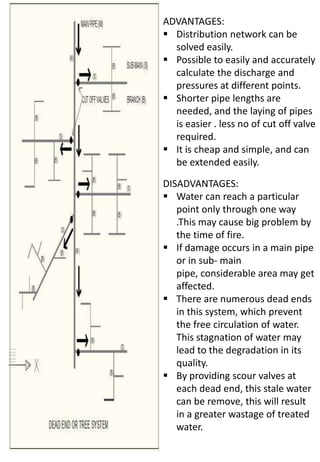
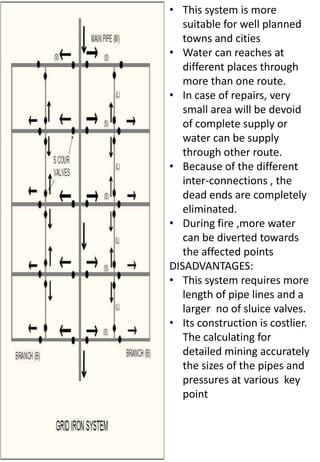
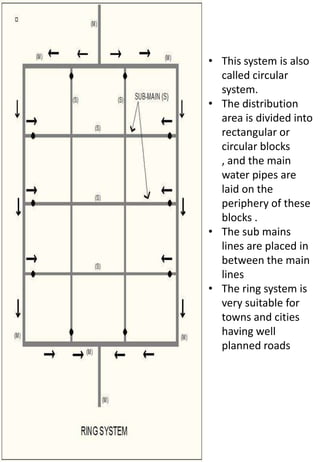
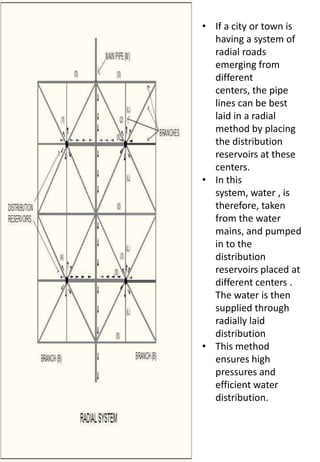
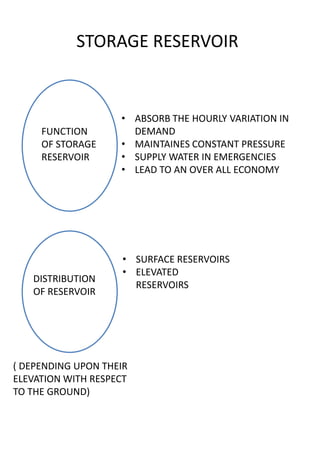
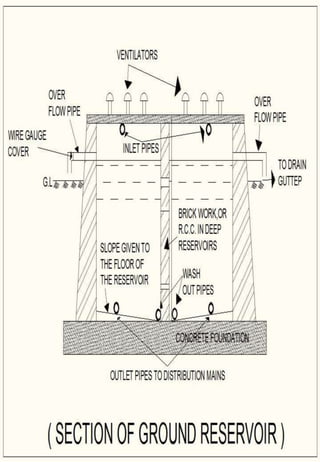
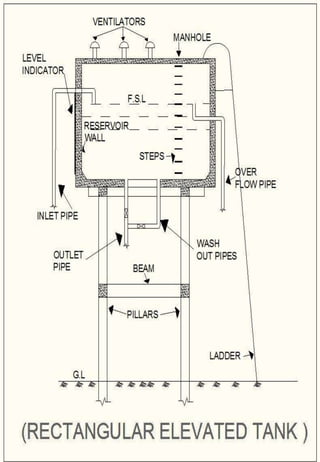
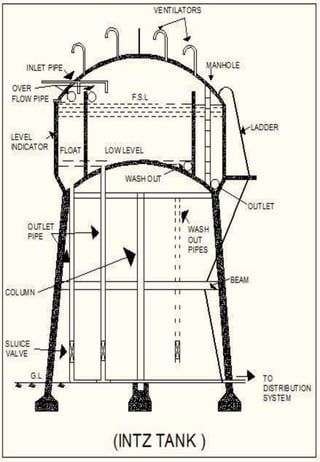
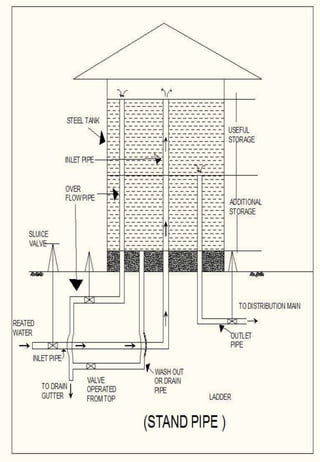
This document discusses different types of water distribution system layouts, including dead end, grid-iron, ring, and radial systems. It also describes the advantages and disadvantages of each system. Storage reservoirs are discussed, including their functions of absorbing demand variations, maintaining pressure, and providing emergency supply. Surface and elevated reservoirs are compared, with elevated reservoirs being more efficient but also more expensive.