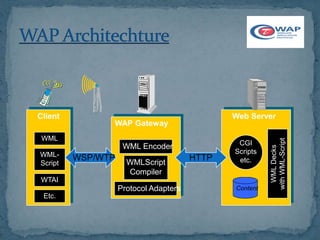
The document discusses the Wireless Application Protocol (WAP), which defines a set of communication protocols for wireless devices to access the internet and advanced telephony services. WAP is an open standard backed by major vendors like Nokia, Ericsson, and Motorola. It allows for competition and lower costs while supporting multiple wireless systems. WAP aims to enhance the user experience on mobile devices by addressing limitations of small screens, limited bandwidth, and battery life.