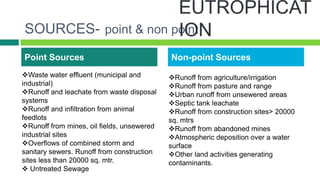
Eutrophication is the process by which a body of water becomes overly enriched with minerals and nutrients that induce excessive growth of algae. This document discusses the basic concepts of eutrophication, the types (natural vs. cultural), sources (point sources like sewage vs. non-point sources like agricultural runoff), effects on the environment and society, and potential remedial measures. The sources of excess nutrients that cause eutrophication are primarily agricultural fertilizers, domestic sewage, and livestock waste. Eutrophication can lead to decreased water quality, loss of habitat, and changes in the plant and animal communities in the affected body of water. Reducing nutrient inputs from fertilizers and sewage is