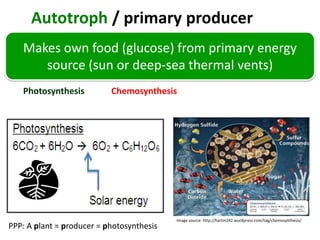
1) Producers like plants use photosynthesis or chemosynthesis to produce their own food, while consumers cannot produce their own food and must eat other organisms.
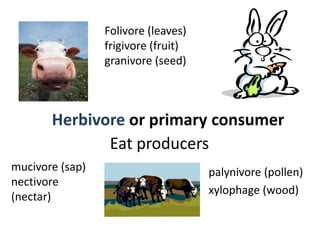
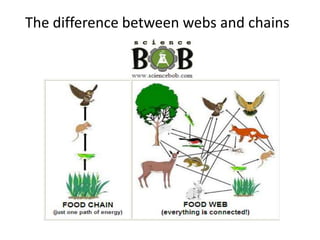
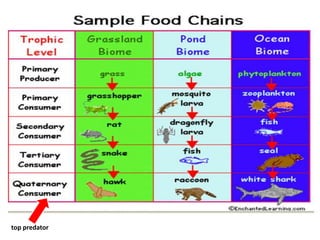
2) Herbivores eat producers, carnivores and omnivores eat other consumers, and top predators have no natural predators and sit at the top of the food chain.
3) Decomposers and detritivores help break down dead organic matter and waste, recycling nutrients back into the food web.