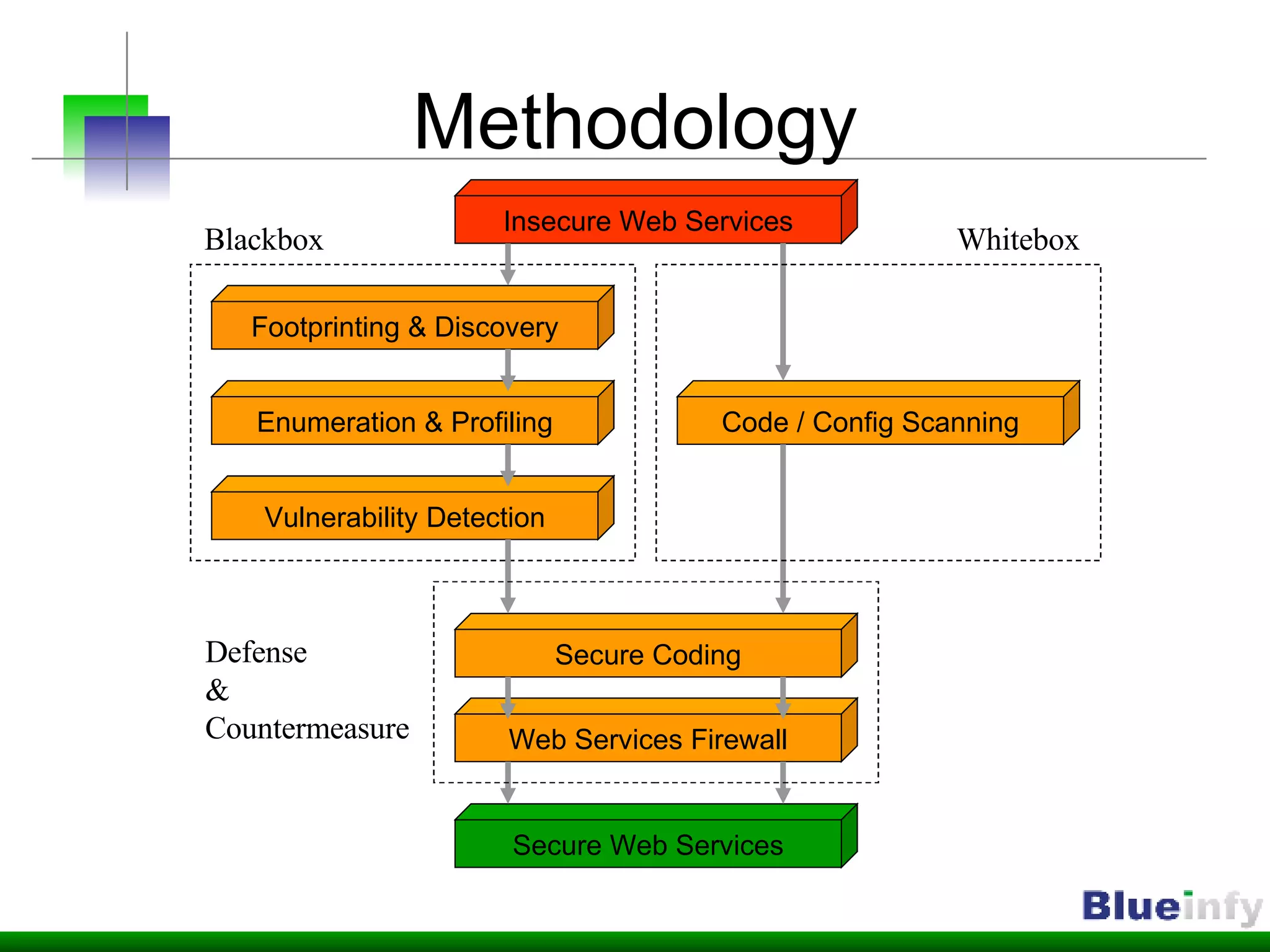
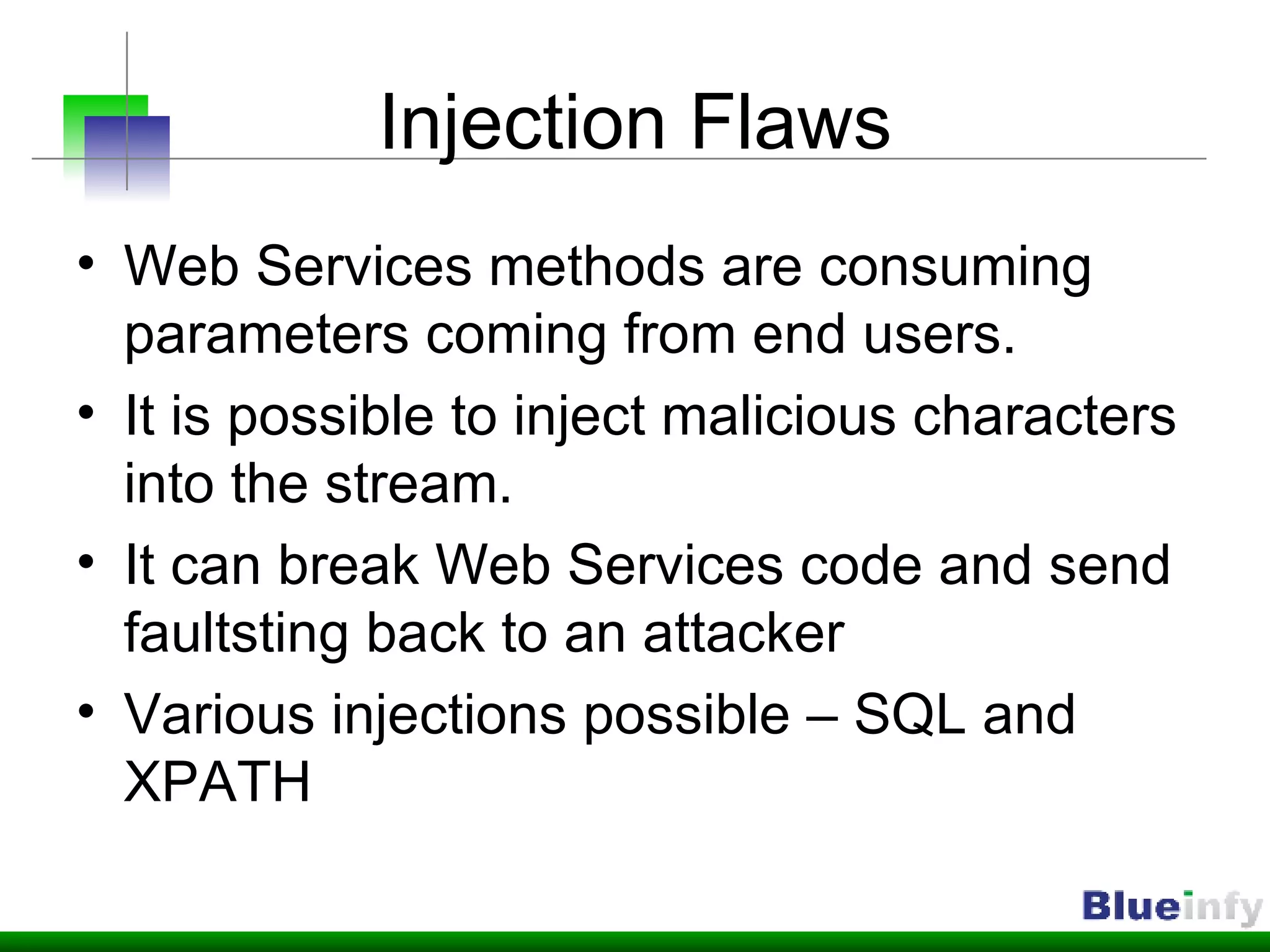
The document summarizes Shreeraj Shah's presentation on securing Ajax and web services. It discusses trends in web 2.0 technologies like Ajax and web services being adopted by many companies, and outlines various attacks and defenses related to securing these technologies, including cross-site scripting, injection flaws, and insecure direct object references in web services. It also proposes methodologies for assessing web services security, including footprinting, profiling, scanning for vulnerabilities, and implementing defenses like firewalls and secure coding practices.
![Founder & Director Blueinfy Solutions Pvt. Ltd. (Brief) Past experience Net Square, Chase, IBM & Foundstone Interest Web security research Published research Articles / Papers – Securityfocus, O’erilly, DevX, InformIT etc. Tools – wsScanner, scanweb2.0, AppMap, AppCodeScan, wsChess etc. Advisories - .Net, Java servers etc. Books (Author) Hacking Web Services (Thomson 2006) Web Hacking (AWL 2003) Web 2.0 Security (Work in progress) Who am I? http://shreeraj.blogspot.com [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/web-20-application-kungfu-1196221949603308-3/75/Web-2-0-Application-Kung-Fu-Securing-Ajax-Web-Services-2-2048.jpg)




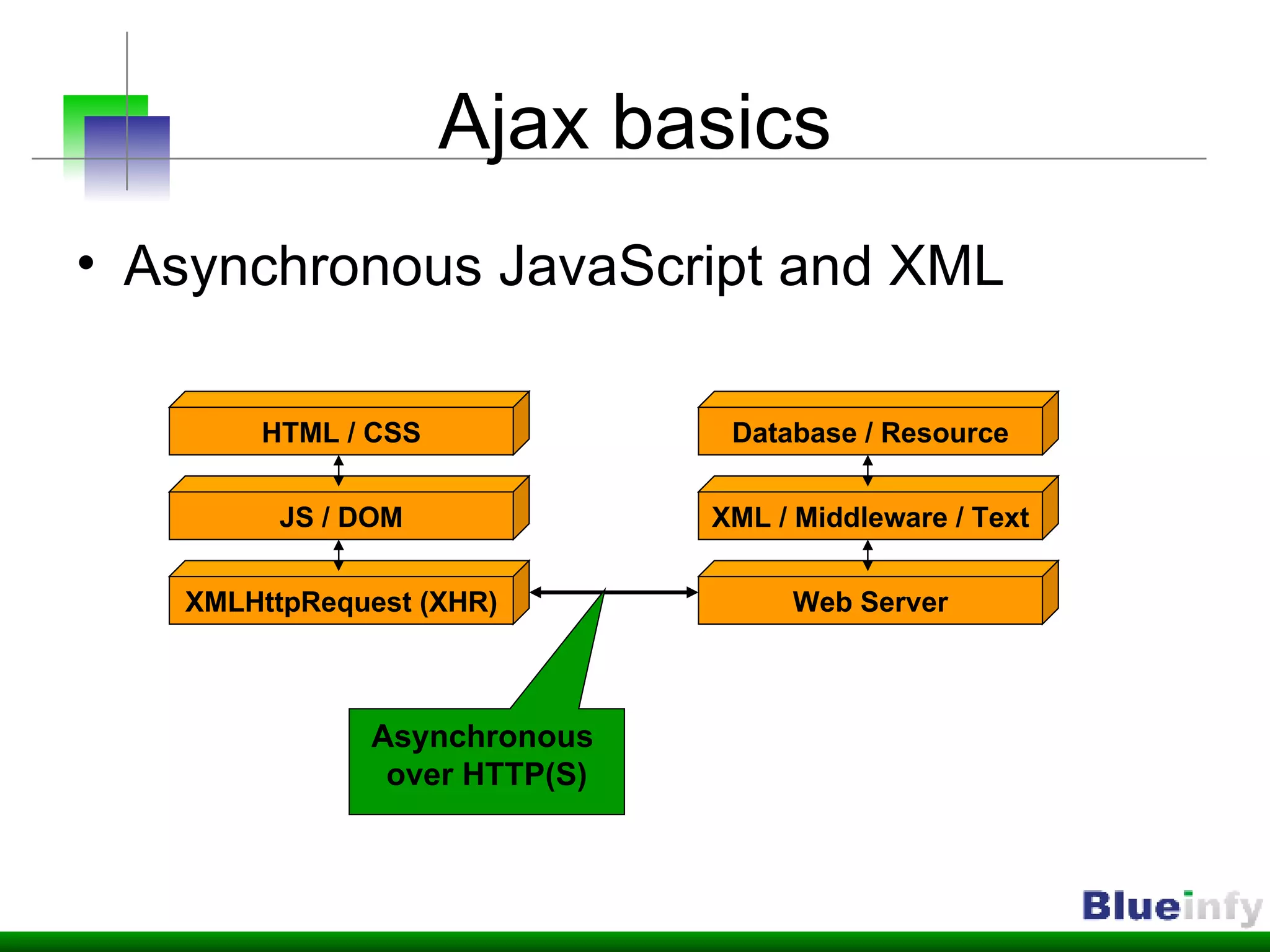


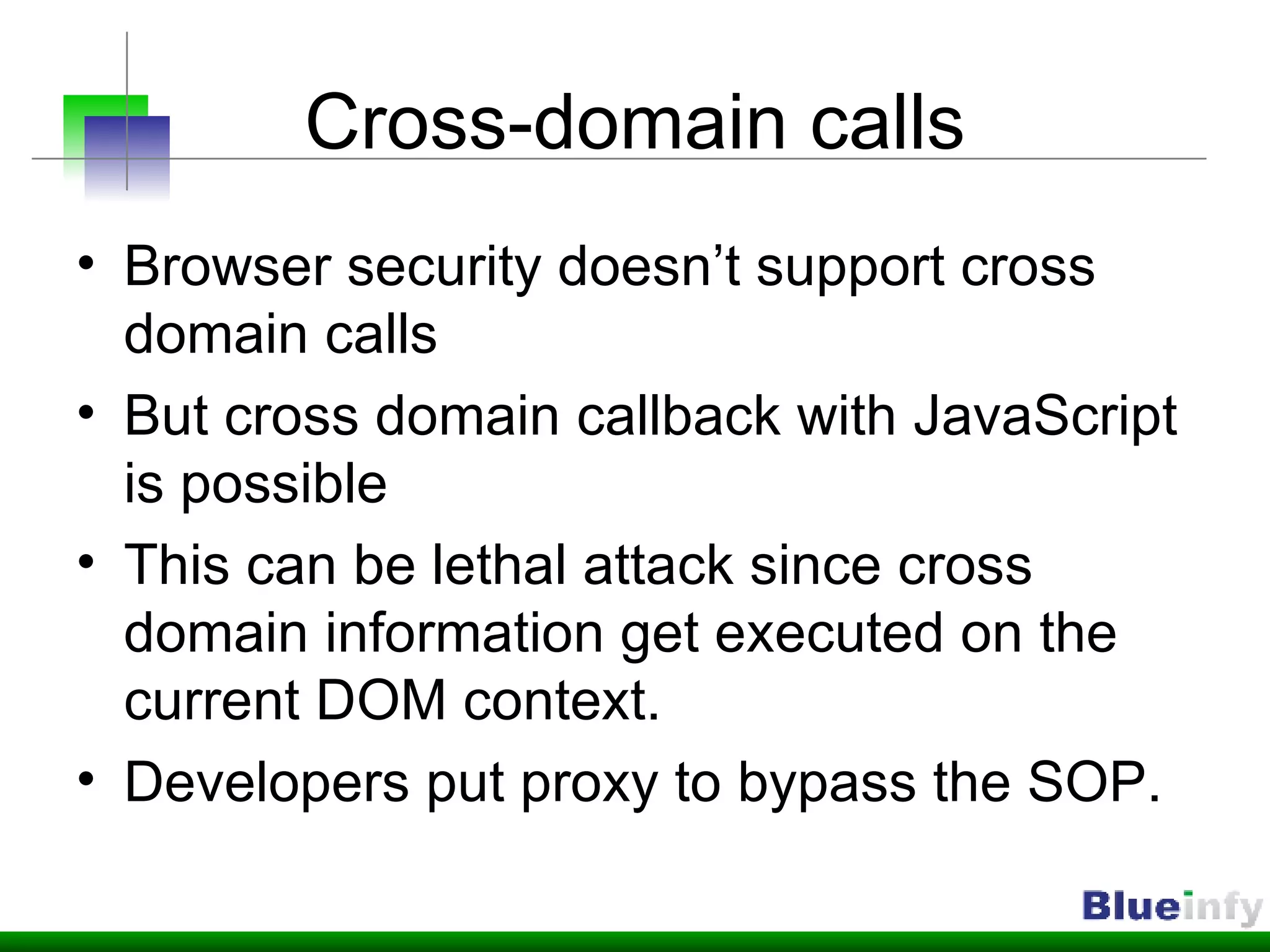





![Ajax serialization issues JSON issues JS – Array manipulation {"bookmarks":[{"Link":"www.example.com","Desc":"Interesting link"}]} new Array(“Laptop”, “Thinkpad”, “T60”, “Used”, “900$”, “It is great and I have used it for 2 years”)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/web-20-application-kungfu-1196221949603308-3/75/Web-2-0-Application-Kung-Fu-Securing-Ajax-Web-Services-19-2048.jpg)

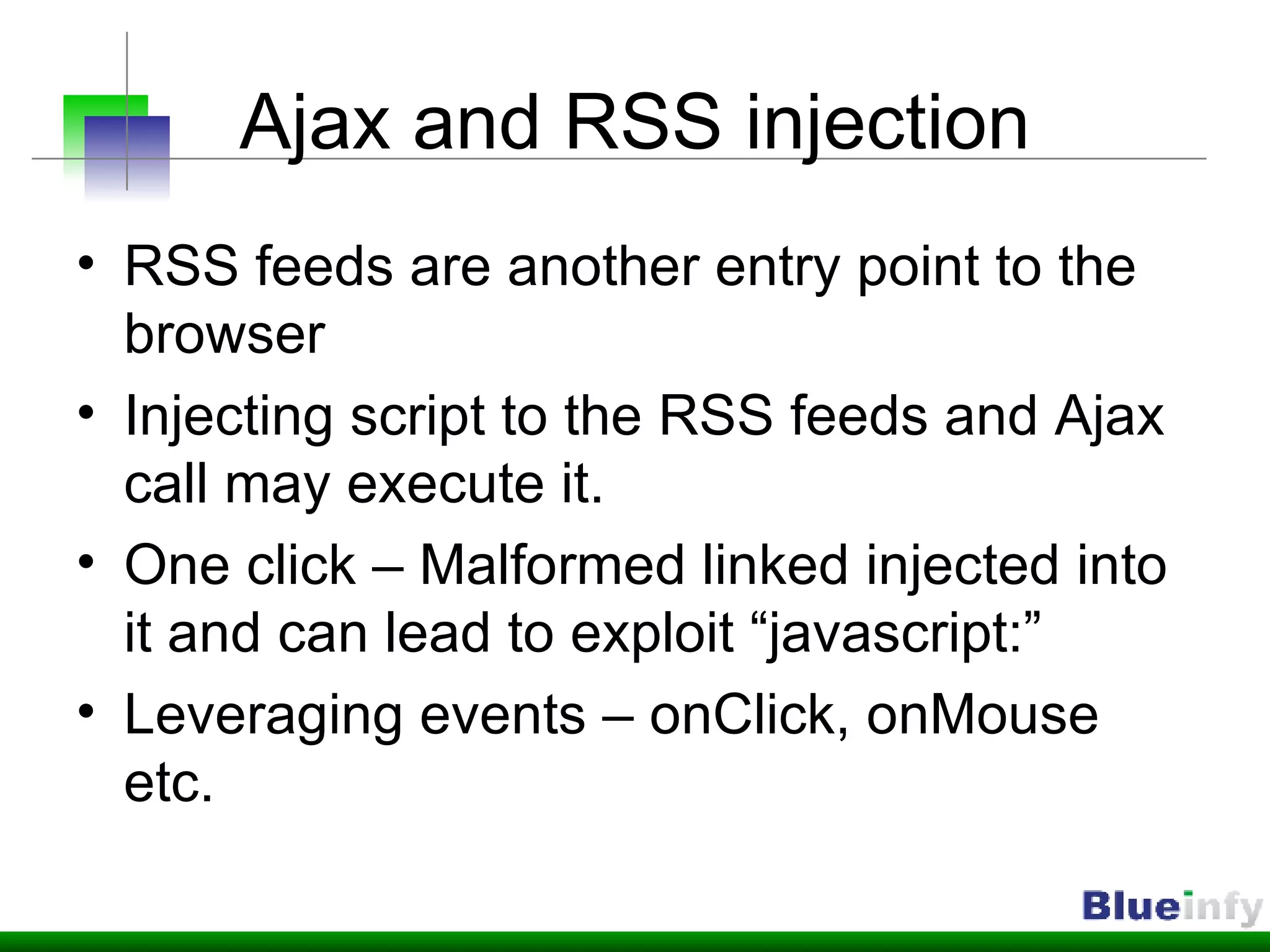










![Thanks! Questions? [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/web-20-application-kungfu-1196221949603308-3/75/Web-2-0-Application-Kung-Fu-Securing-Ajax-Web-Services-42-2048.jpg)