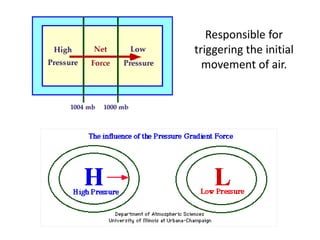
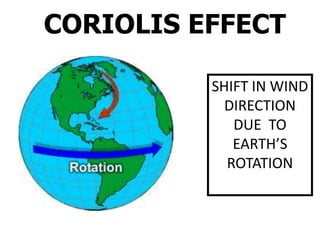
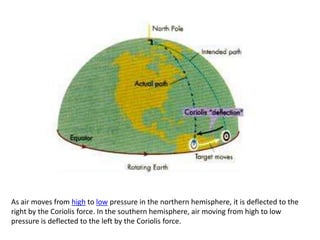
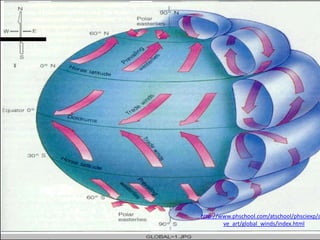
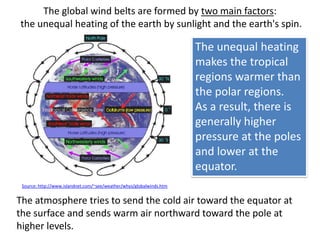
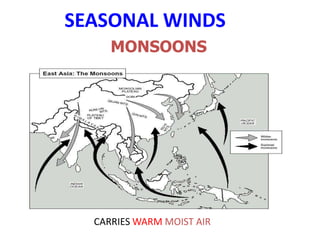
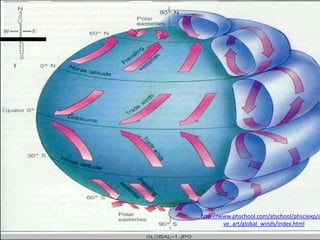
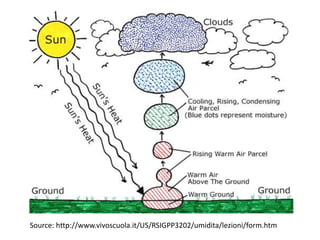
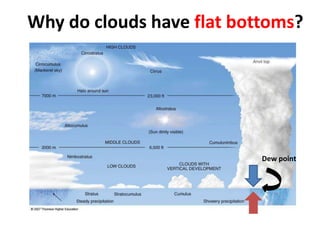
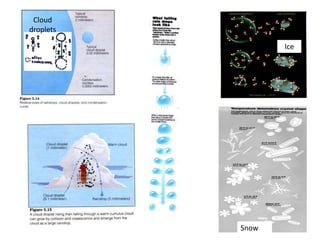
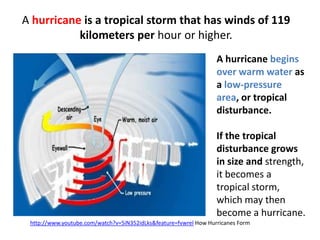
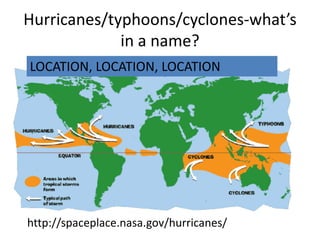
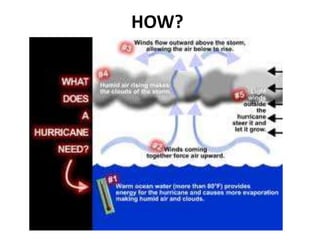
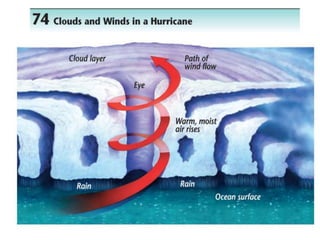
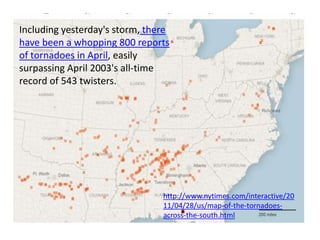
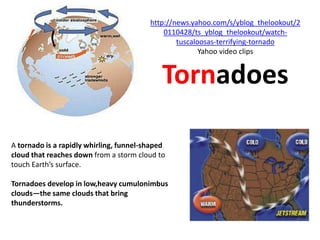
The document discusses wind, clouds, and precipitation. It explains that unequal heating of the air causes winds as warm air rises and cooler air moves in. This global pattern of air circulation creates wind belts. Clouds form when moisture condenses on particles in the air as the air rises and cools. Precipitation occurs as water vapor condenses and falls to earth as rain, snow, or hail. Hurricanes and tornadoes develop due to the interaction of warm and cold air masses.