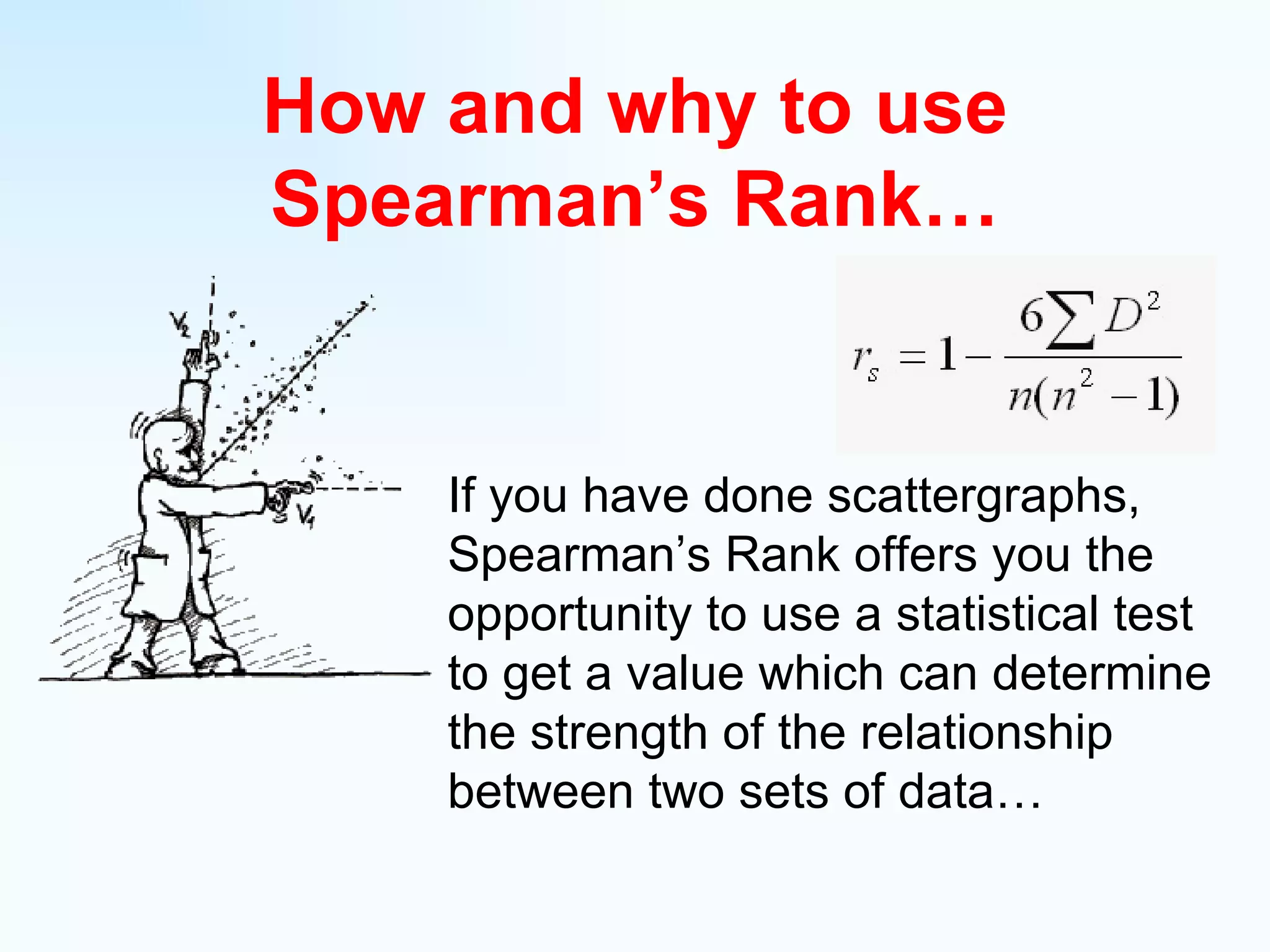
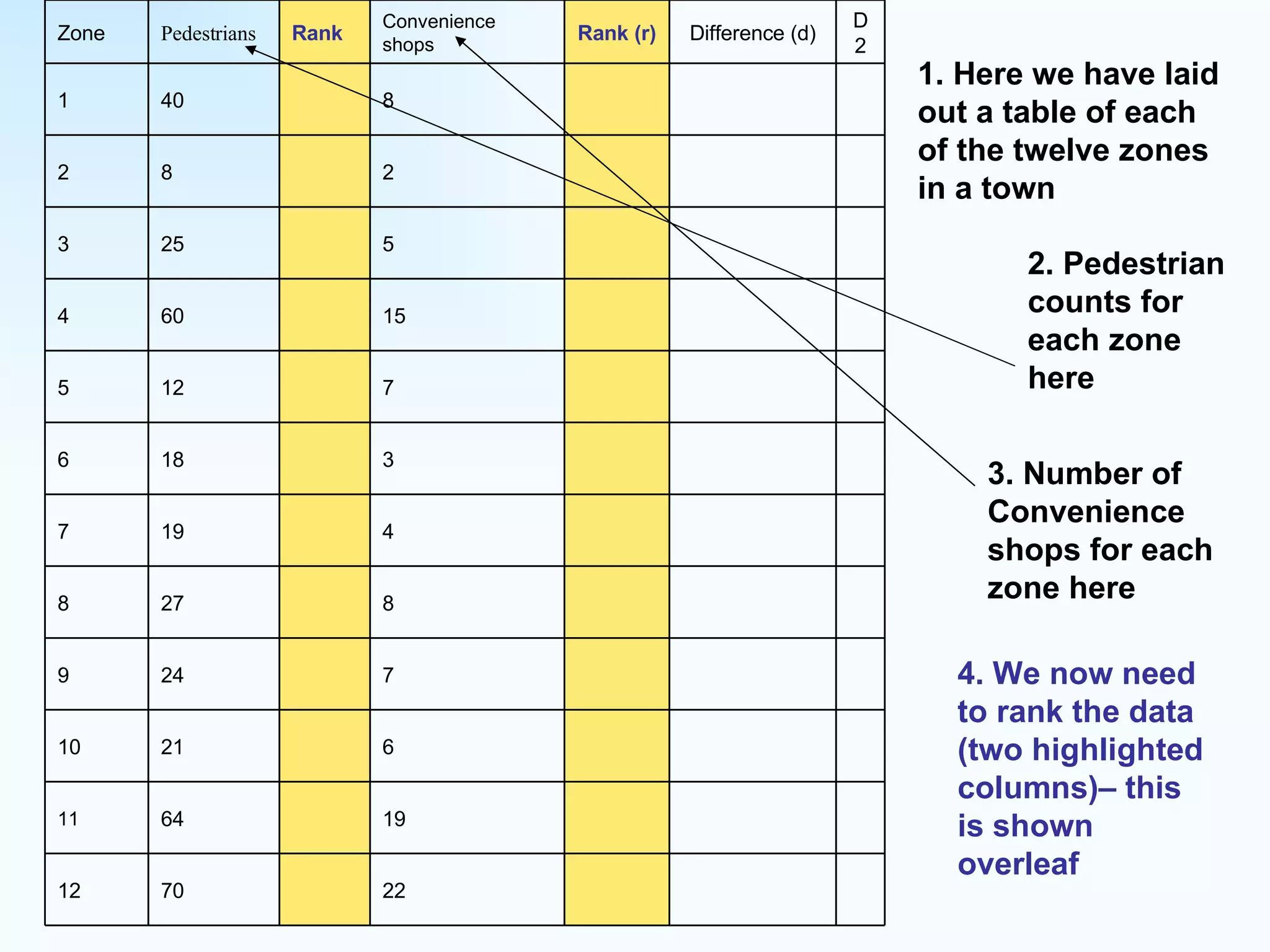
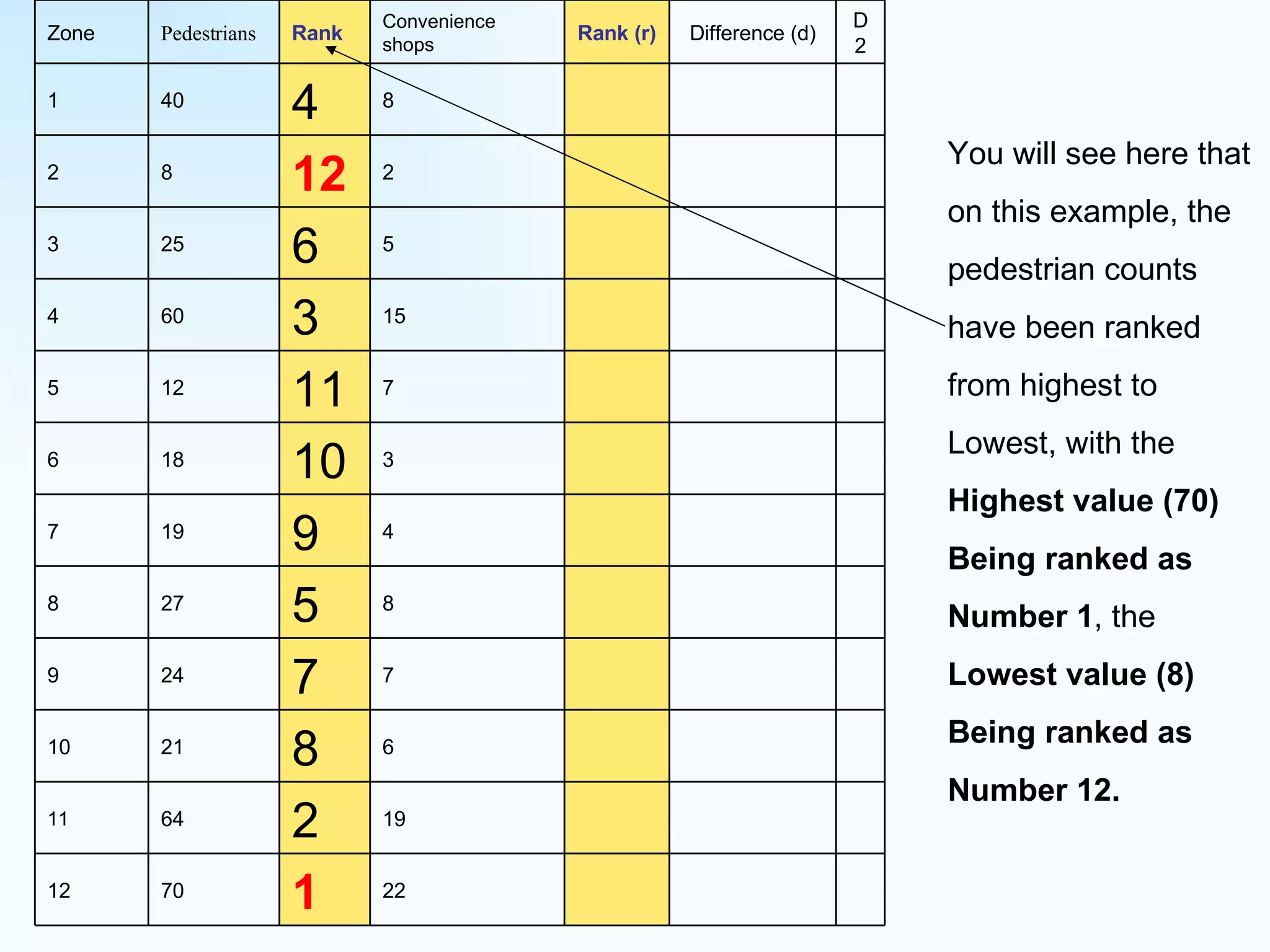
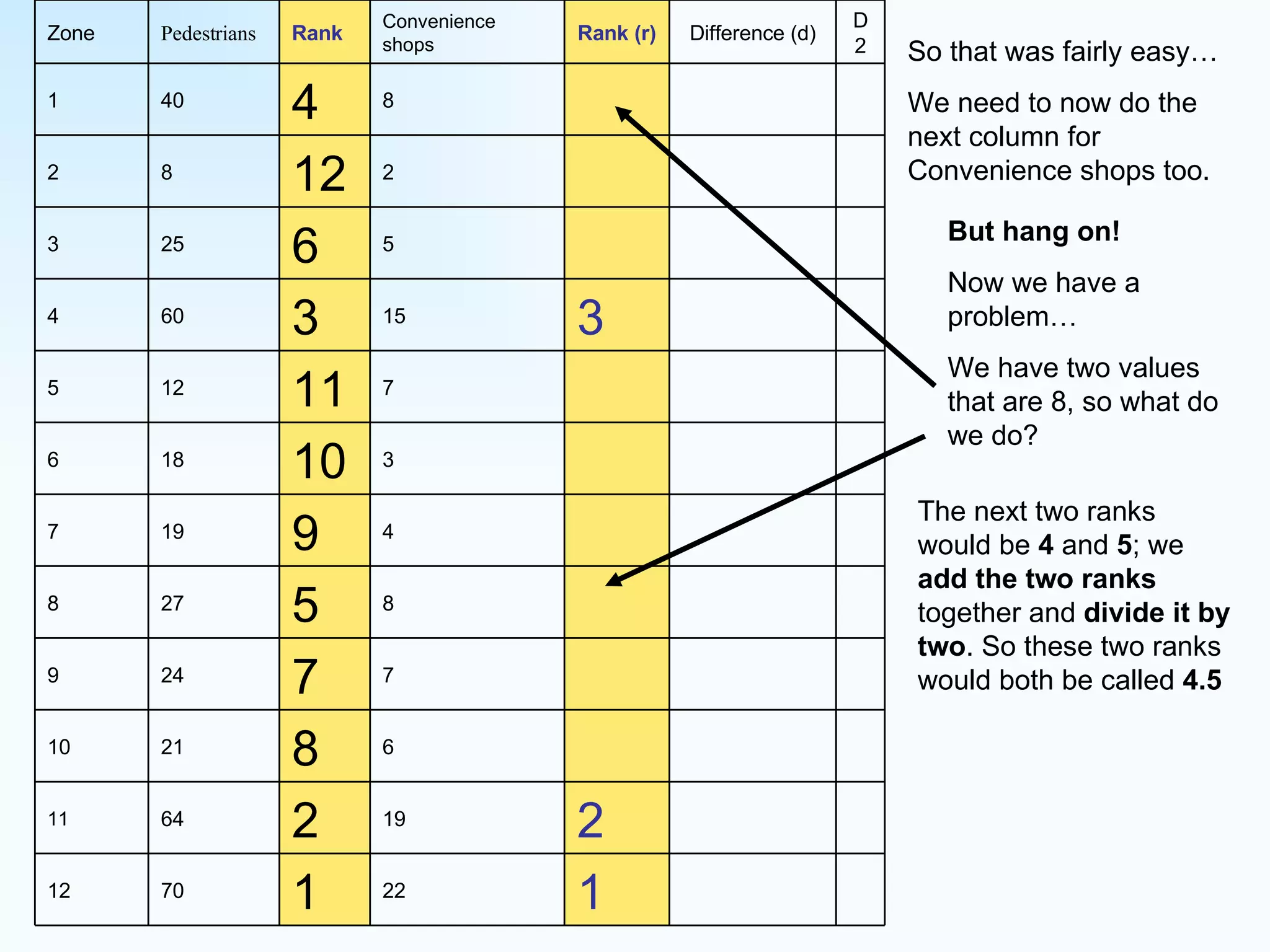
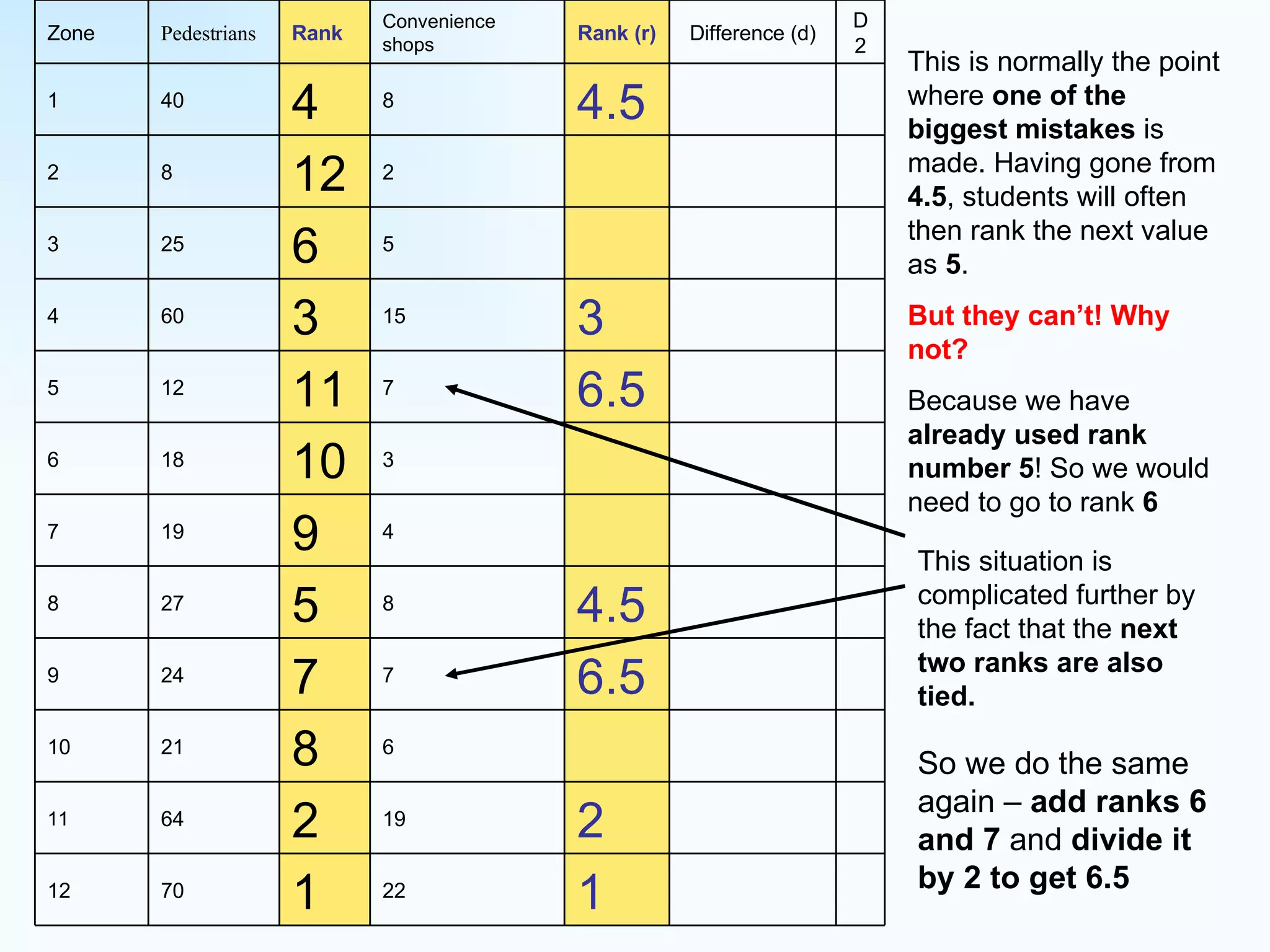
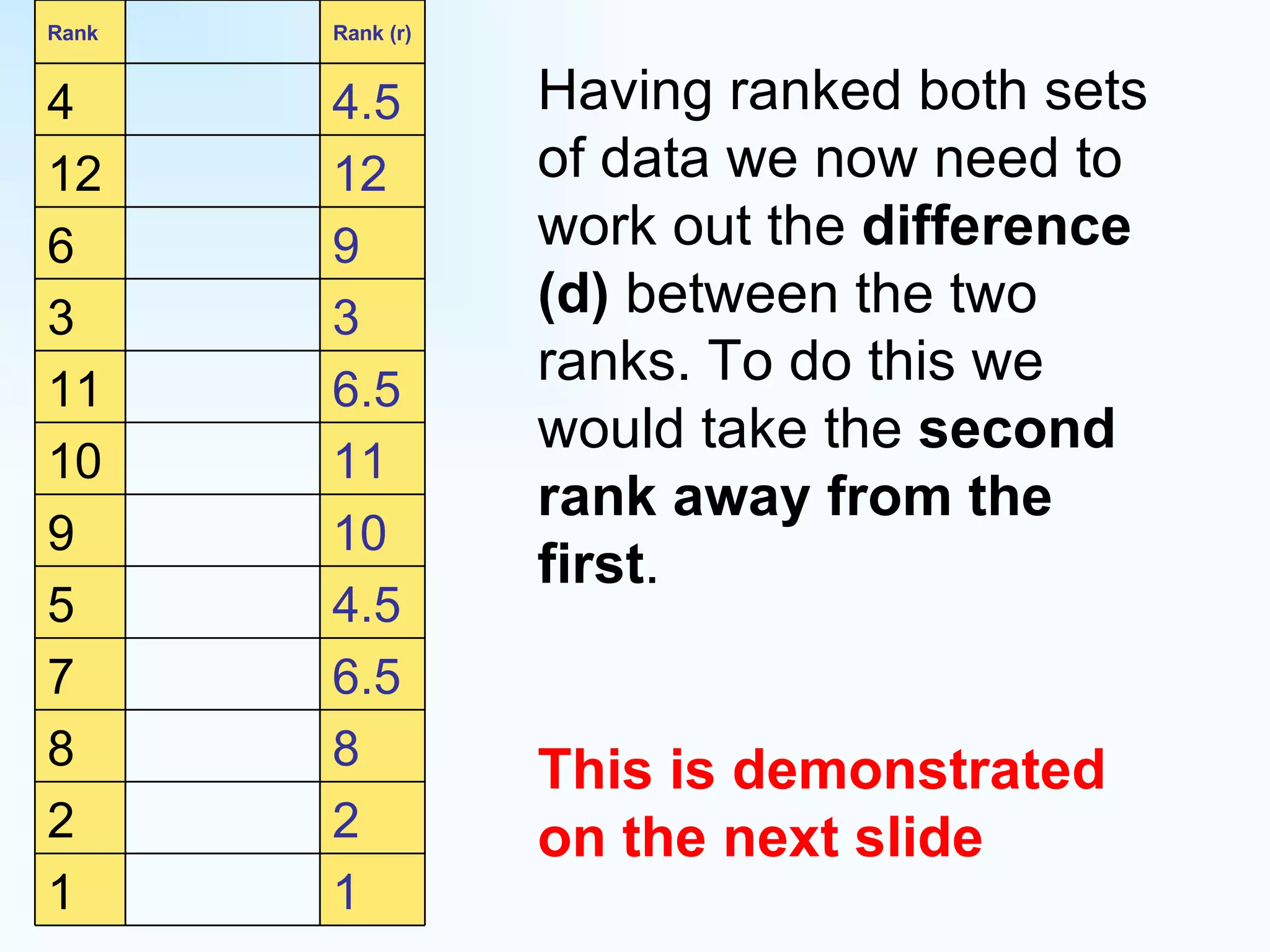
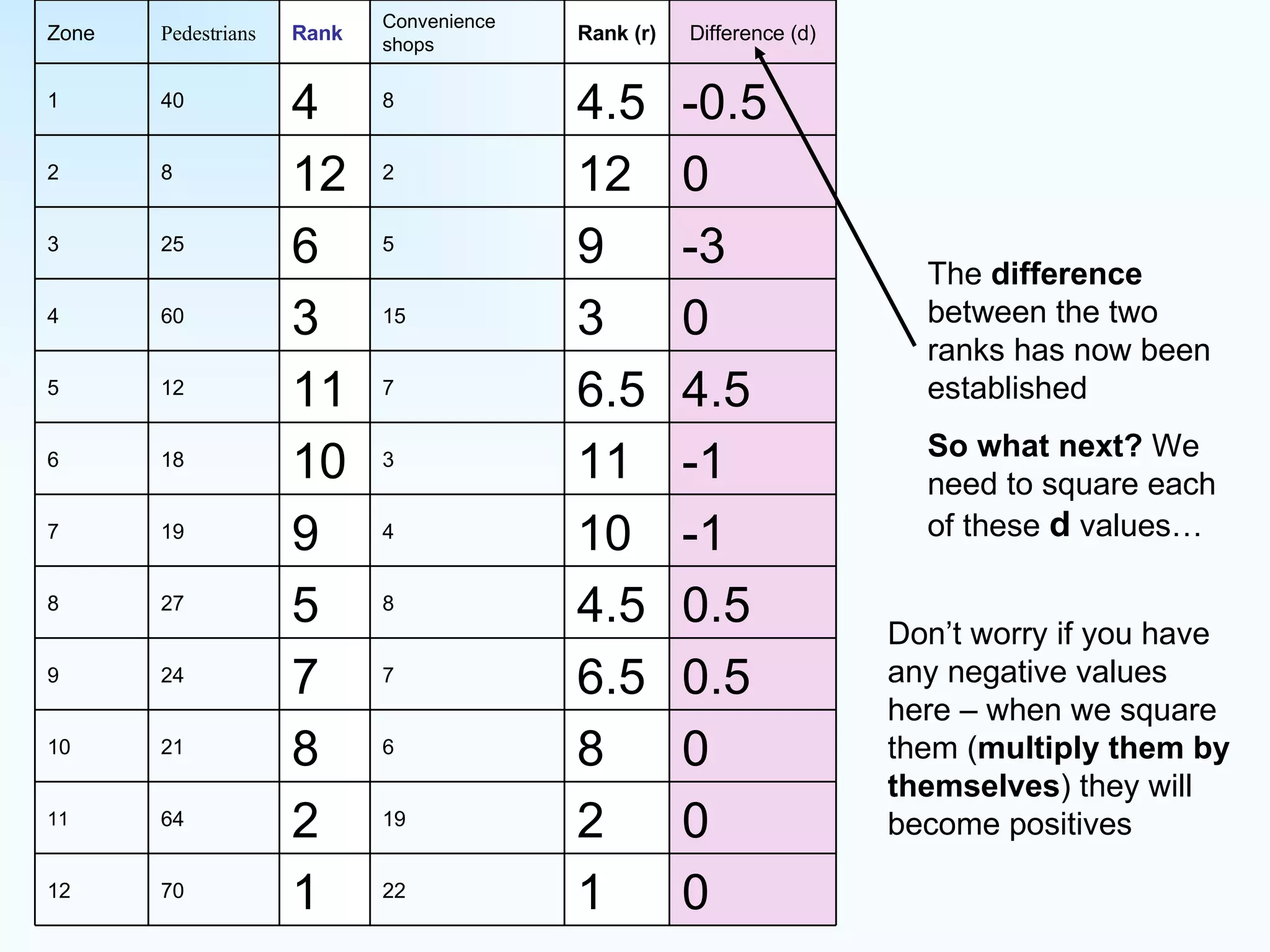
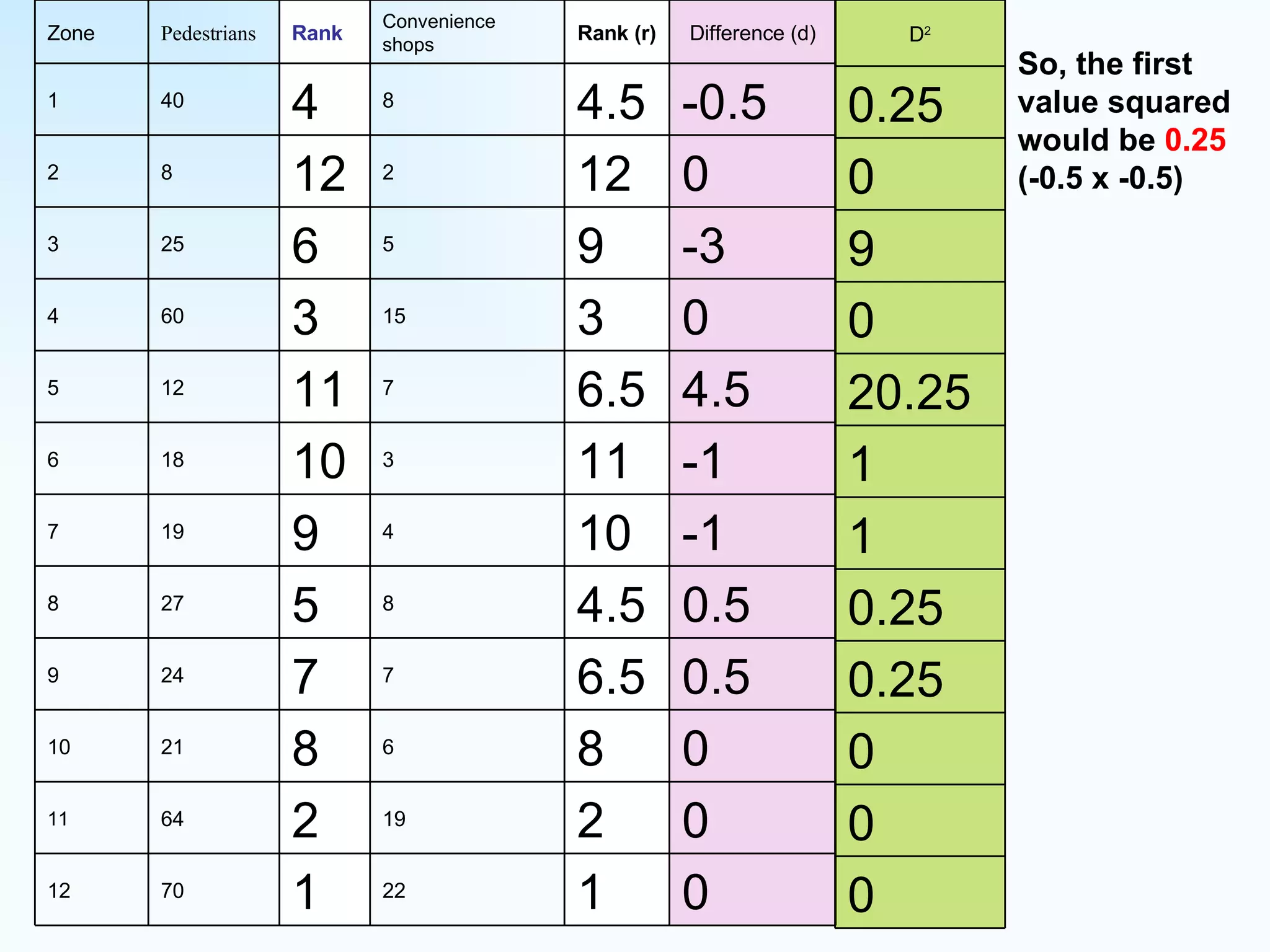
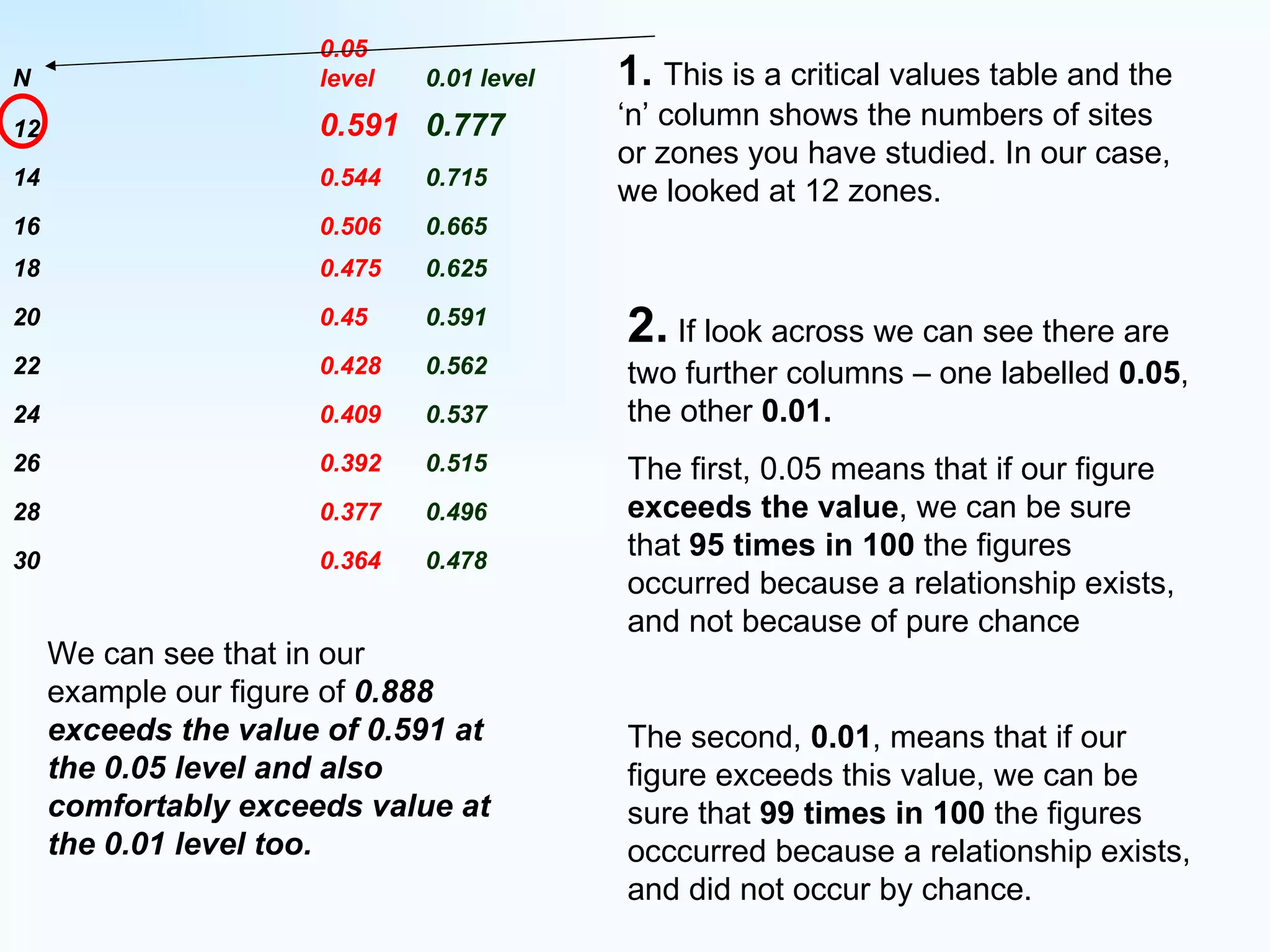
The document explains how to use Spearman's rank correlation to assess the strength of the relationship between two sets of data, using an example related to pedestrian counts and convenience shops in a town. It details the steps of ranking, calculating differences, squaring those differences, and applying the Spearman equation to derive a correlation coefficient. The final result, indicating a strong positive relationship, suggests that higher pedestrian counts correlate with a greater number of convenience shops, which is confirmed by significance levels in critical value tables.