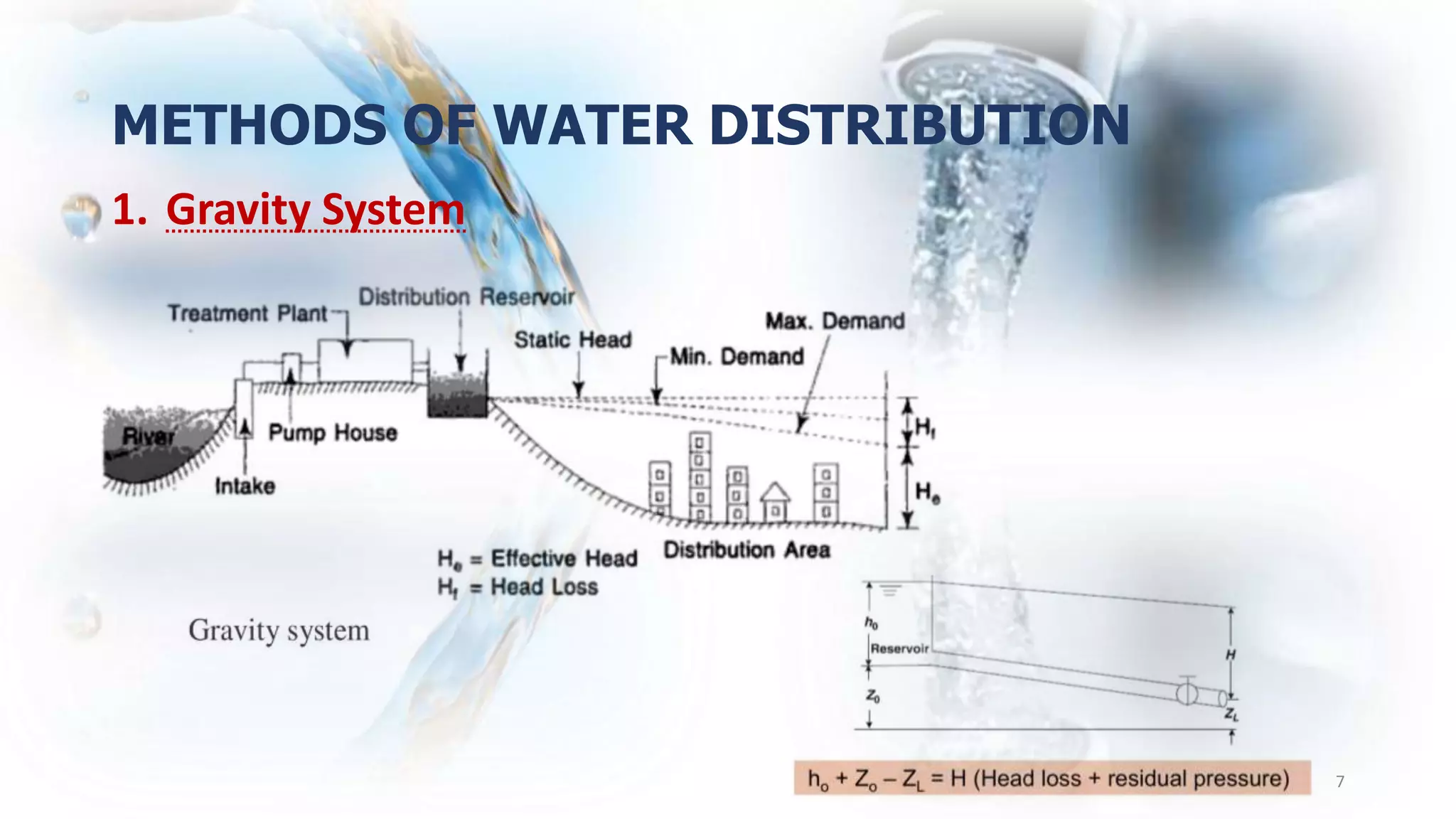
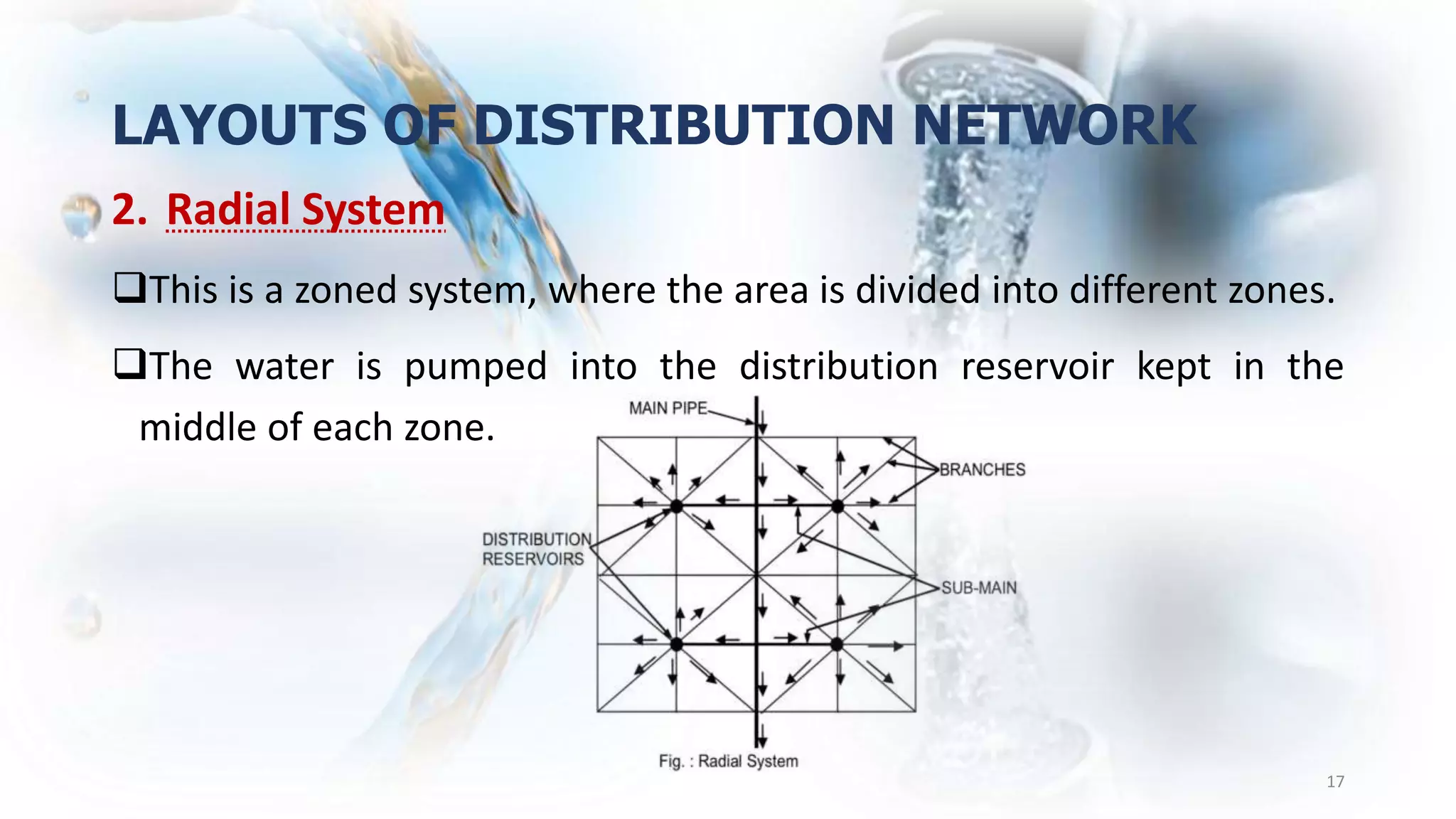
The document discusses water distribution systems. It explains that water from a source is temporarily stored and supplied to consumers through a network of pipelines called the distribution system. The distribution system consists of pumps, reservoirs, pipes and instruments to measure pressure and flow. It aims to deliver potable water to consumers with appropriate quality, quantity and pressure. Common distribution methods include gravity systems, pumping systems, and combined gravity and pumping systems. The layout of distribution networks can include dead-end, radial, grid-iron or ring systems. Distribution reservoirs store and regulate water flow and pressure in the distribution mains. Their design considers operating storage, emergency storage and fire storage requirements.