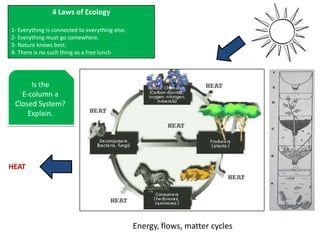
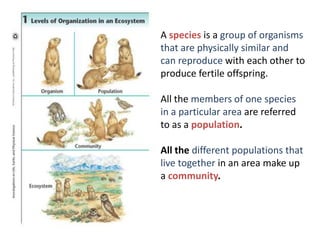
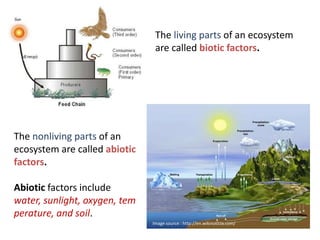
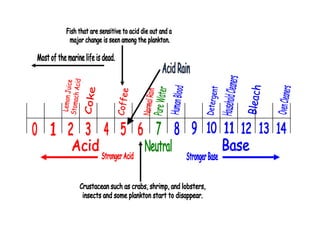
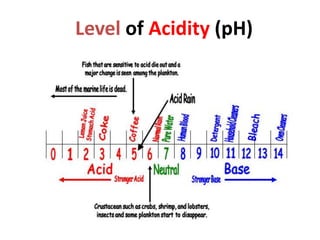
Here are 5 important things needed to sustain the E-column and what would happen if not followed:
1. Maintain proper water flow - Without water flow, waste would accumulate and oxygen levels would decrease, harming organisms.
2. Control temperature - Temperature outside the optimal range would stress or kill organisms.
3. Remove excess waste - Accumulated waste would poison the system.
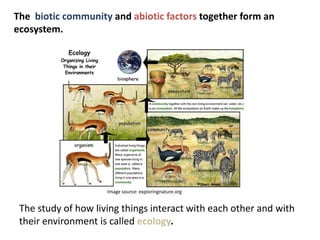
4. Maintain organism diversity - Loss of any group would disrupt nutrient cycling and food webs.
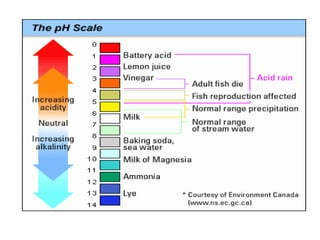
5. Monitor abiotic factors like pH and oxygen - Changes could make the environment unsuitable for organisms.
If these things are not maintained, the whole ecosystem would become imbalanced and collapse over time as conditions became inhosp