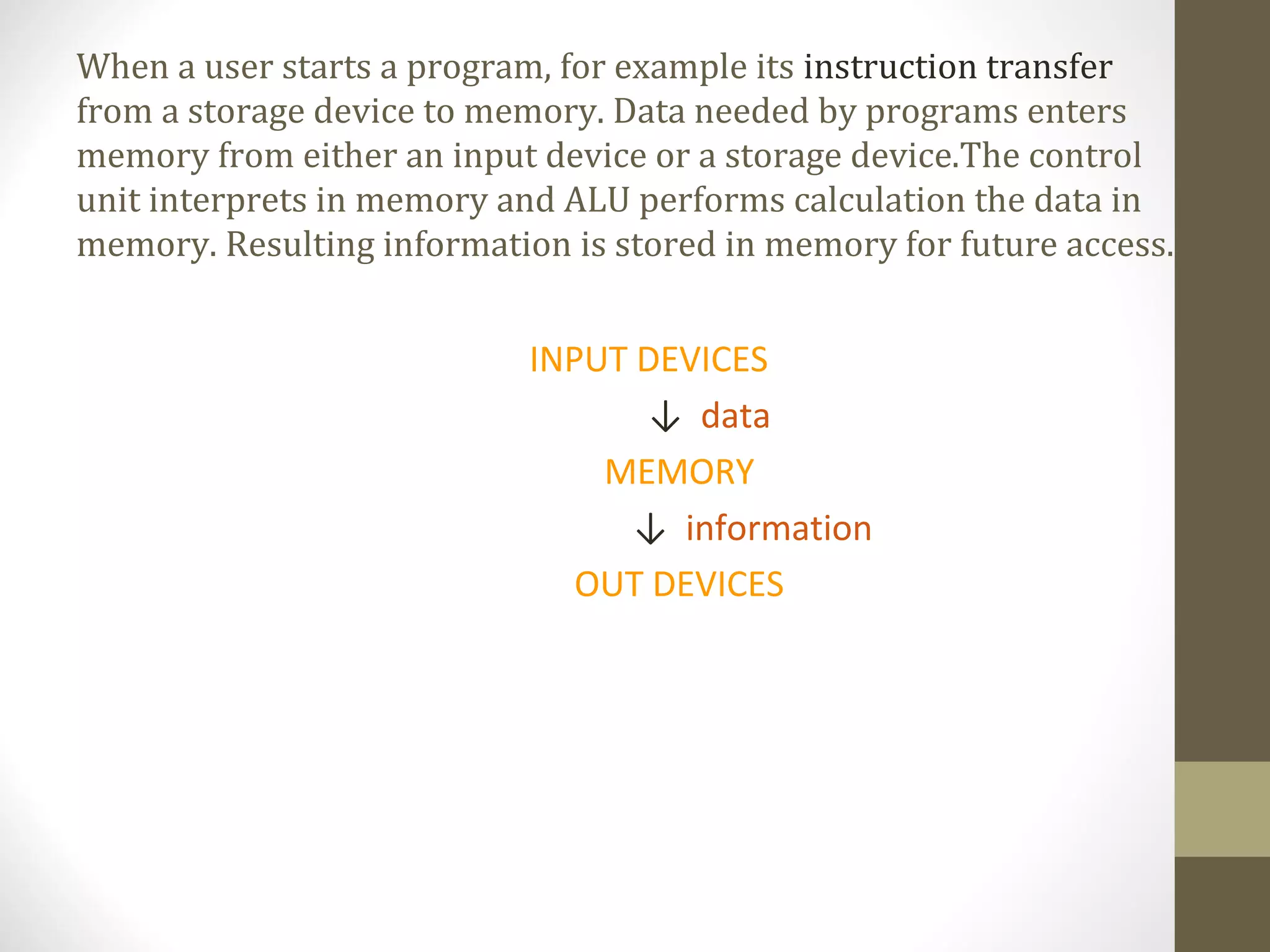
A processor, also called the central processing unit (CPU), interprets and carries out instructions to operate a computer. Modern processors often have multiple cores on a single chip. Common multi-core processors are dual-core and quad-core. The control unit directs operations like the arithmetic logic unit (ALU) which performs calculations using data from memory. Memory stores operating systems, programs, and data for processing and output to devices.