Embed presentation
Download to read offline










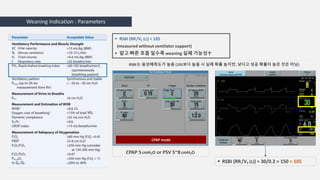







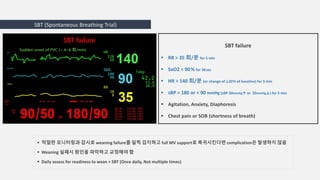















This document discusses mechanical ventilation and the weaning process. It outlines the 7 stages of weaning and indicators for readiness to wean, including parameters like respiratory rate, tidal volume, rapid shallow breathing index, and maximum inspiratory pressure. It describes methods for spontaneous breathing trials and criteria for weaning failure. Difficult weaning can be caused by respiratory, cardiac, psychological, ventilator or nutritional factors. Daily assessment is important to evaluate readiness and avoid complications from prolonged mechanical ventilation.

































