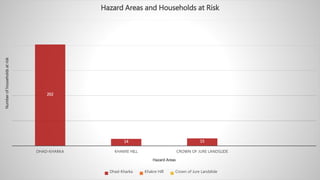
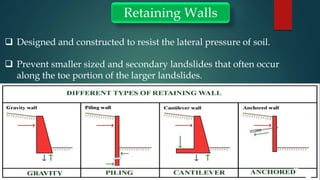
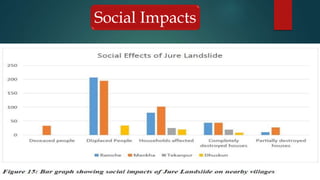
Water induced disaster risks pose a serious threat in Ramche VDC of Nepal. The area is vulnerable to landslides, floods and other hazards due to its geology and heavy monsoon rains. In 2014, the Jure landslide killed 156 people. To prevent future disasters, risk management measures are needed, including hazard mapping, relocating residents, improving drainage, using bioengineering techniques, and developing early warning systems. The Jure landslide had major social, economic, and psychological impacts on the community that still require addressing, such as providing permanent housing and infrastructure. Without proper management, Ramche faces the risk of another devastating landslide.