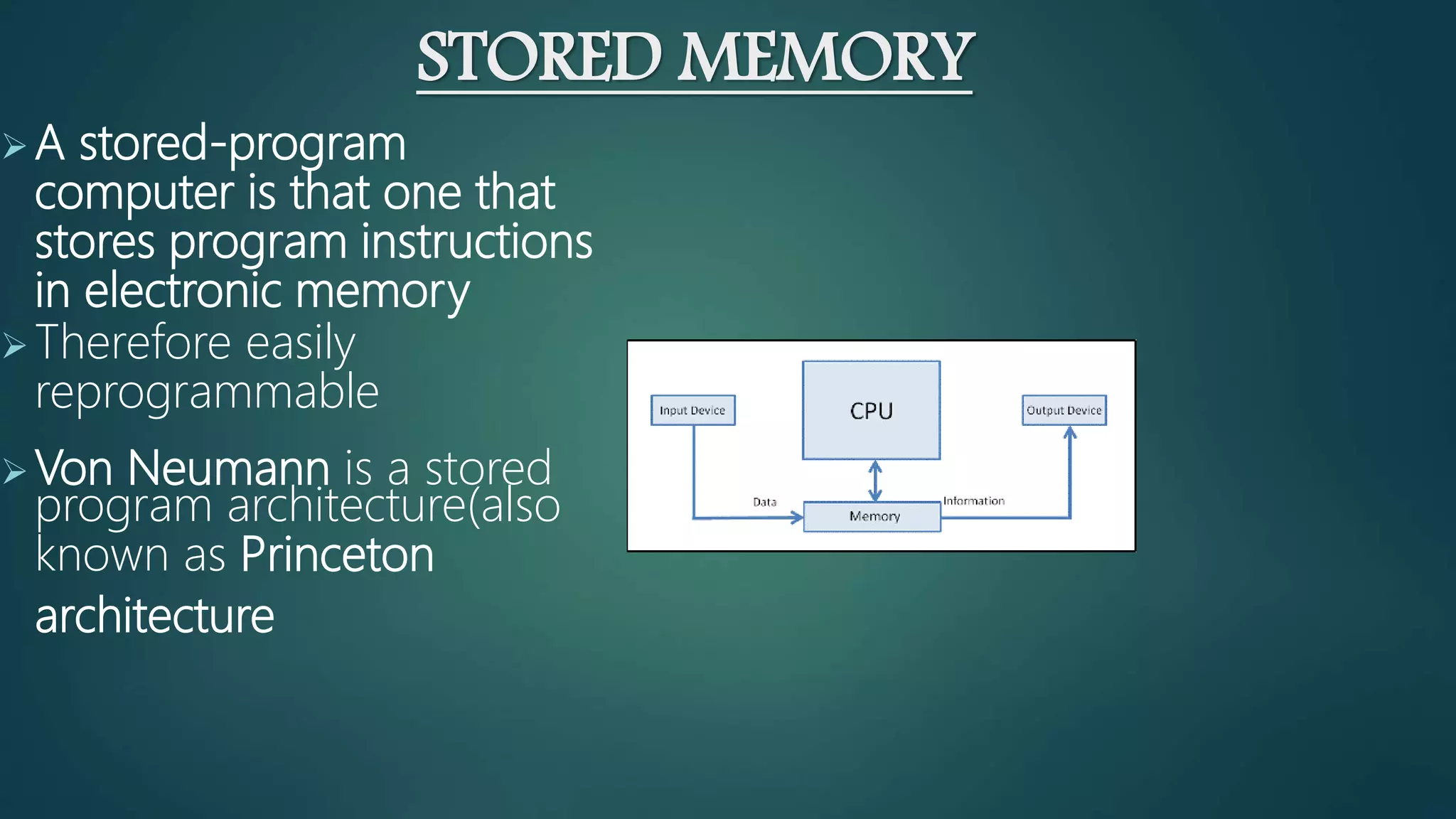
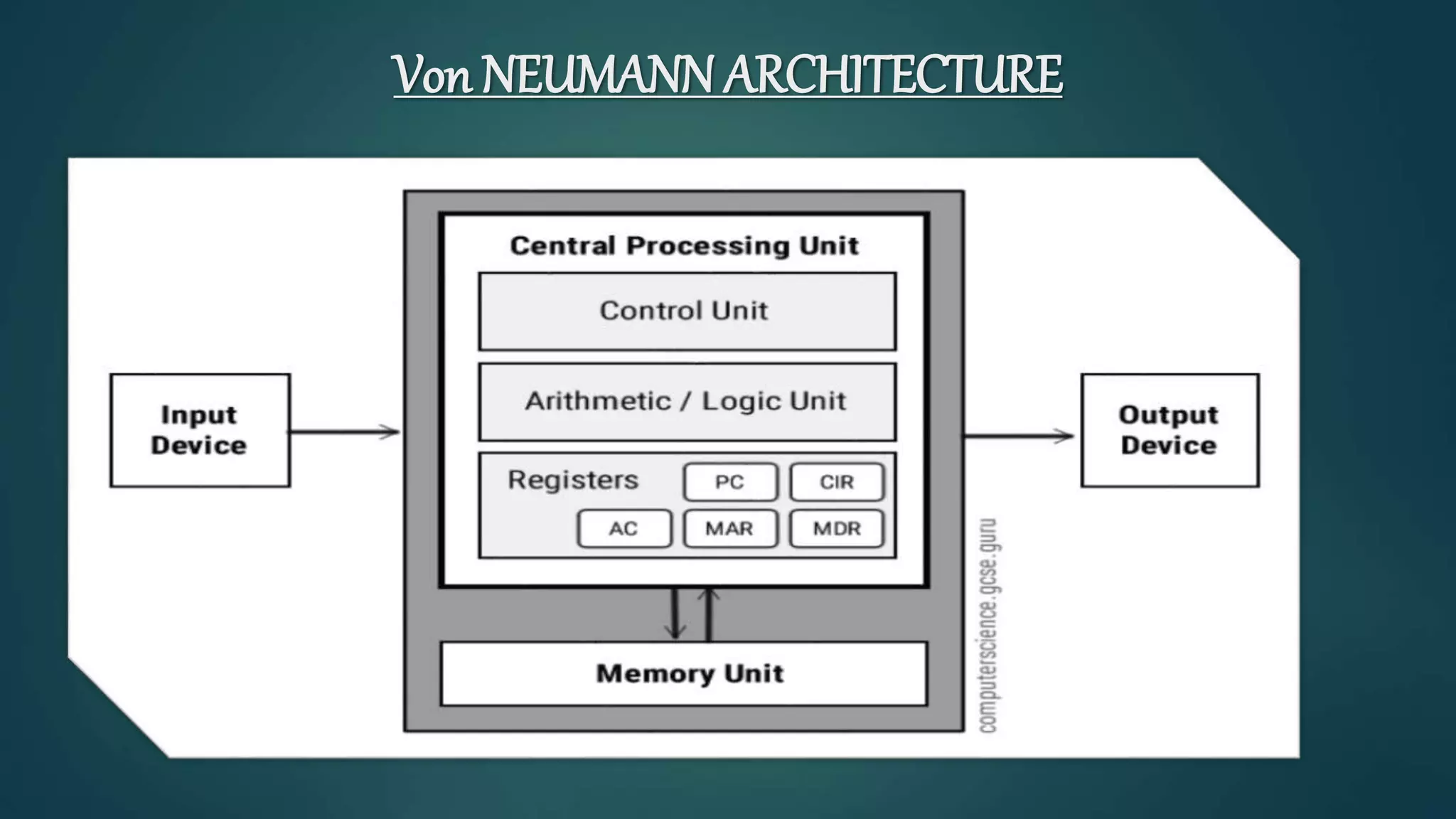
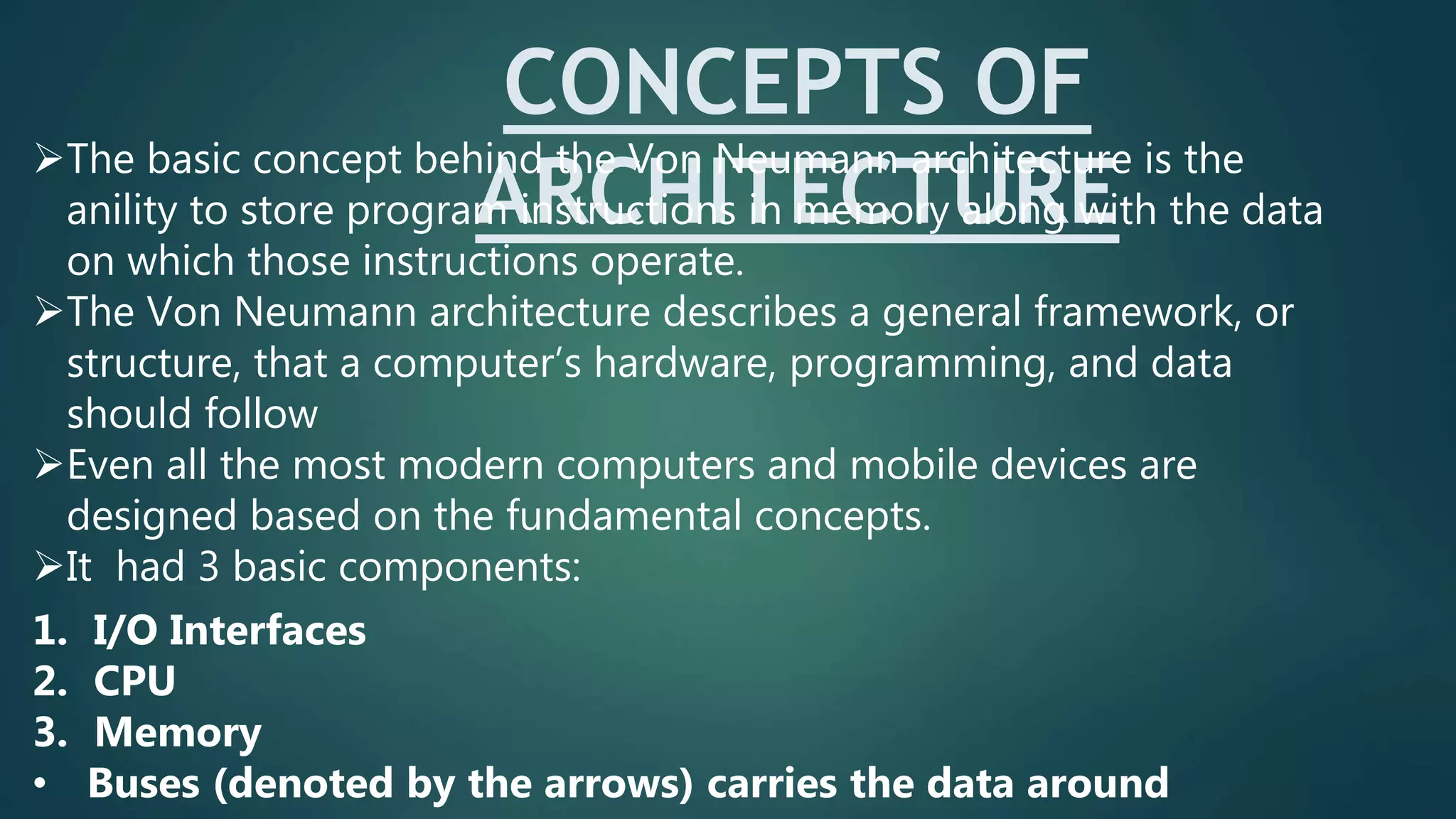
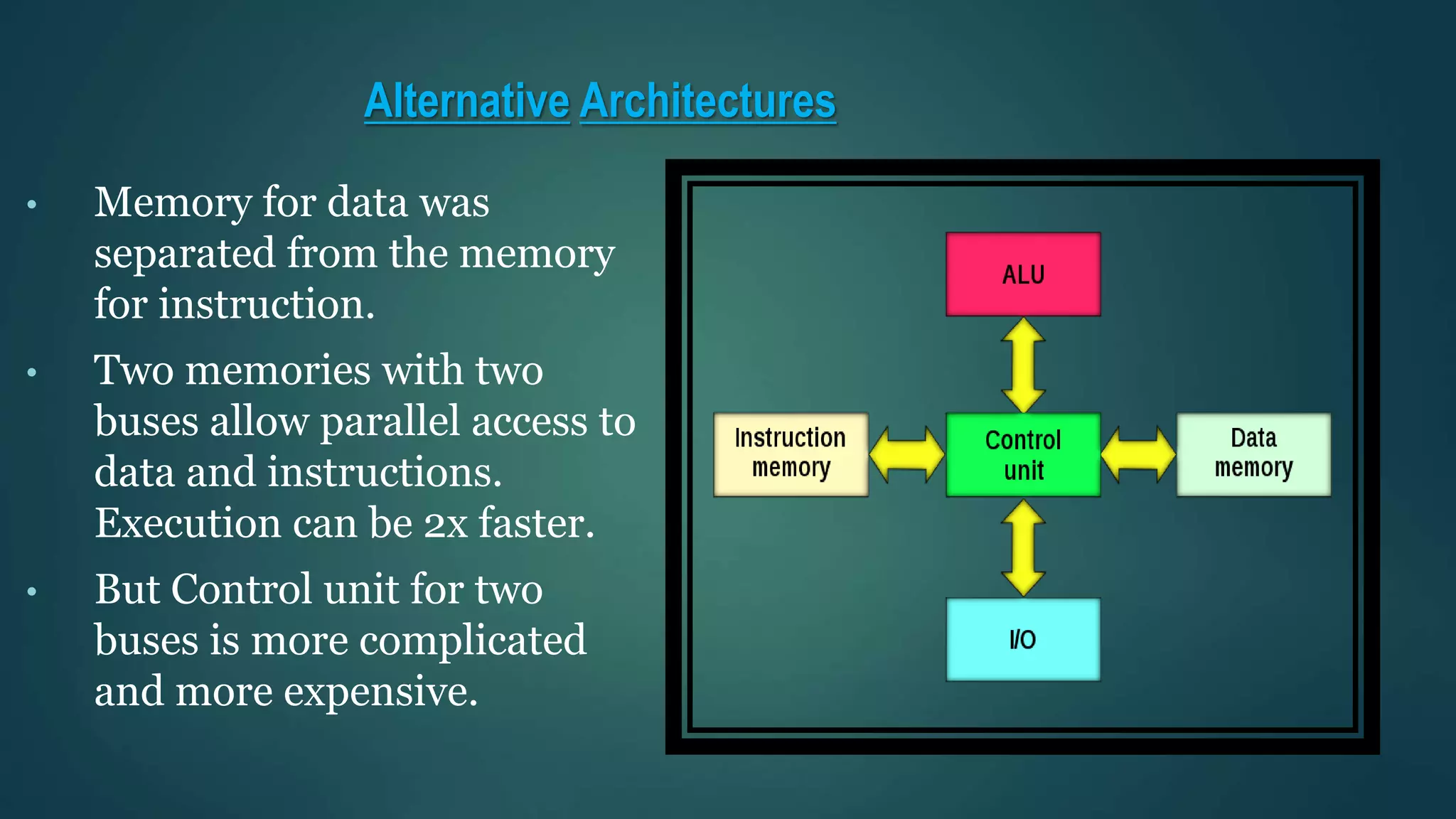
The document discusses the Von Neumann architecture, which was developed by mathematician John von Neumann. It describes the basic concepts of the Von Neumann architecture, which includes storing program instructions in memory along with data. The key components are the I/O interfaces, central processing unit (CPU), and memory, connected by buses. The CPU contains a control unit, arithmetic logic unit, and registers. The Von Neumann architecture is still used in modern computers today due to its advantages of simplicity, though it also has disadvantages like serial processing.