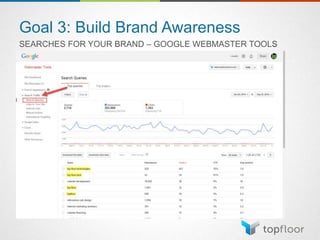
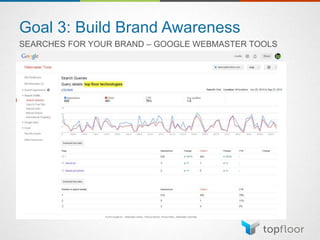
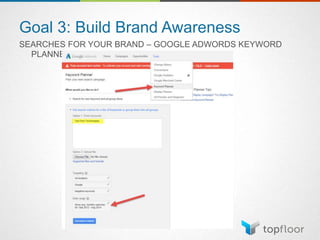
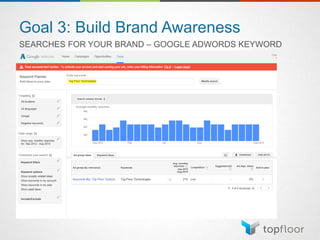
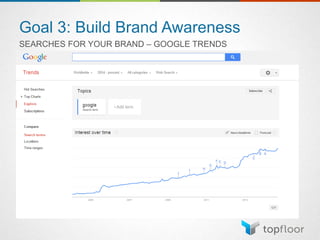
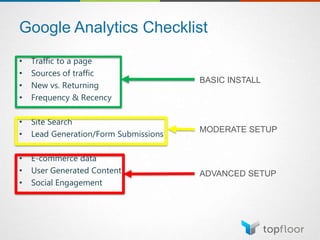
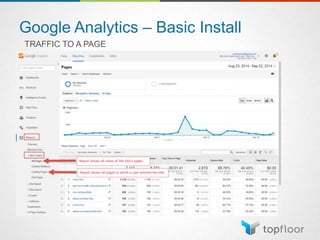
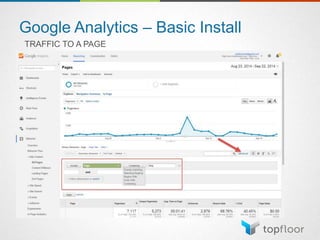
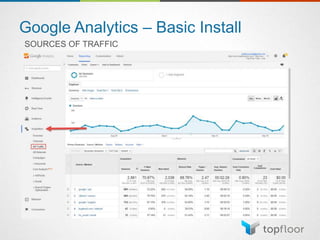
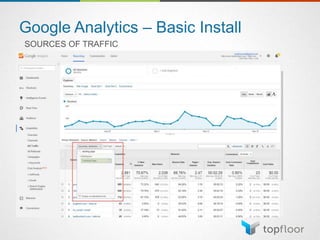
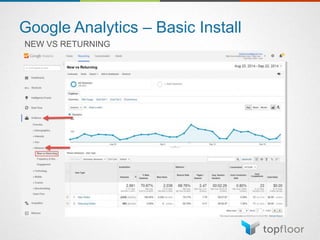
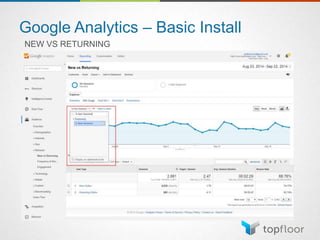
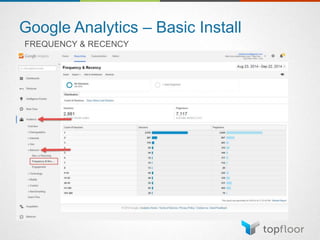
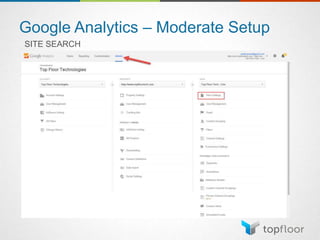
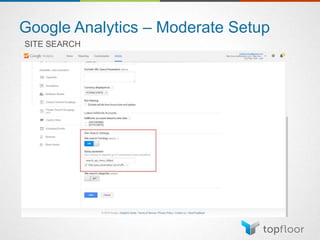
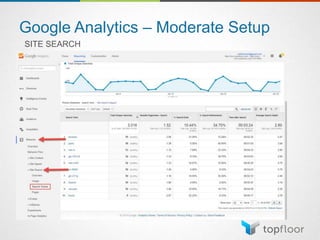
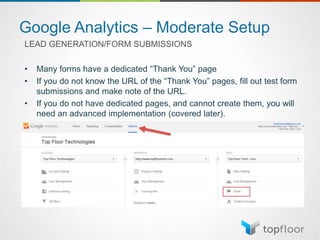
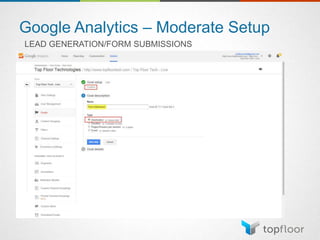
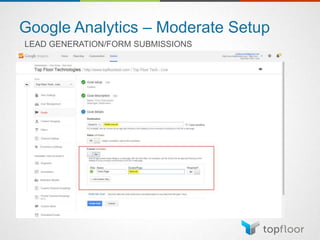
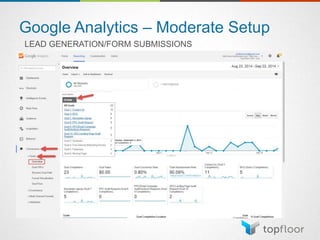
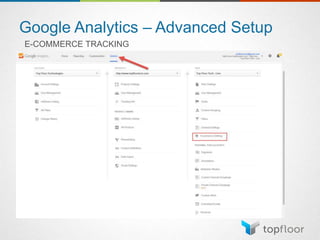
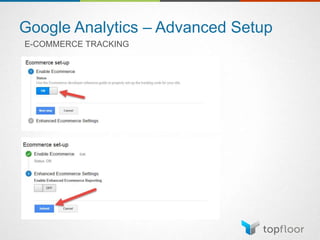
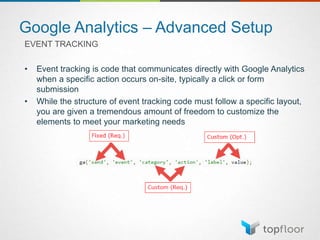
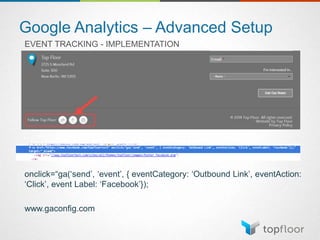
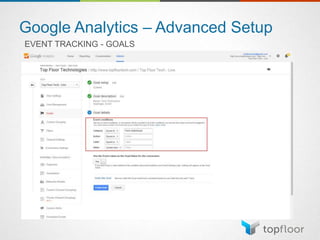
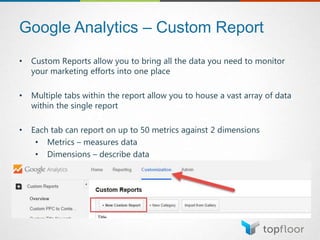
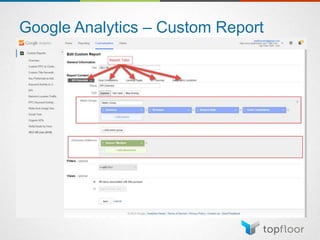
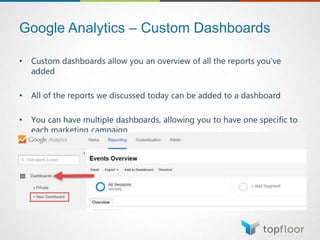
The document outlines strategies for measuring marketing effectiveness, highlighting key performance metrics for various marketing goals such as promoting products, increasing blog followership, and building brand awareness. It emphasizes the importance of understanding metrics in context, utilizing tools like Google Analytics for data collection, and employing advanced tracking techniques. Additionally, it covers setting up custom reports and dashboards for comprehensive marketing monitoring.