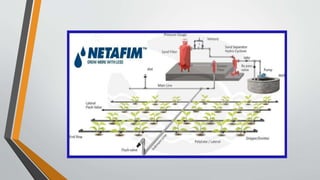
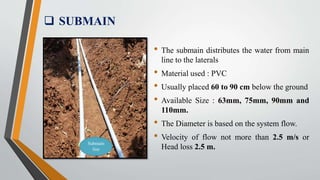
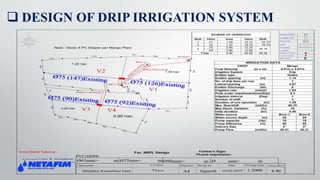
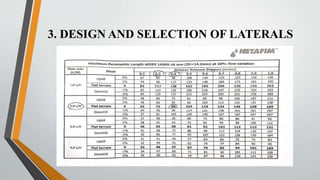
This document provides an overview of an in-plant training conducted at Netafim Irrigation India Pvt. Ltd. in Vadodara. It discusses the company profile, principles of micro irrigation systems, components and design of drip irrigation systems, and the role of the Gujarat Green Revolution Company in promoting micro irrigation in Gujarat. The training covered topics such as the study and design of drip irrigation systems, field surveys, installation, and the benefits of fertigation. The document provides details on the various components of drip irrigation systems and the procedures for designing, installing, and implementing such systems.