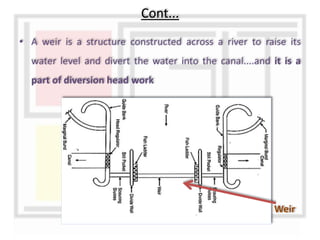
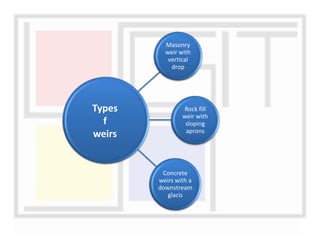
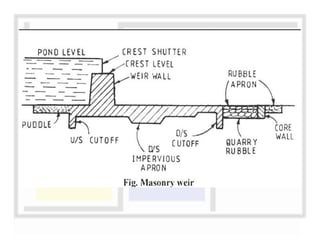
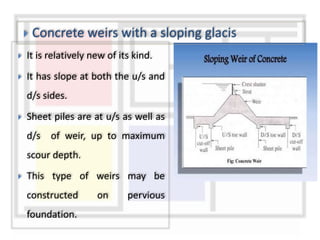
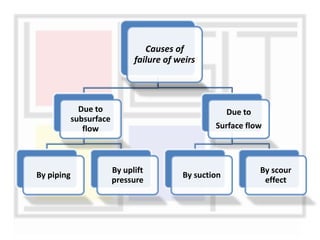
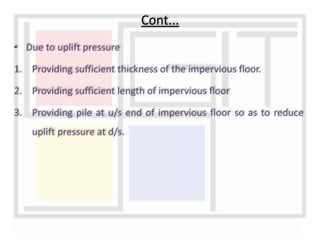
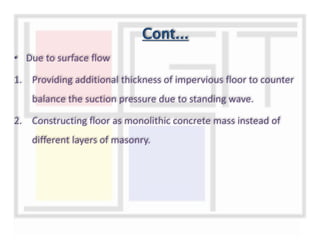
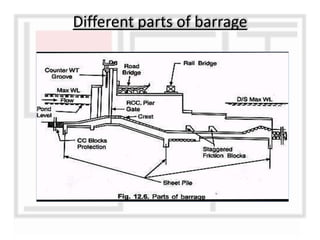
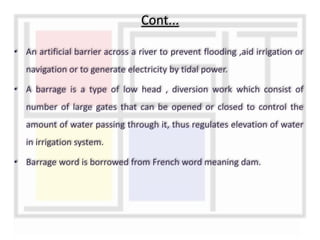
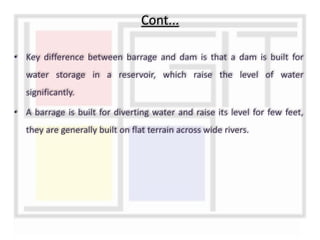
A weir is a solid structure built across a river to raise the water level and divert water into canals. There are different types of weirs including masonry weirs with vertical drops, rock fill weirs with sloping aprons, and concrete weirs with downstream slopes. Weirs can fail due to subsurface piping, uplift pressure, surface water suction or scouring. Remedies include installing sheet piles and ensuring sufficient floor thickness and length. A barrage is similar to a weir but uses gates rather than a solid structure to control water levels. Barrages are more expensive than weirs but allow better control of water levels and less silting during floods by raising the gates.