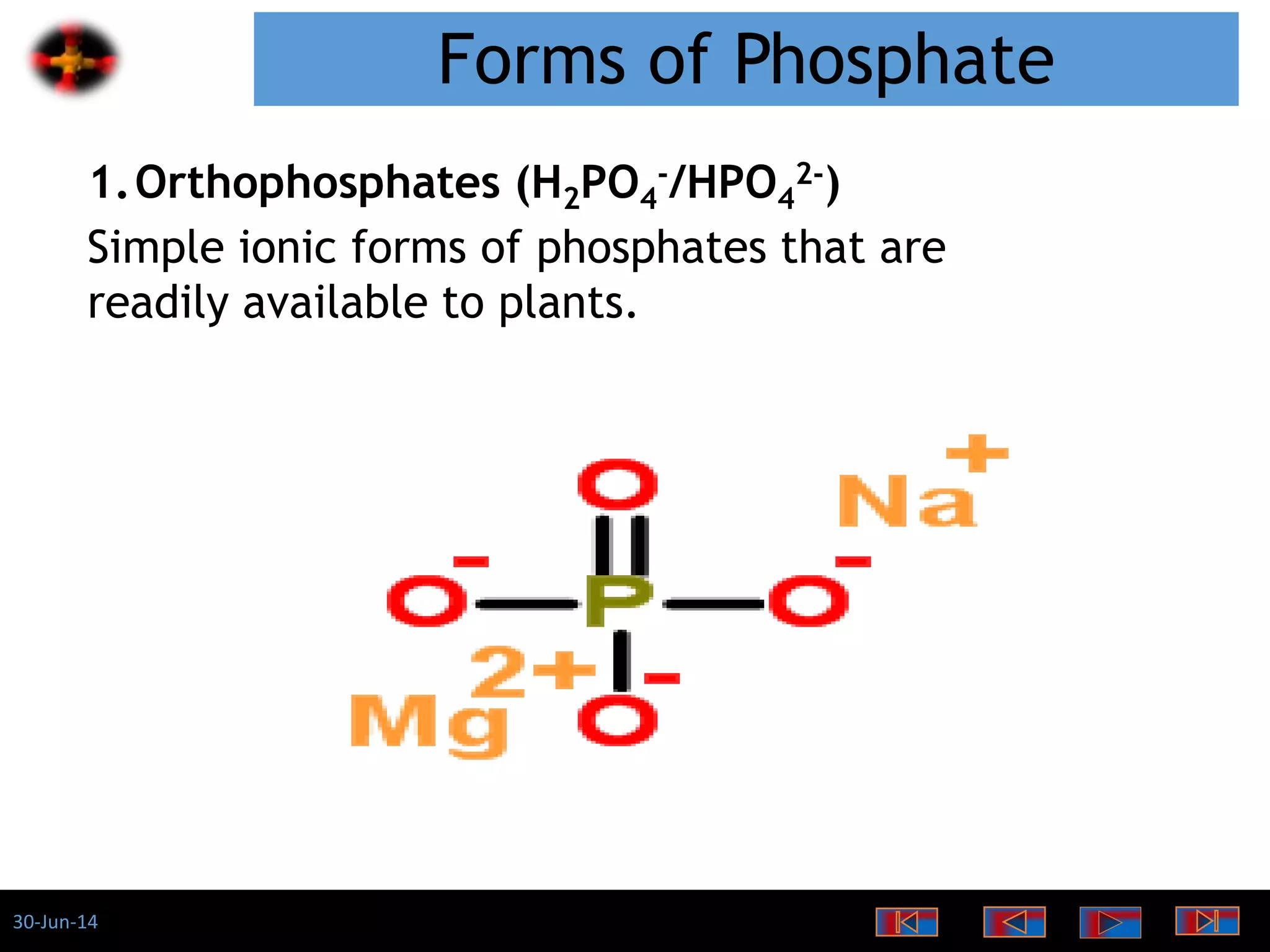
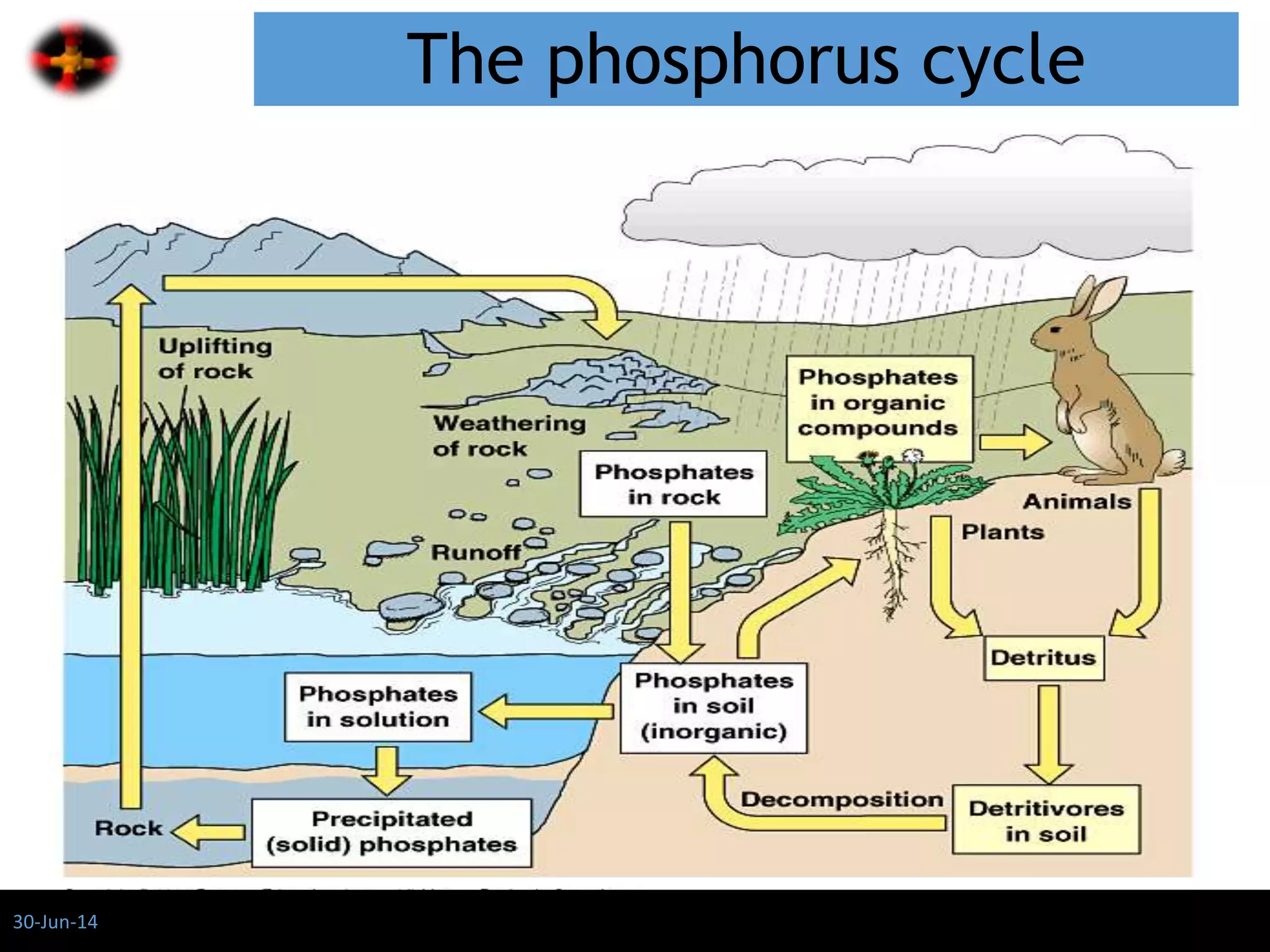
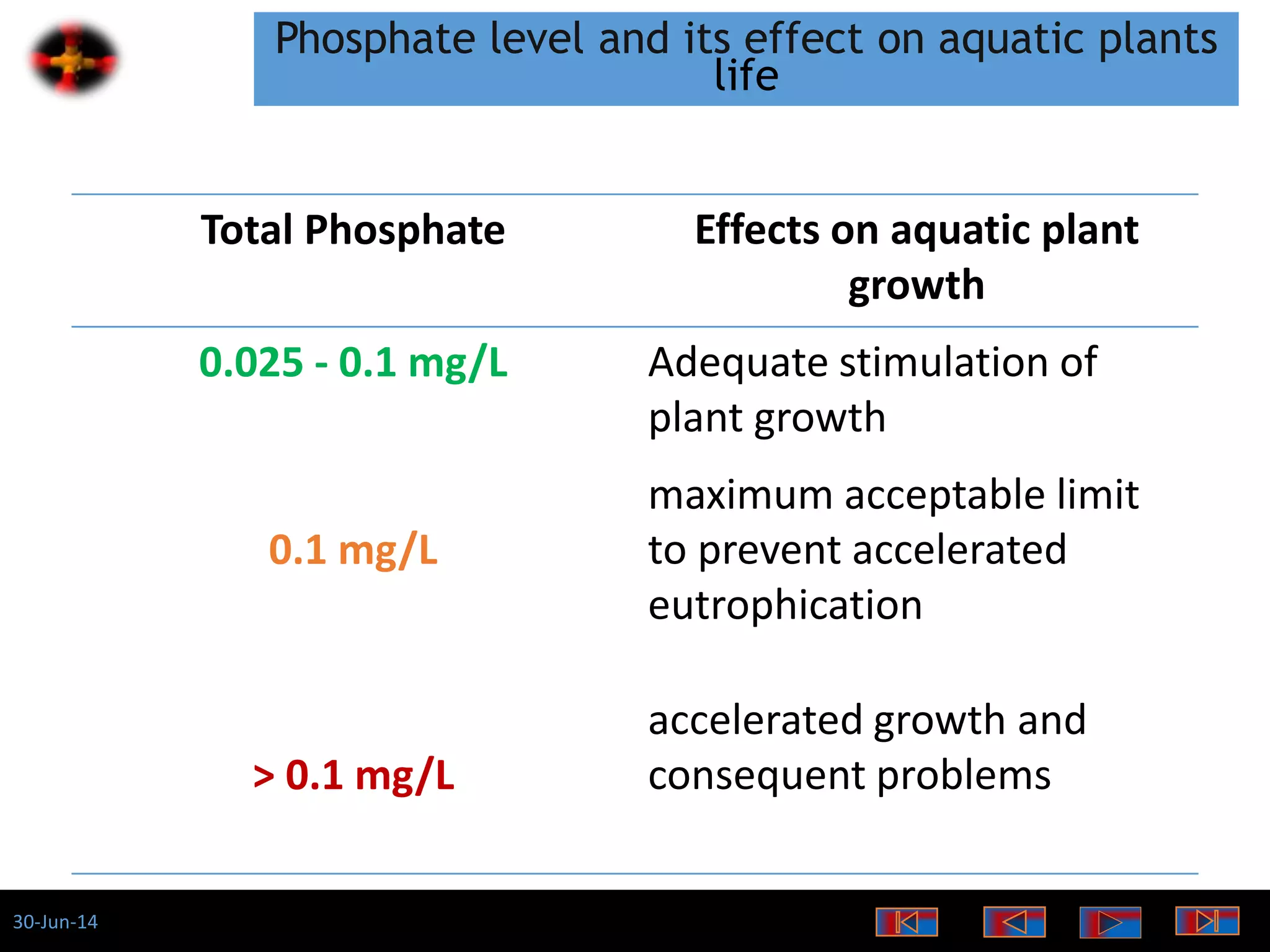
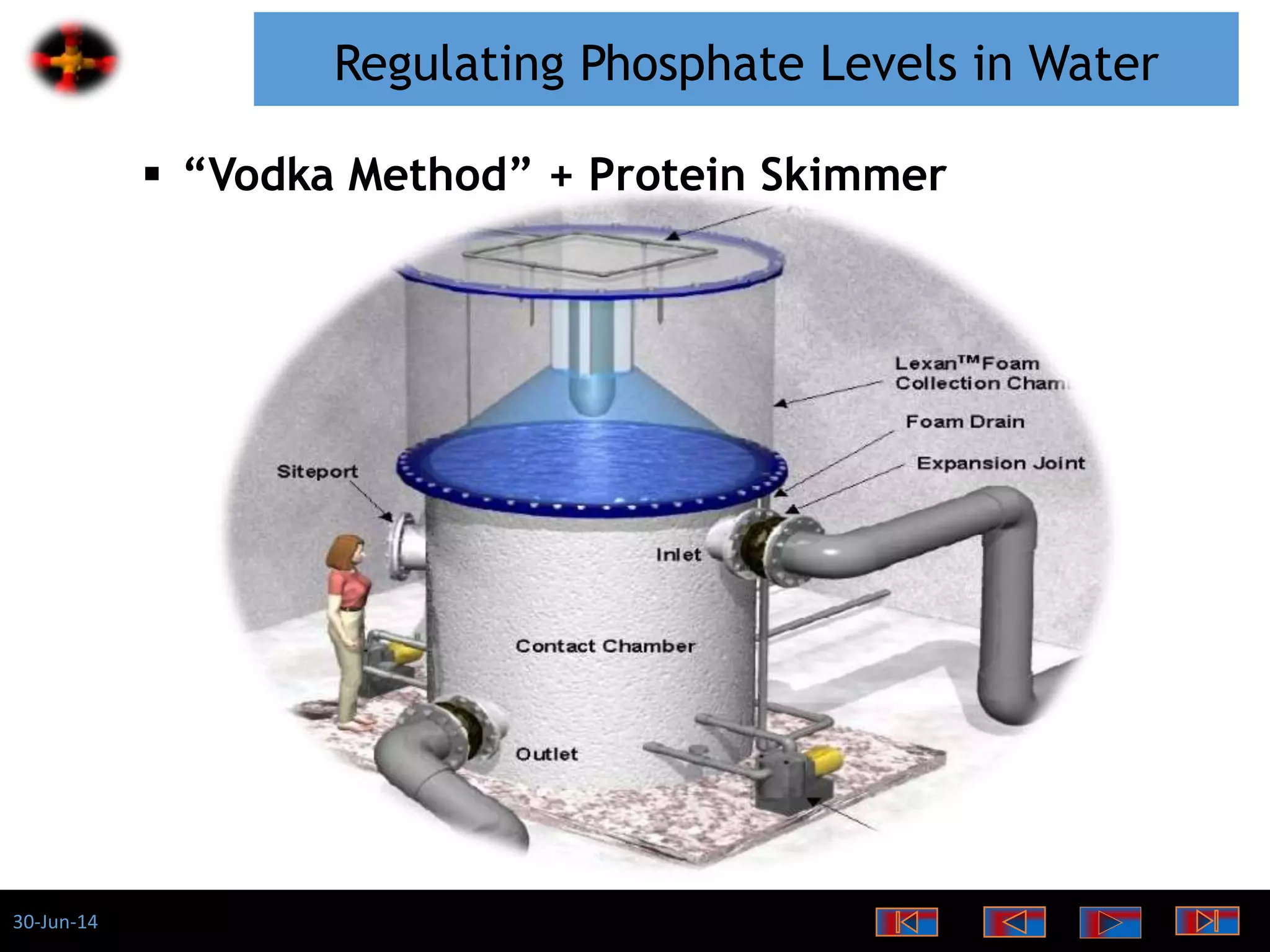
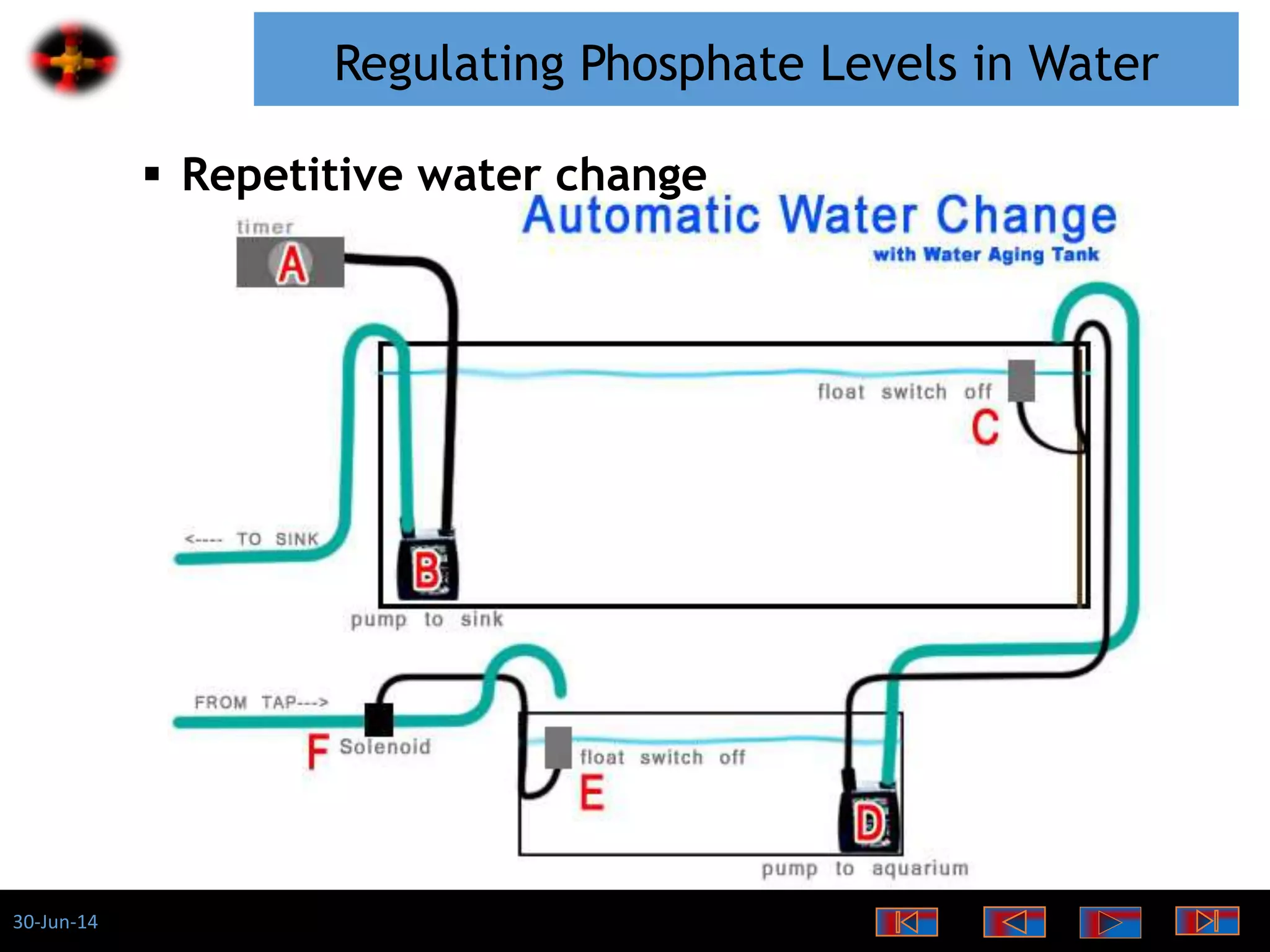
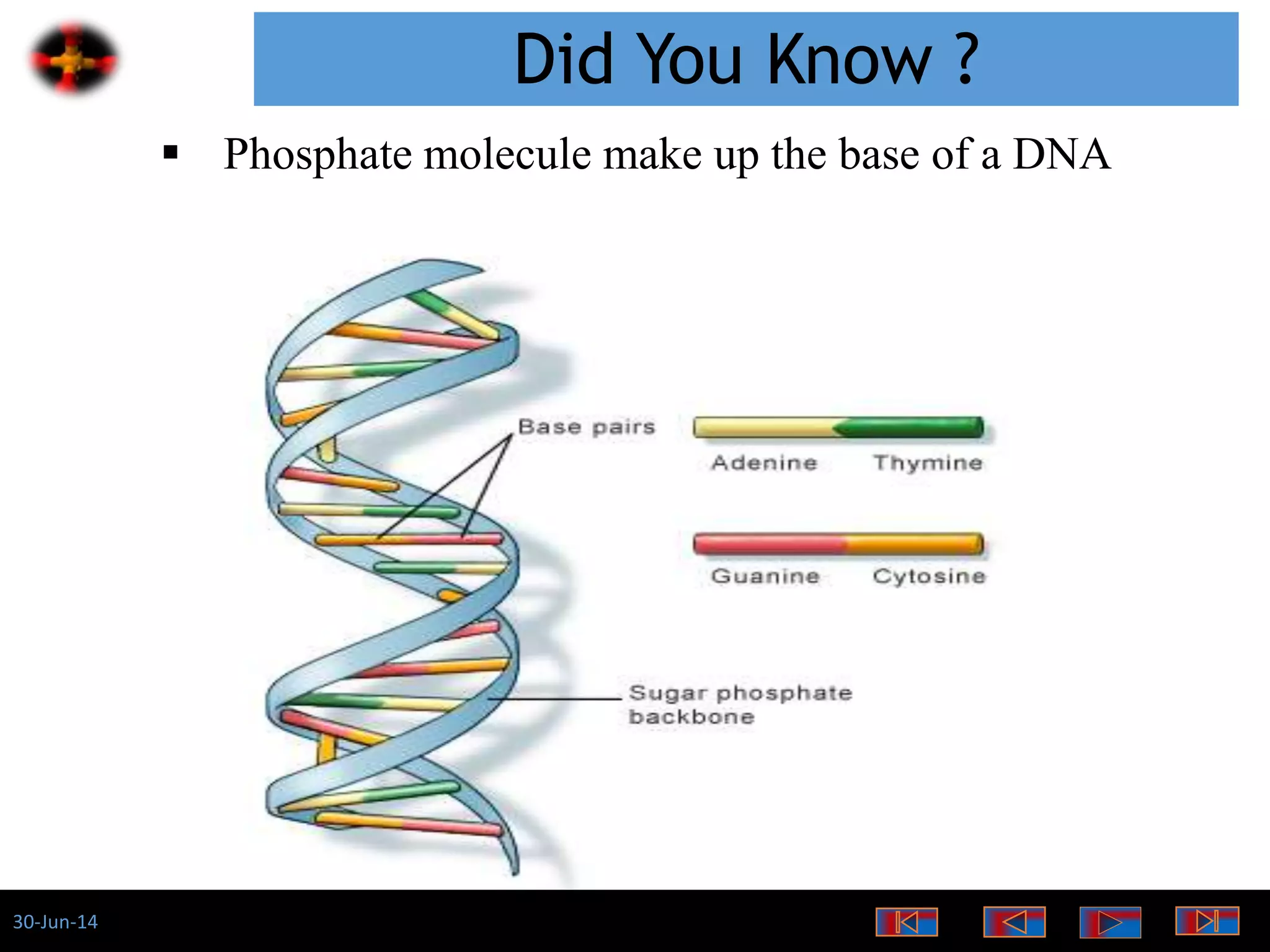
The document discusses the role of phosphates as a water quality parameter, highlighting their forms, uses, and effects on aquatic life along with the testing and regulation of phosphate levels. It emphasizes the importance of phosphates for plant growth, discusses issues like eutrophication due to excess phosphates, and provides information on methods to test and regulate phosphate levels in water. Additionally, it briefly mentions historical facts and influences of phosphates on various water quality parameters.