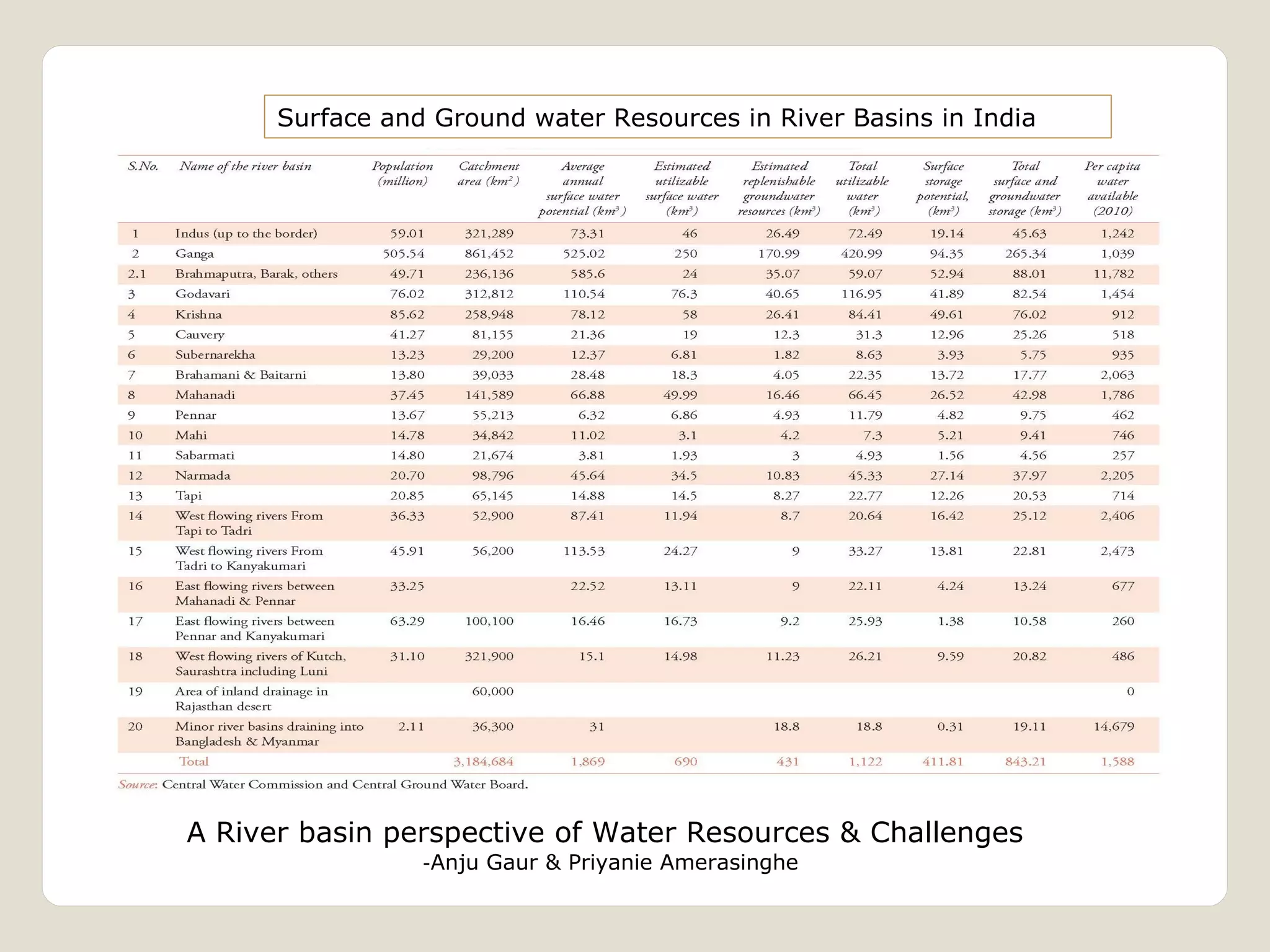
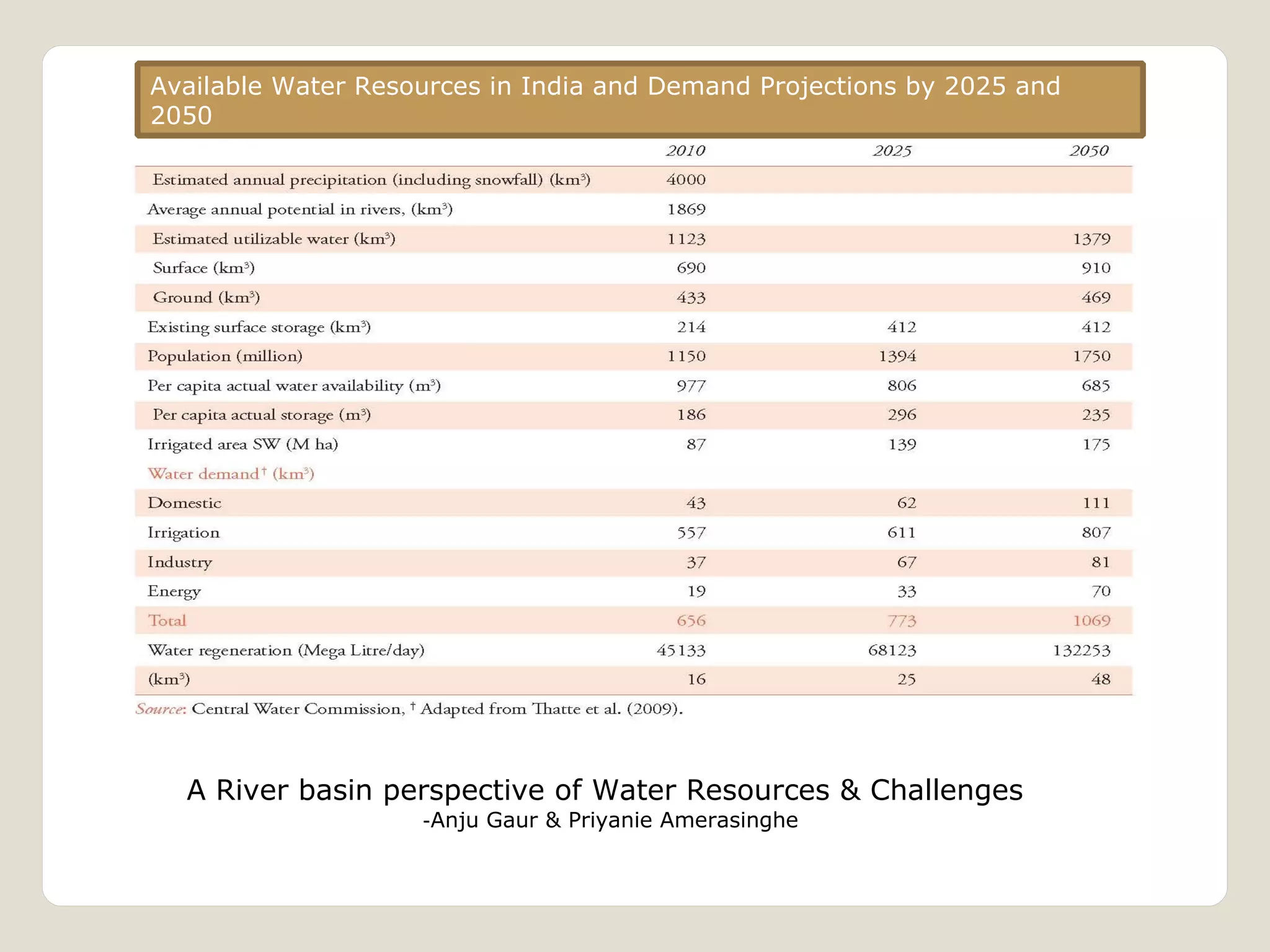
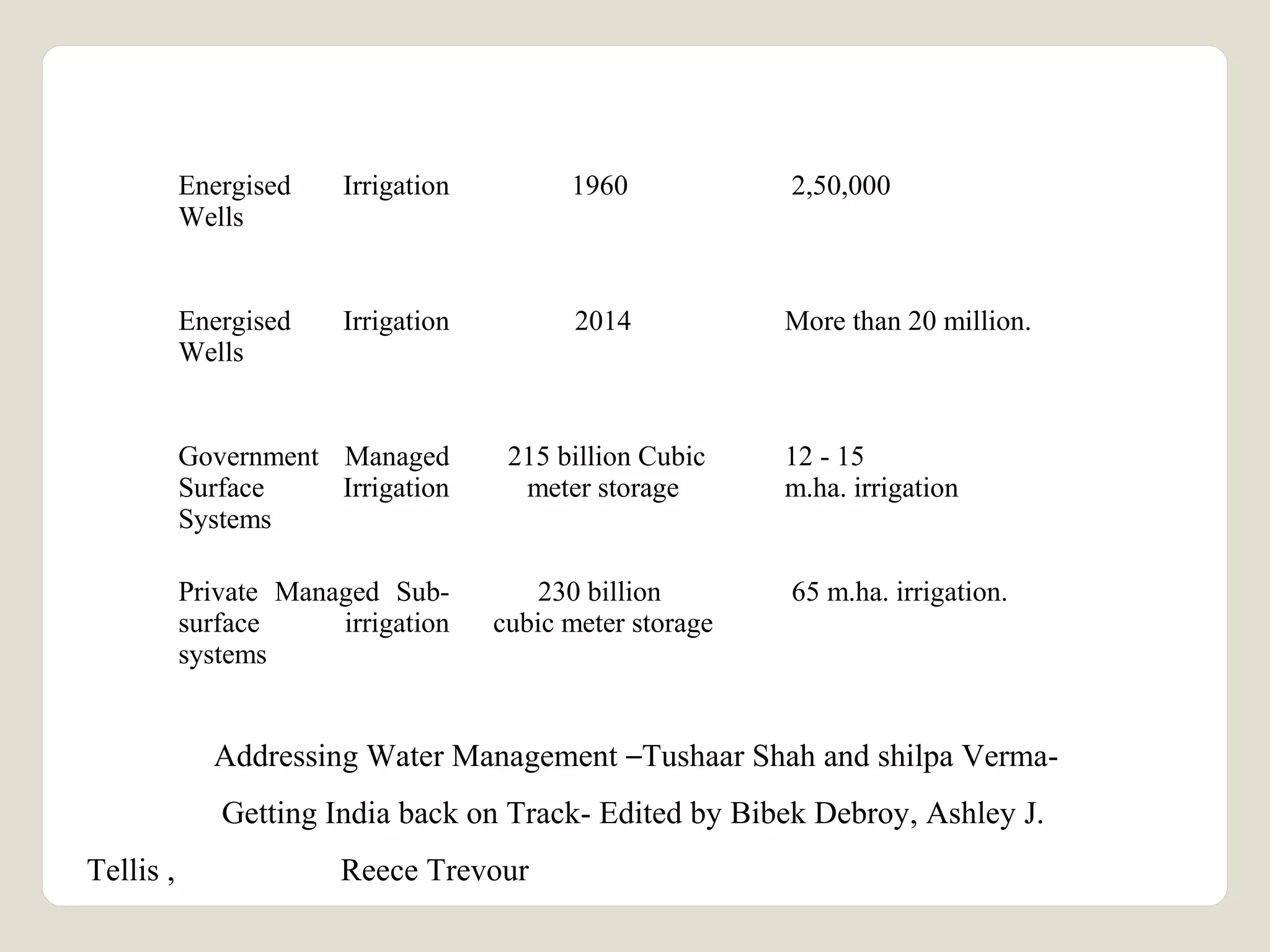
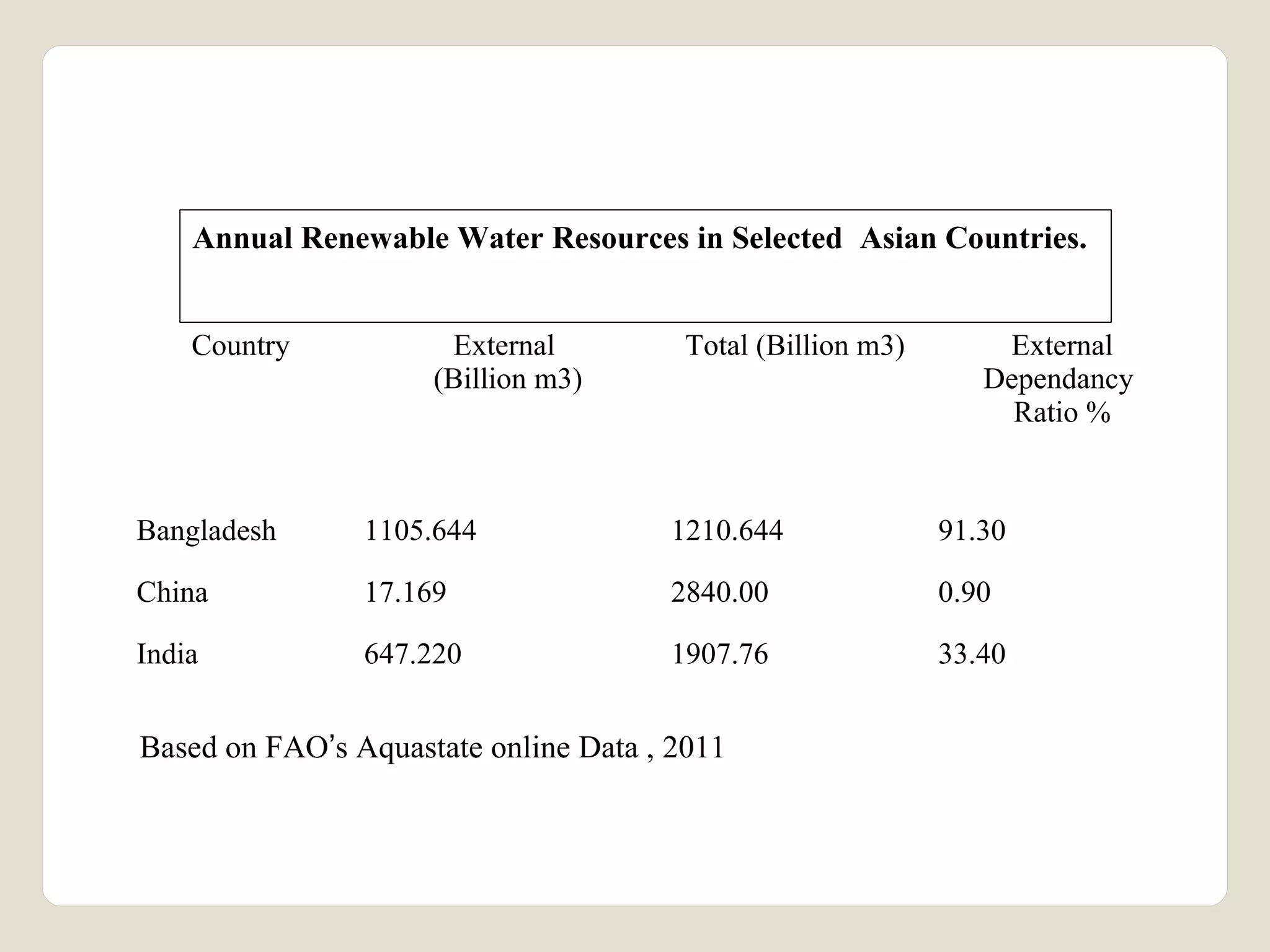
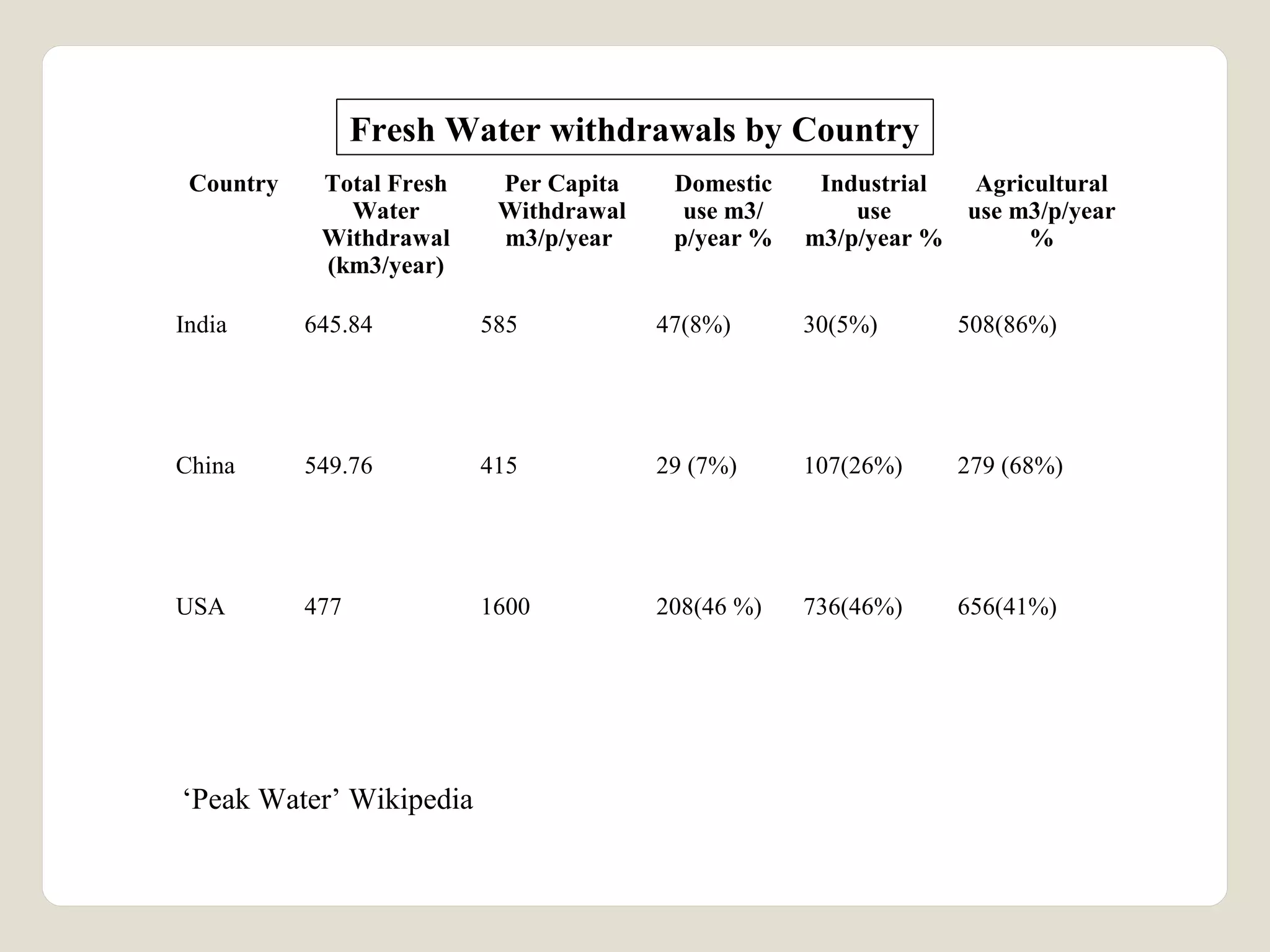
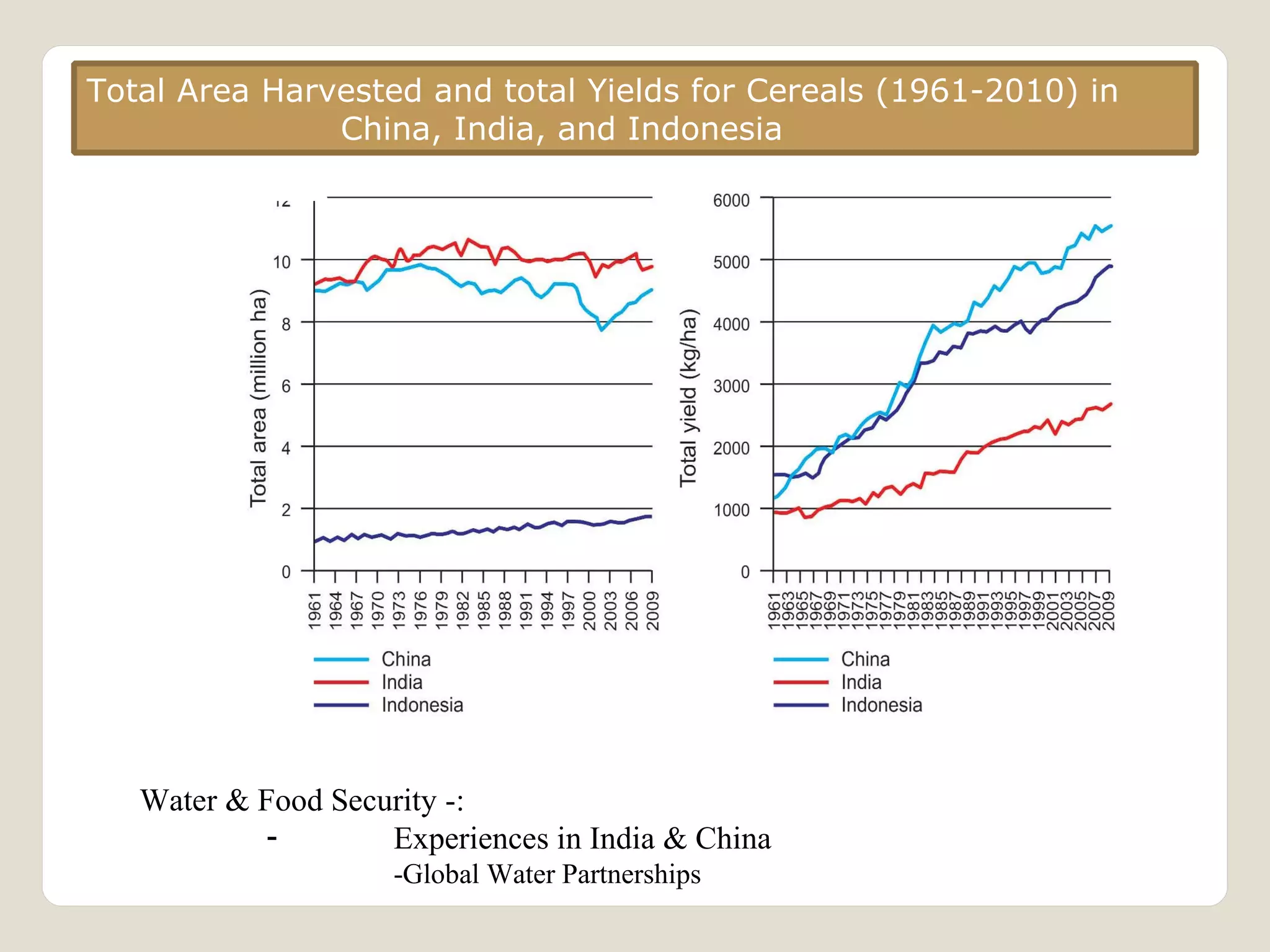
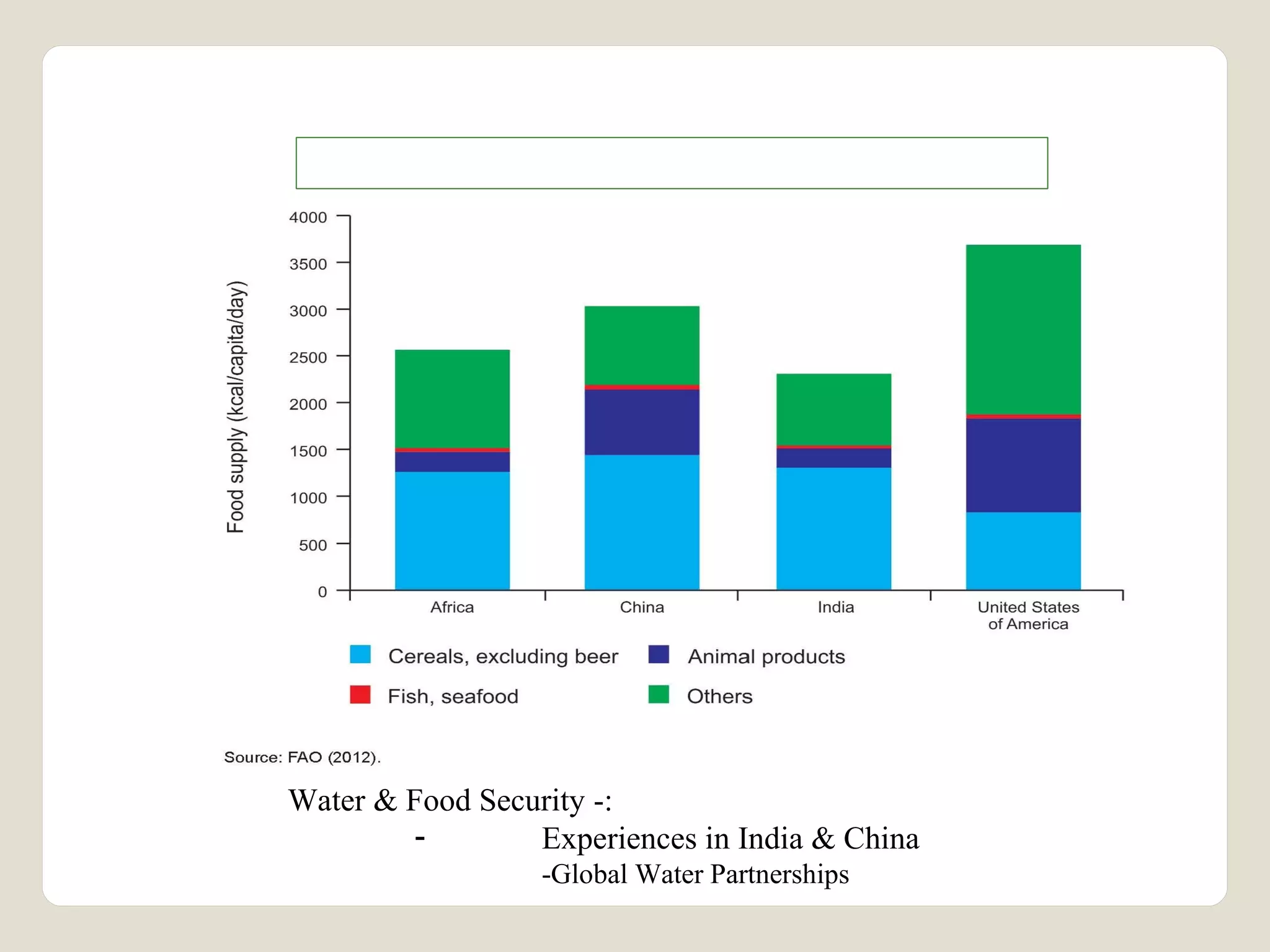
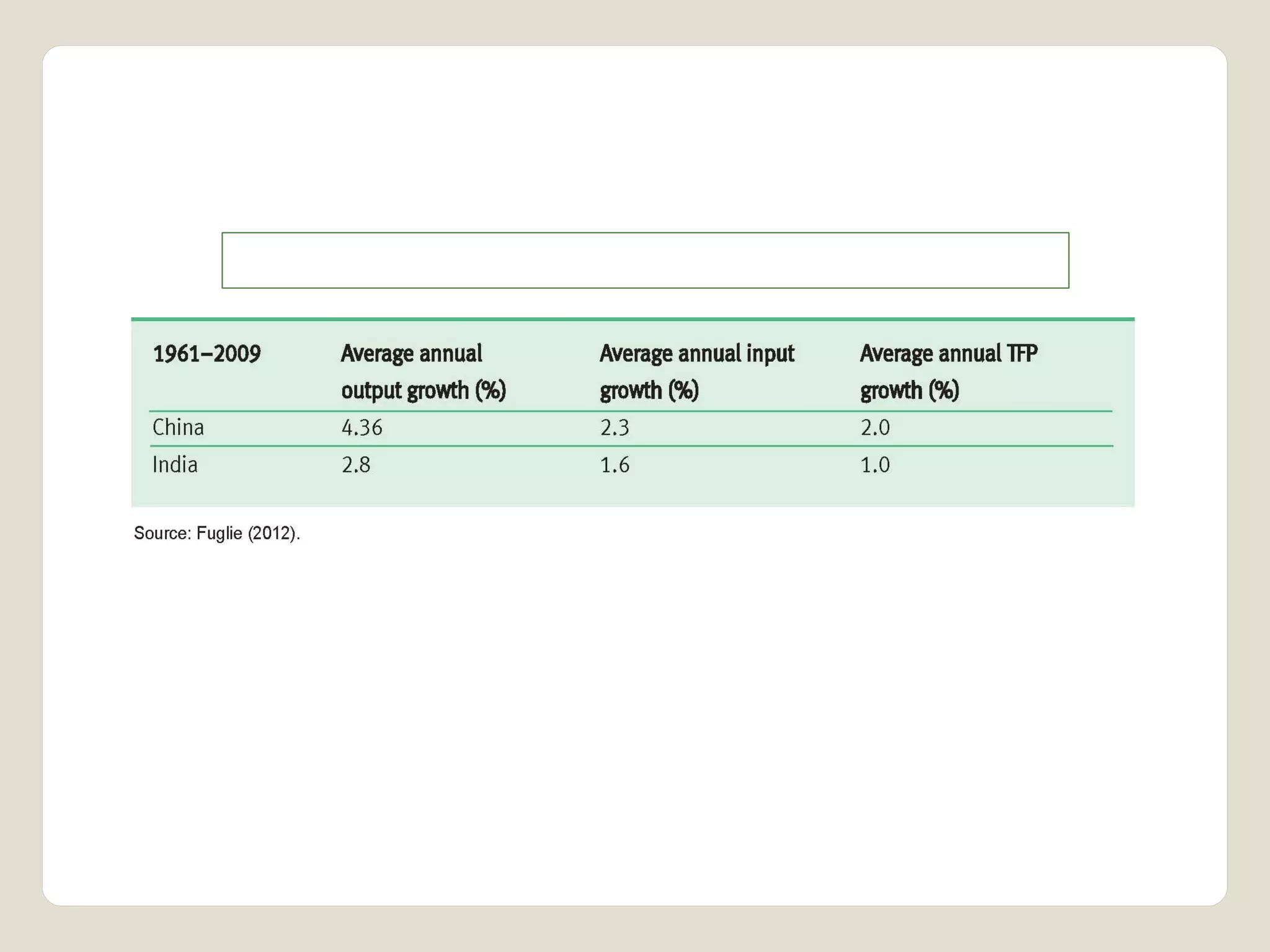
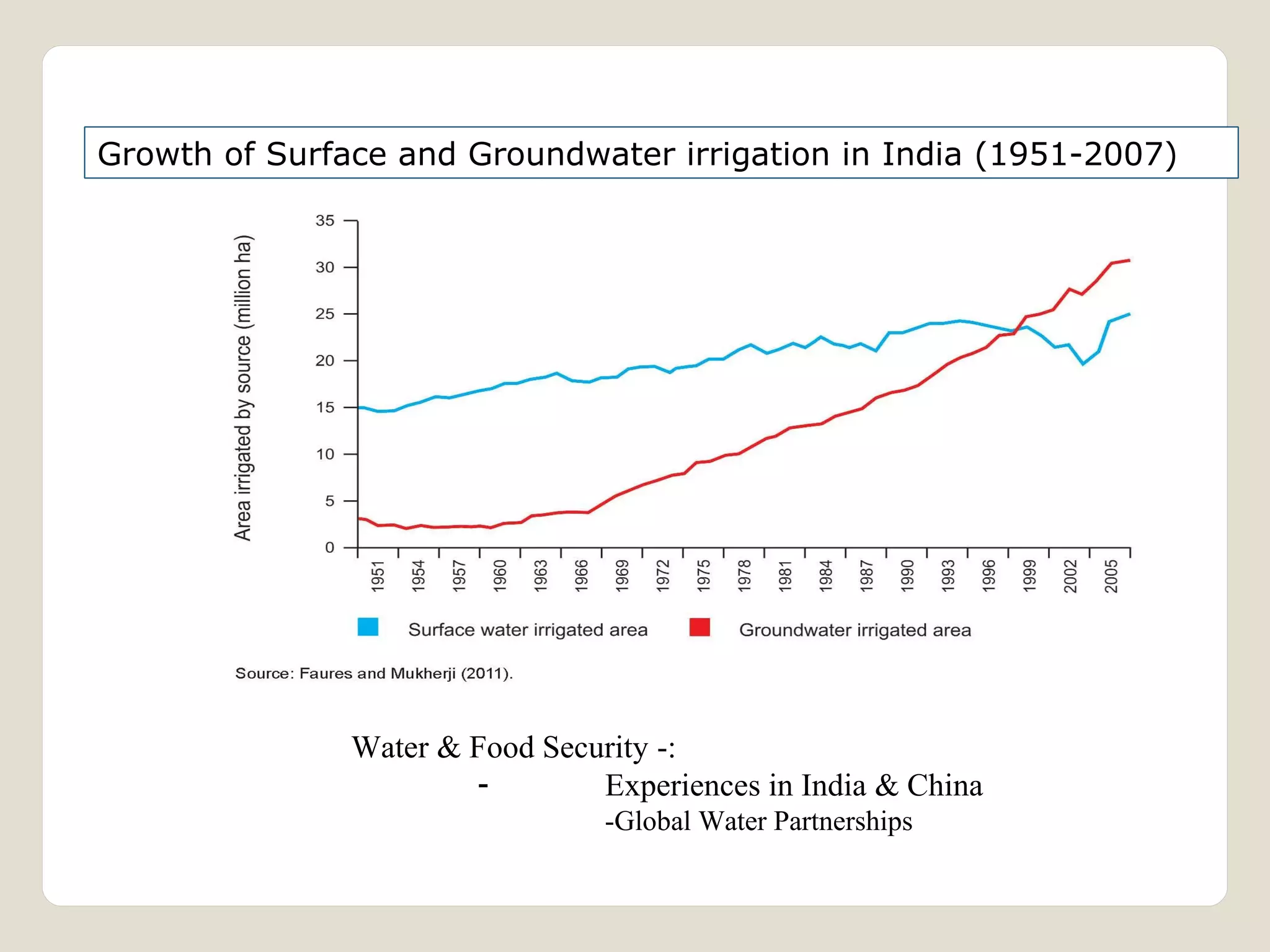
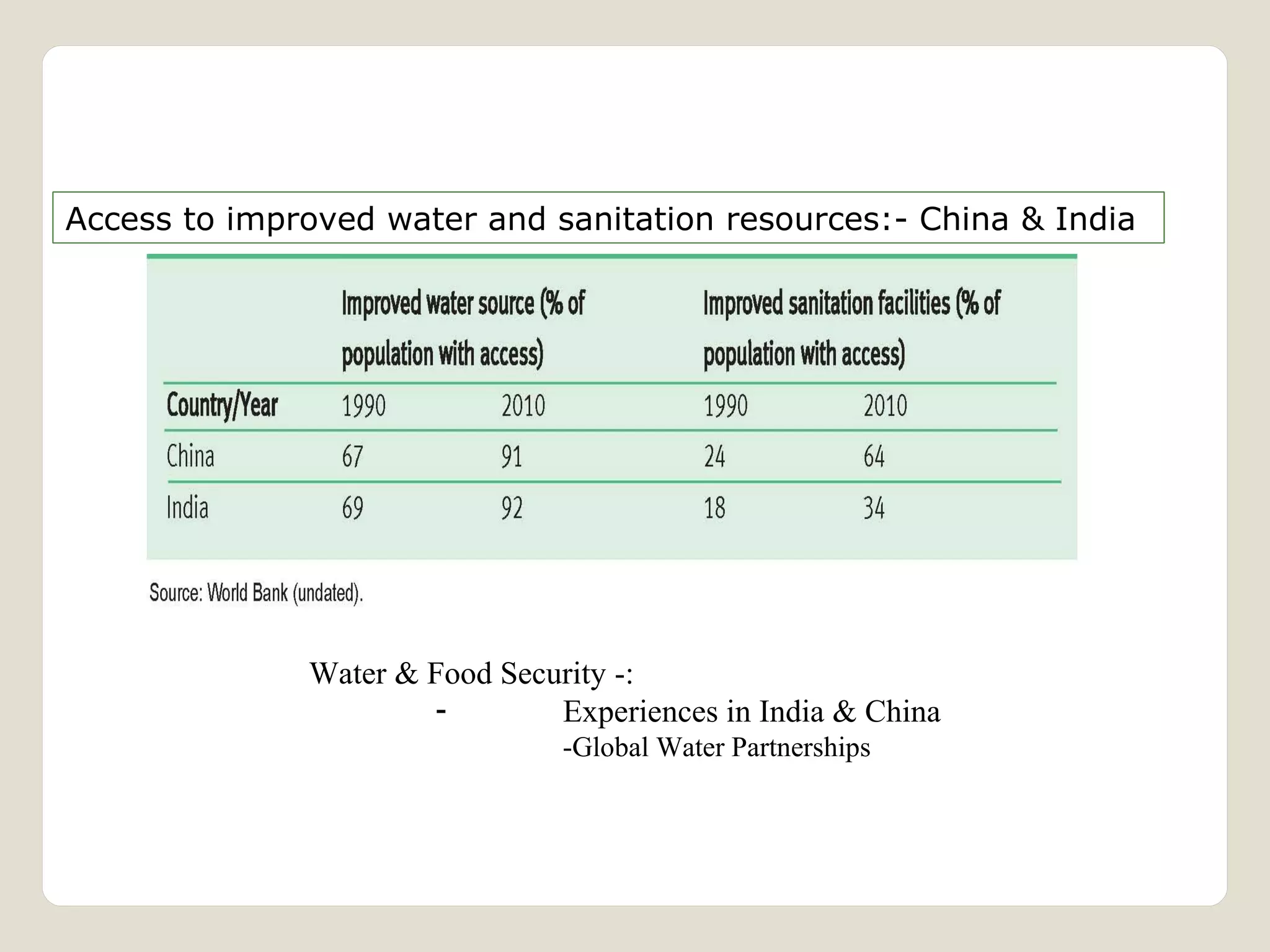
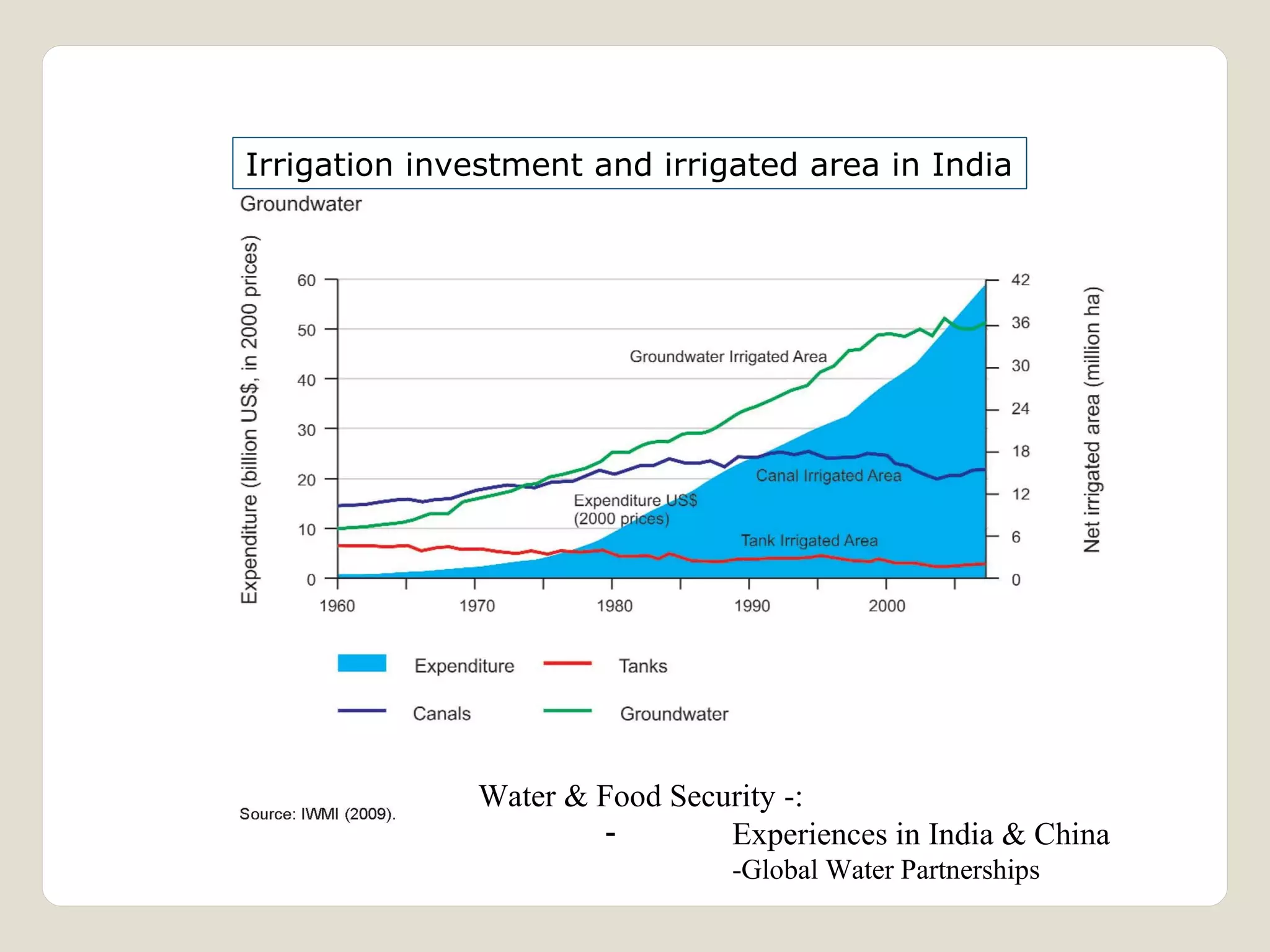
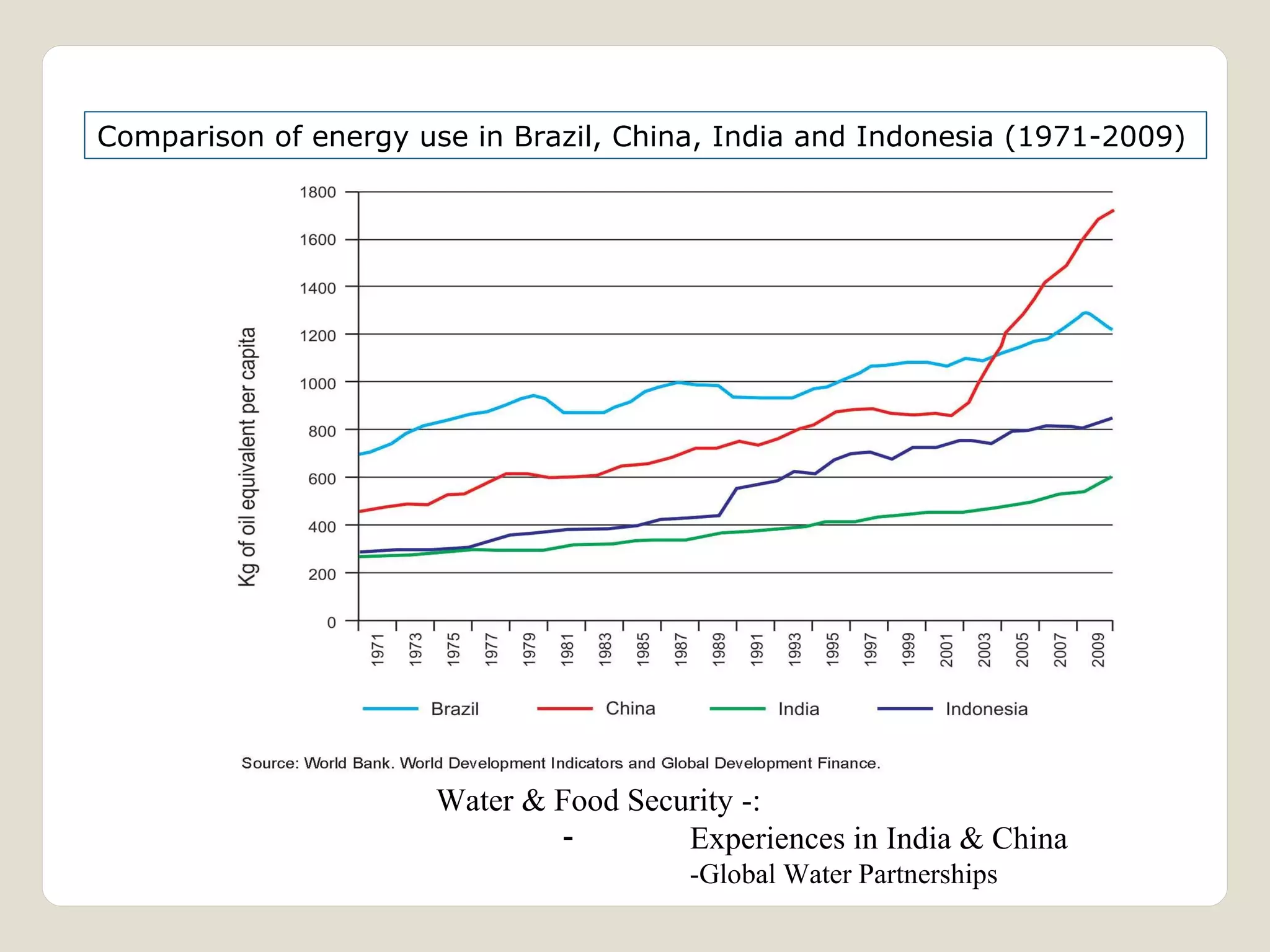
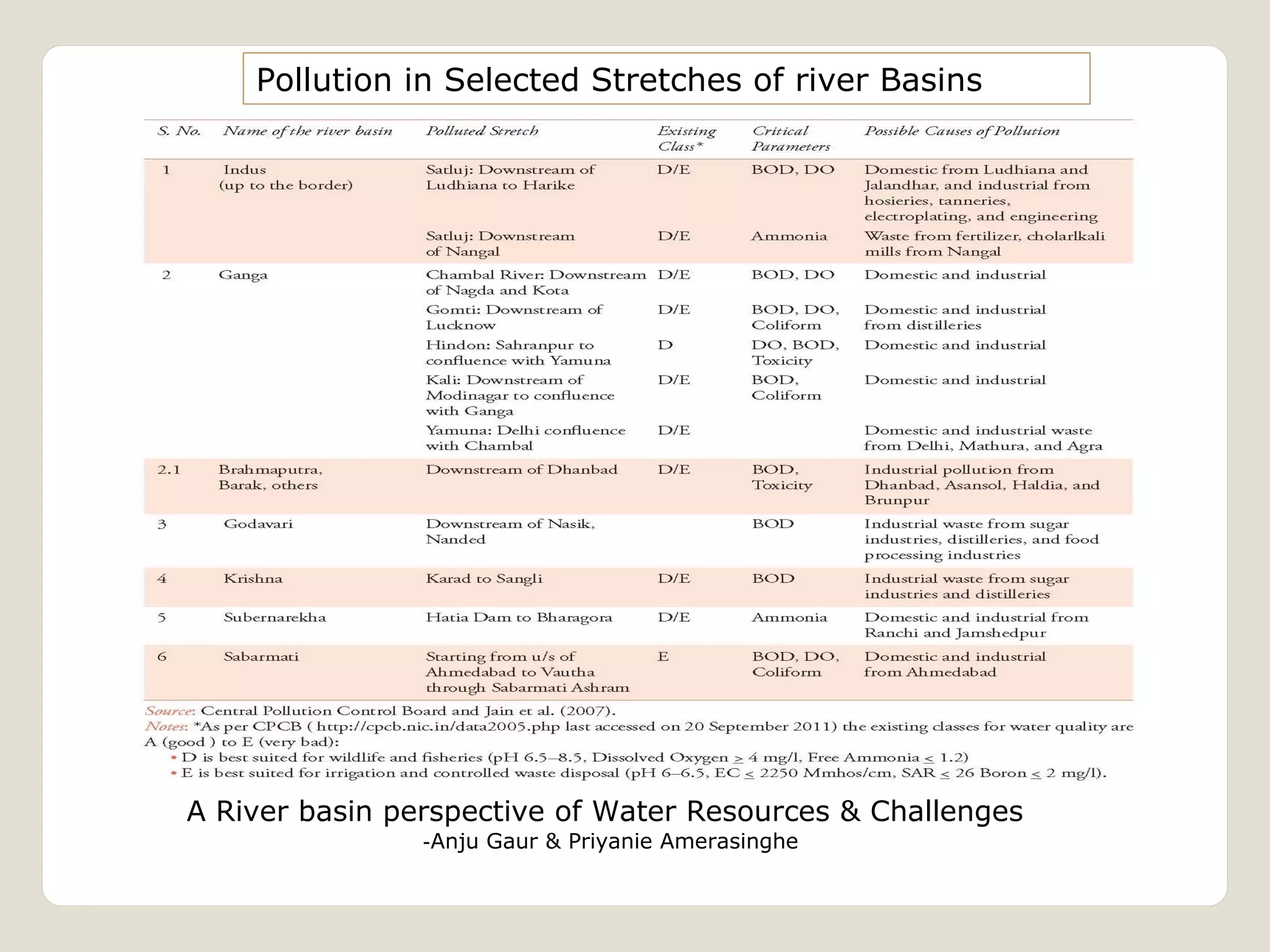
The document discusses water availability and use in India. It notes that India's annual renewable water resources per capita have declined from 5000 cubic meters in 1950 to 1200 cubic meters currently, putting the country in a state of water stress. Several factors contribute to India's water issues, including uneven spatial and temporal distribution of water resources, less storage availability, high external dependence, sub-optimal resource utilization, and increasing deterioration of water quality through pollution. Addressing India's water challenges will require improved management of the country's water resources.