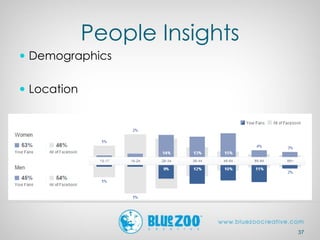
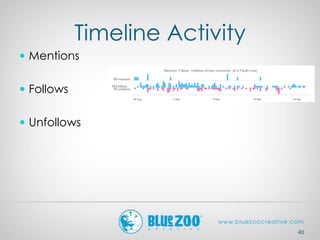
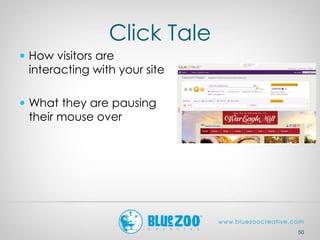
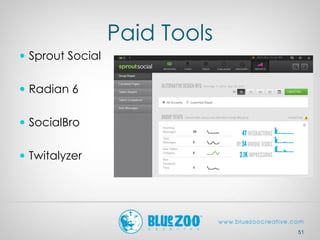
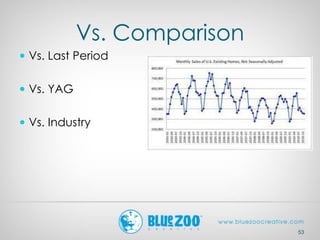
This document provides an overview of analytics and metrics that can be used to measure website and social media performance. It discusses Google Analytics and the types of data it can track, including visits, pageviews, traffic sources, user behavior, and conversions. It also covers metrics for Facebook, Twitter, Pinterest, and other social networks like followers, engagement, and demographics. The document emphasizes measuring both hard metrics like clicks and sales as well as softer metrics for social media like user sentiment. It concludes with comparing performance to past periods, competitors, and industry benchmarks.