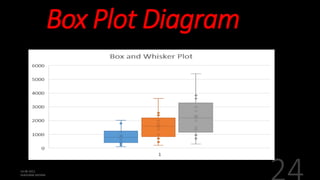
This document defines and explains various measures of central tendency, dispersion, and distribution used in descriptive statistics. It discusses modes, medians, means, percentiles, quartiles, range, interquartile range, standard deviation, z-scores, and other key statistical concepts. These metrics are used to summarize and describe the central position and variability of data in distributions.