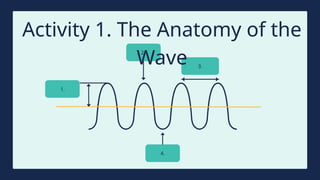
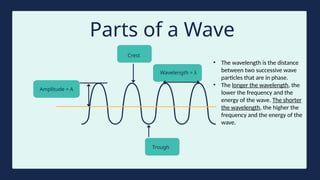
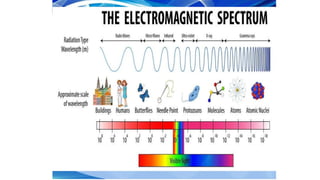
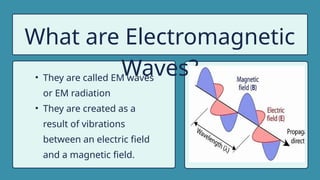
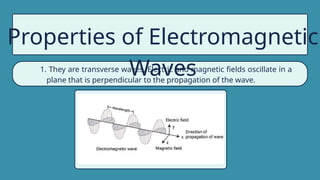
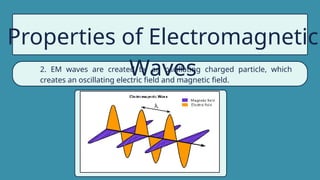
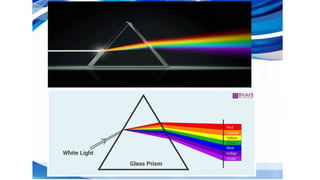
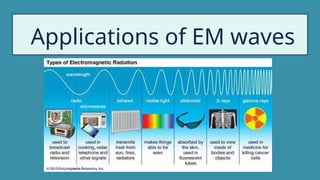
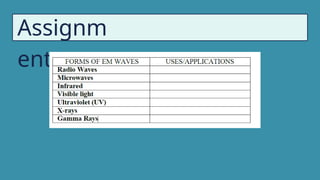
The document provides instructions for a pretest on electromagnetic waves, including key concepts and their definitions such as wave, crest, trough, amplitude, wavelength, and frequency. It covers the properties of electromagnetic waves, their relationship with light, and highlights the contributions of pioneering scientists like James Clerk Maxwell and Heinrich Hertz. Additionally, it outlines the electromagnetic spectrum and emphasizes that EM waves do not require a medium for propagation.