Drip irrigation and sprinkler irrigation are two common irrigation methods discussed in the document, with drip irrigation applying small quantities of water directly to plant roots through a network of pipes and emitters, while sprinkler irrigation sprays water into the air to fall on soil surfaces resembling rainfall using pumped water and sprinkler heads. The document outlines the components, operation, advantages, and limitations of each system along with their suitability for different crop types and soil conditions.


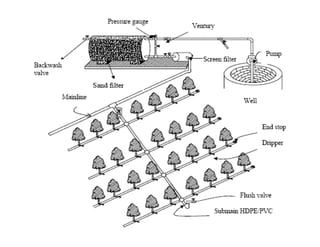
![1] Drip irrigation
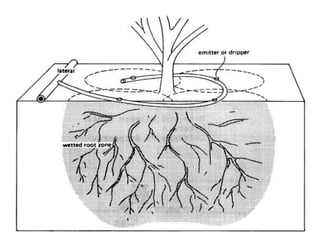
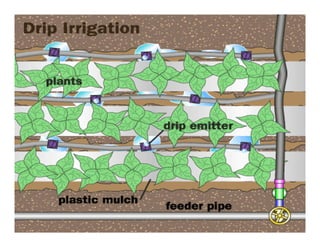
Also known as trickle irrigation
Drip irrigation refers to
application of water i small
li ti f t in ll
quantity at the rate of mostly less
than 12 Lit/hr as drops to the
zone of the plants through a
f h l h h
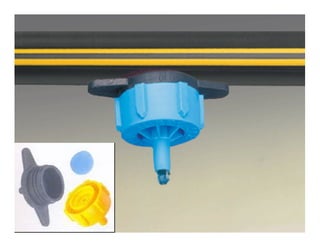
network of plastic pipes fitted
with emitters.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/waterapplicationmethodspartii-110409225749-phpapp02/85/Water-application-methods-part-ii-3-320.jpg)










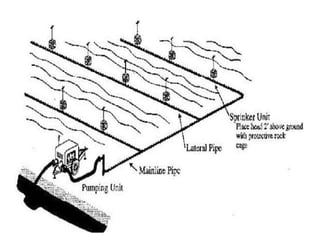
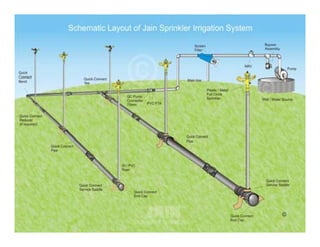
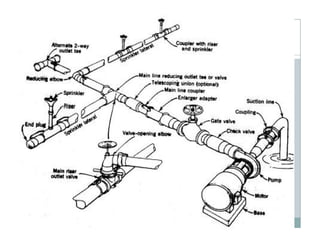
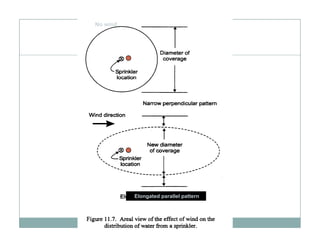
![1] Sprinkler irrigation
In the sprinkler method of irrigation
irrigation,
water is sprayed into the air and
allowed to f ll on the ground surface
ll d fall h d f
somewhat resembling rainfall. The
g
spray is developed by the flow of
water under pressure through small
orifices or nozzles. The pressure is
usually obtained by pumping.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/waterapplicationmethodspartii-110409225749-phpapp02/85/Water-application-methods-part-ii-20-320.jpg)