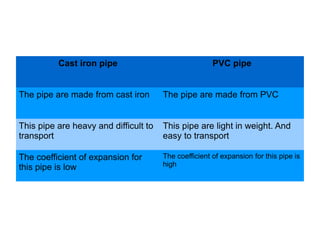
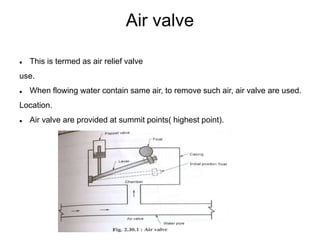
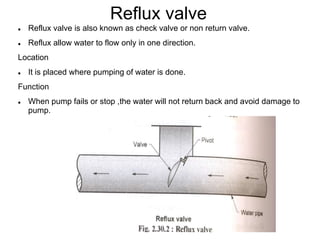
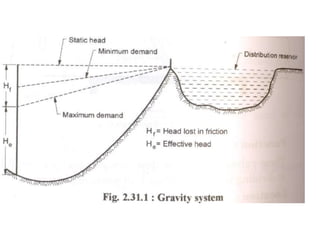
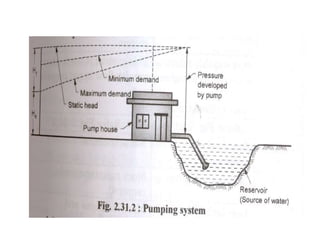
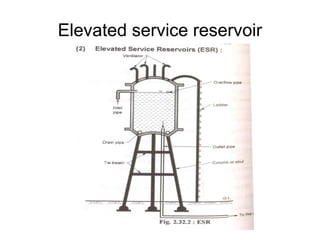
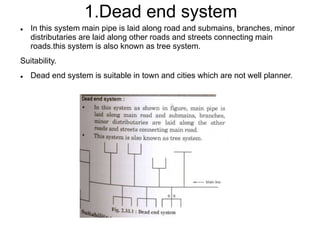
This document summarizes key aspects of water conveyance and distribution systems. It discusses different pipe materials like cast iron, PVC, and copper. It also describes common valves like air valves, reflux valves, relief valves and sluice valves. The document outlines gravity, pumping and combined water distribution systems. It analyzes reservoir types and layouts like dead-end, gridiron, circular and radial systems. Overall, the presentation covers essential components and methods for transporting water from its source to end users.