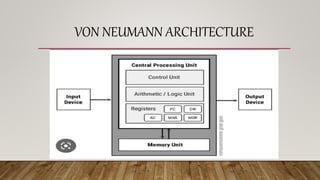
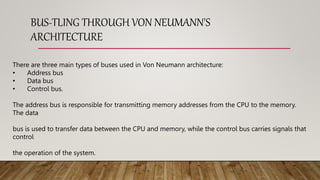
The von Neumann architecture is a stored program architecture that uses a central processing unit (CPU), memory, and input/output interfaces. It introduced the concept of storing both program instructions and data in memory. The CPU contains a control unit, arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and registers. The control unit fetches instructions from memory and directs data flow. The ALU performs arithmetic and logic operations. Registers temporarily store data and instructions. Buses connect the main components and transfer data and instructions throughout the system. This architecture enables computers to be reprogrammable and laid the foundation for modern computer design.