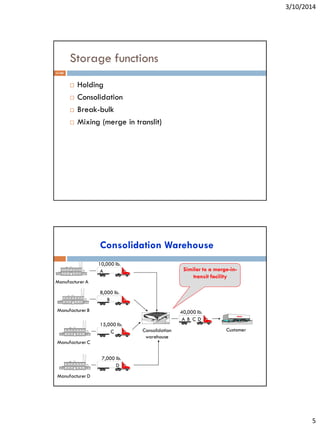
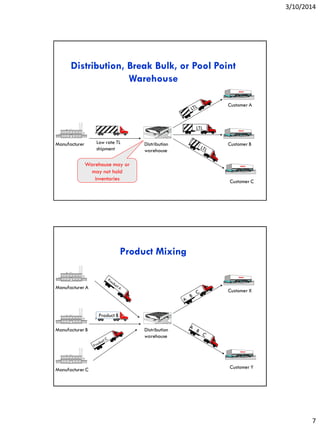
This document discusses storage fundamentals in inventory strategy. It explains that warehouses and material handling are needed to maintain inventories in order to improve coordination between supply and demand. Specific reasons for storage include reducing transportation and production costs, coordinating supply and demand, and assisting production and marketing processes. The document also describes different types of warehouses based on the products stored, the level of storage, and product flows. It discusses storage functions like holding, consolidation, and break-bulk and analyzes alternatives for warehouse ownership, leasing, and rental.