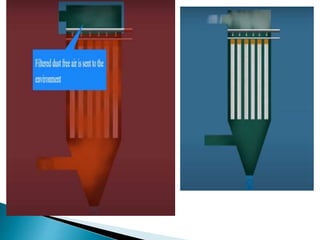
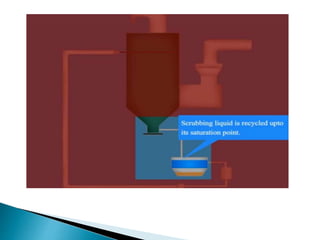
The document provides a detailed explanation of particulate matter (PM), its sources, classification, and effects on health and the environment. It categorizes PM based on size (coarse and fine particles) and origin (natural or man-made), discussing their health impacts and the regulatory measures in place for controlling emissions in industrialized countries. Various dust collection systems used to manage PM emissions, including inertial collectors, fabric filters, wet scrubbers, and electrostatic precipitators, are also described.