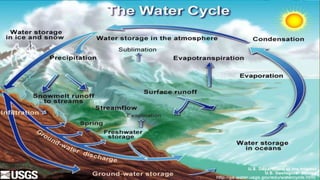
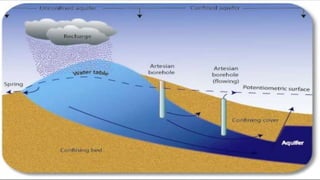
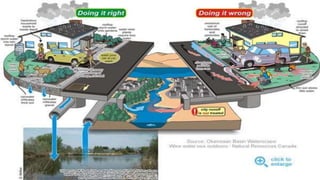
The document discusses the importance of water resources for various uses including agriculture, industry, and domestic purposes, highlighting both surface and groundwater. It addresses issues like overutilization, pollution, and conflicts over water resources due to increasing demand and unequal distribution. The document also explores management strategies, including local management practices and the construction of dams, which while beneficial, also present significant environmental and social challenges.