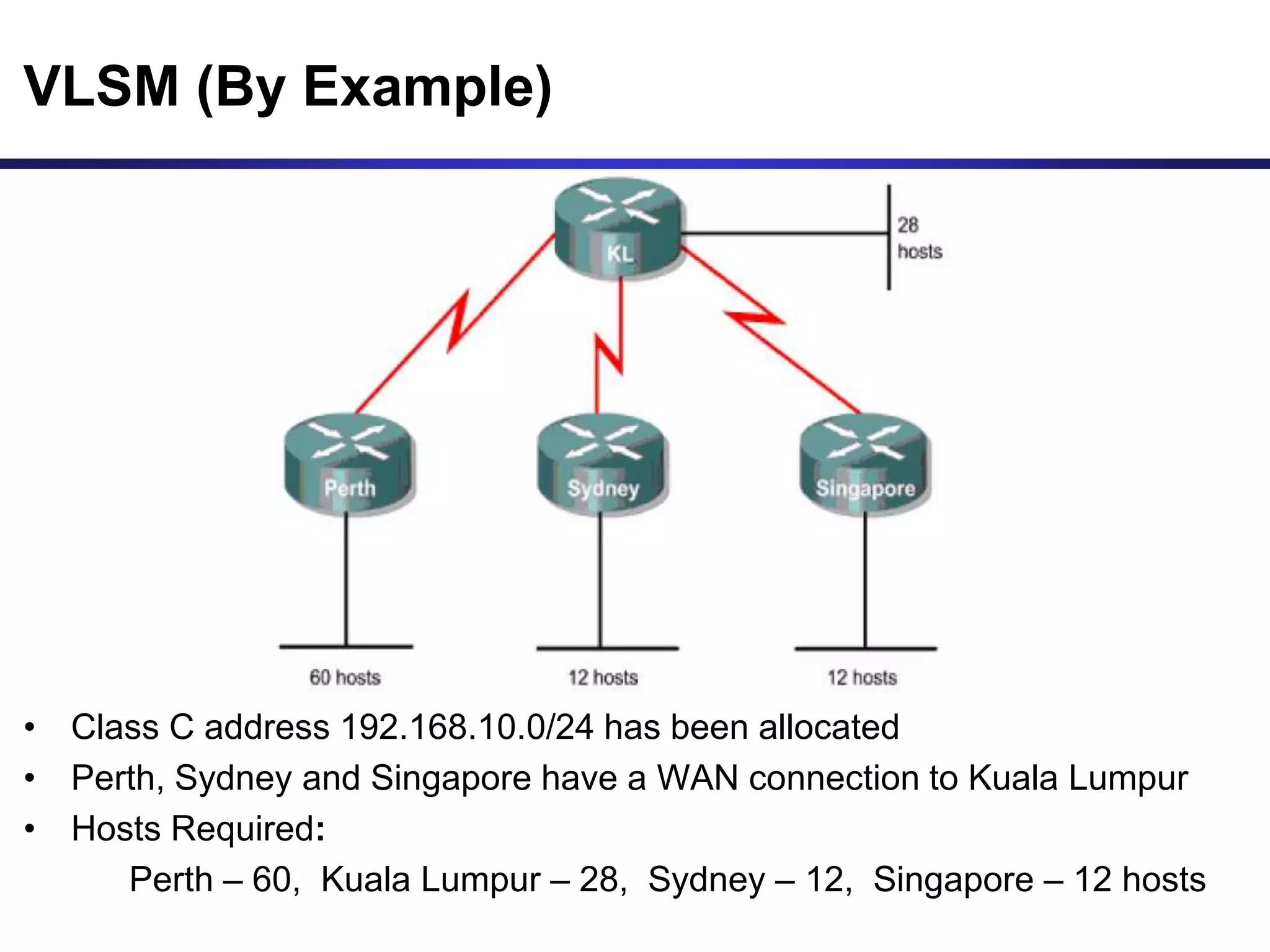
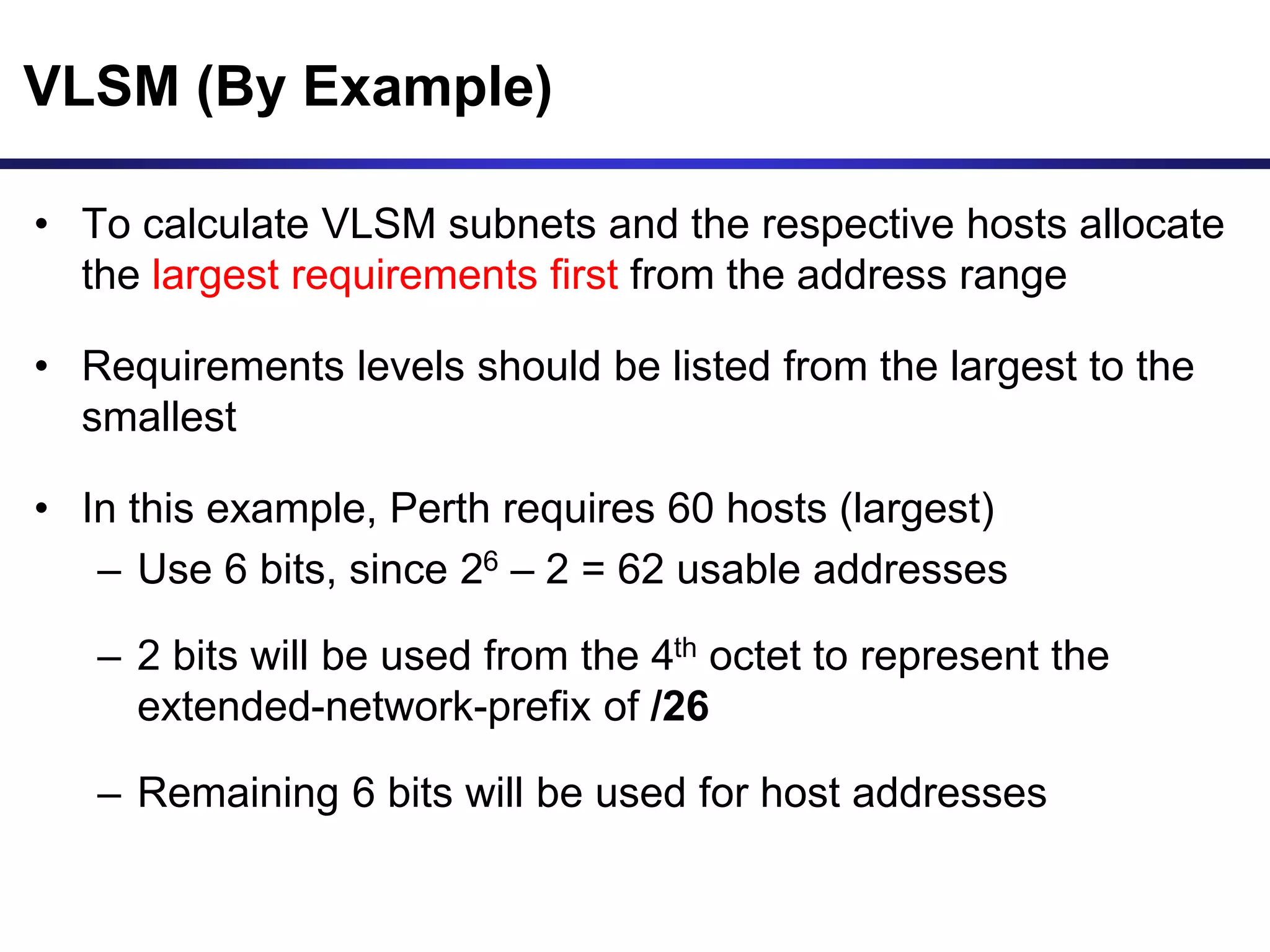
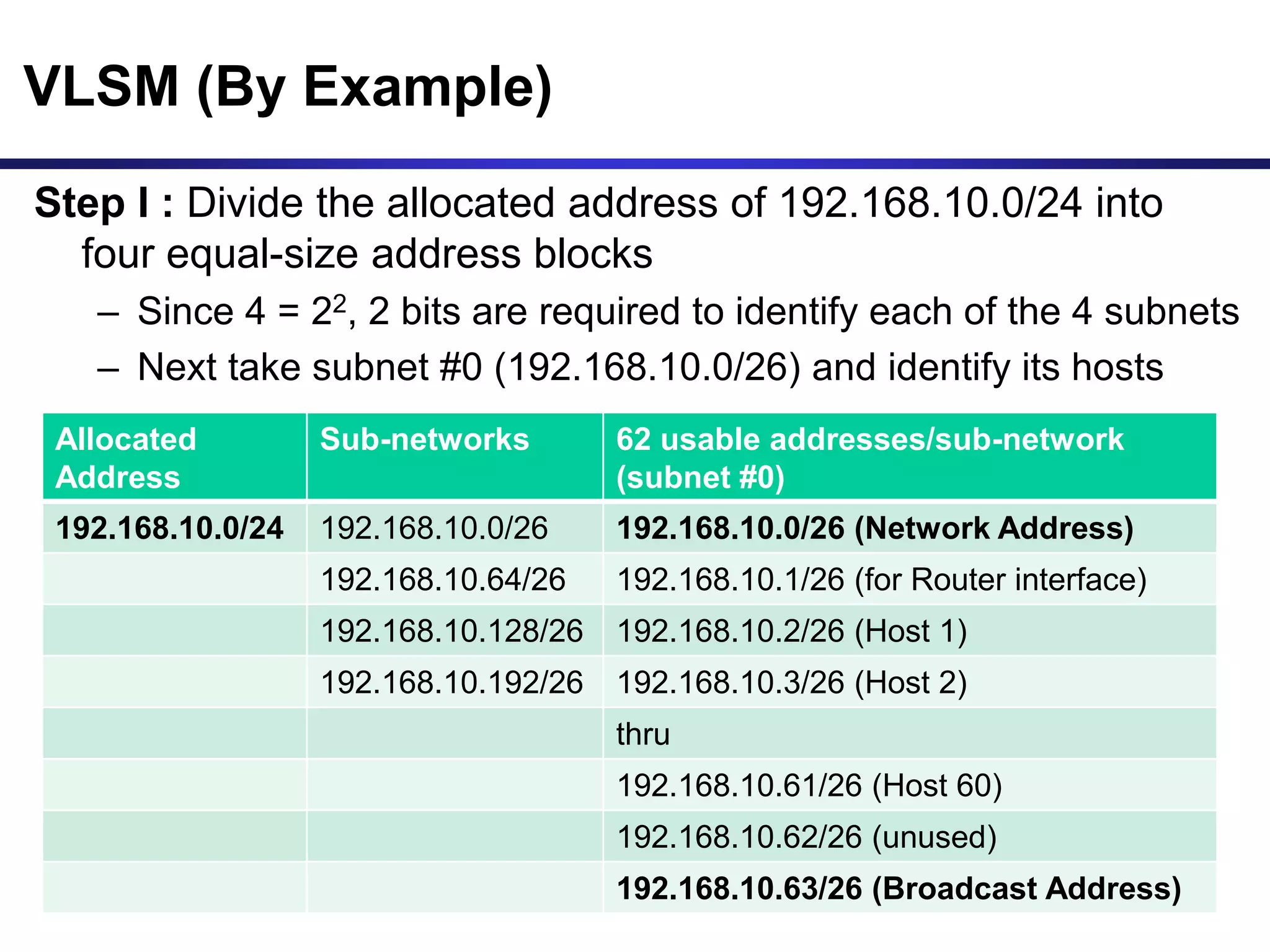
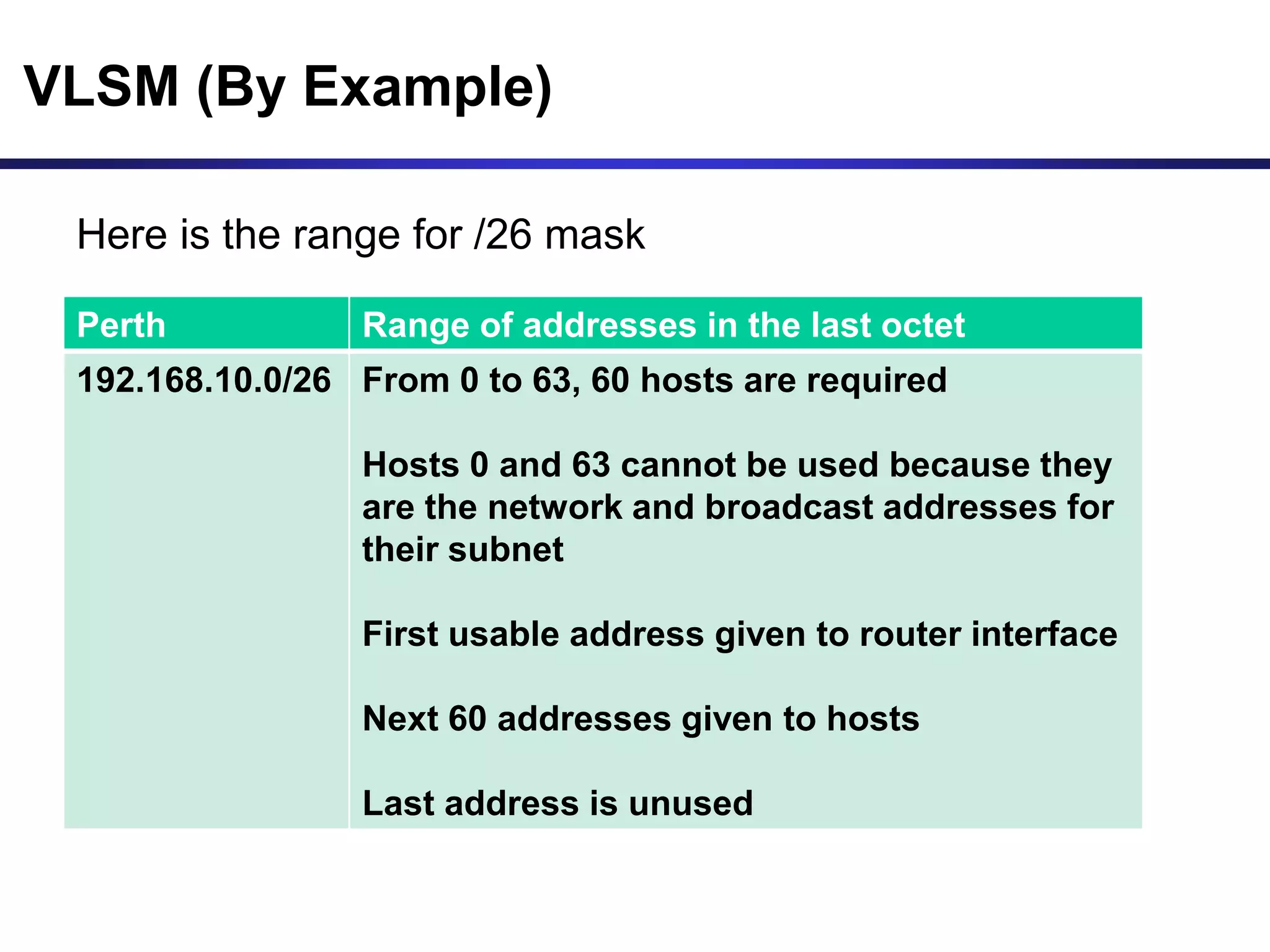
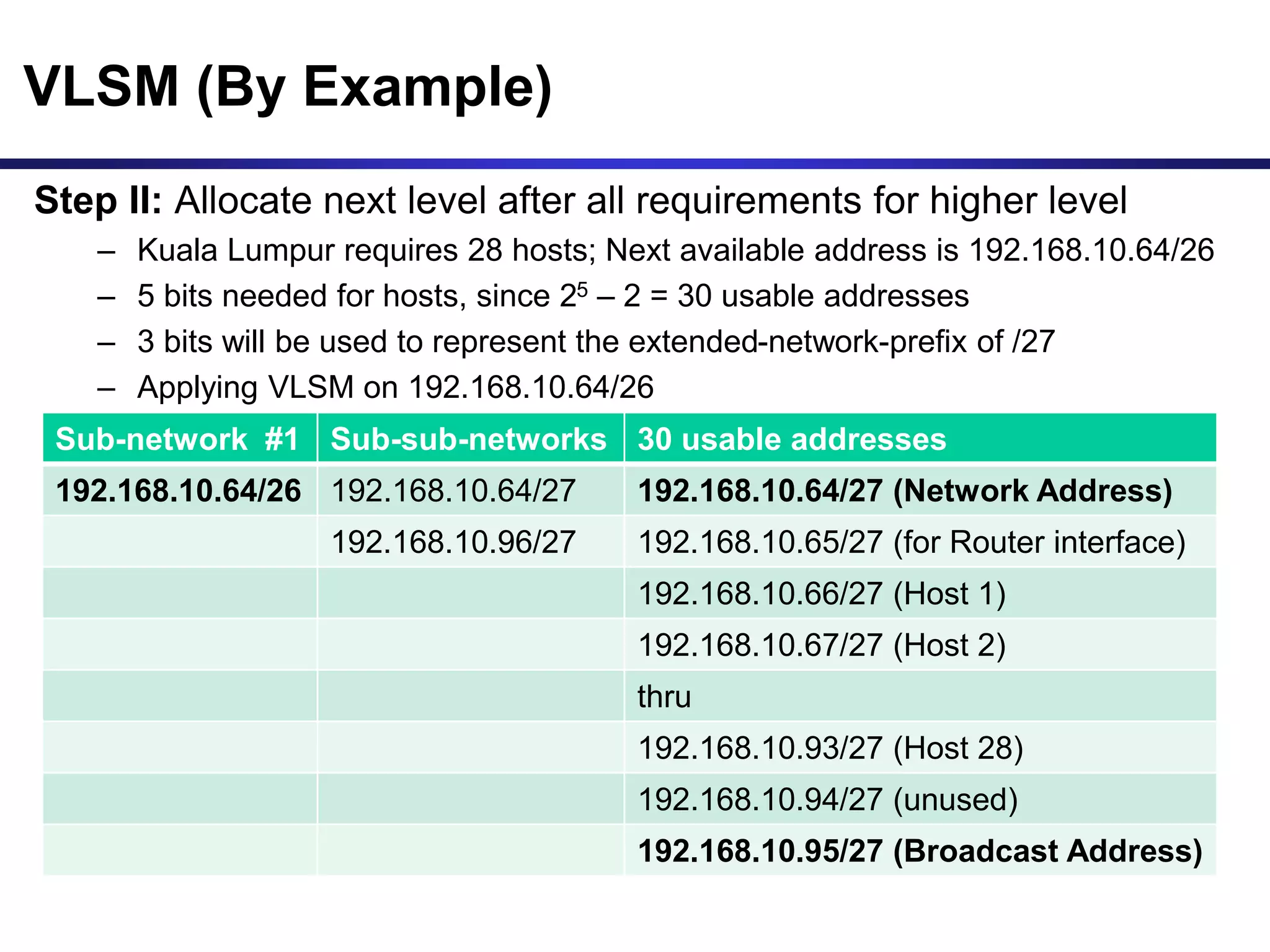
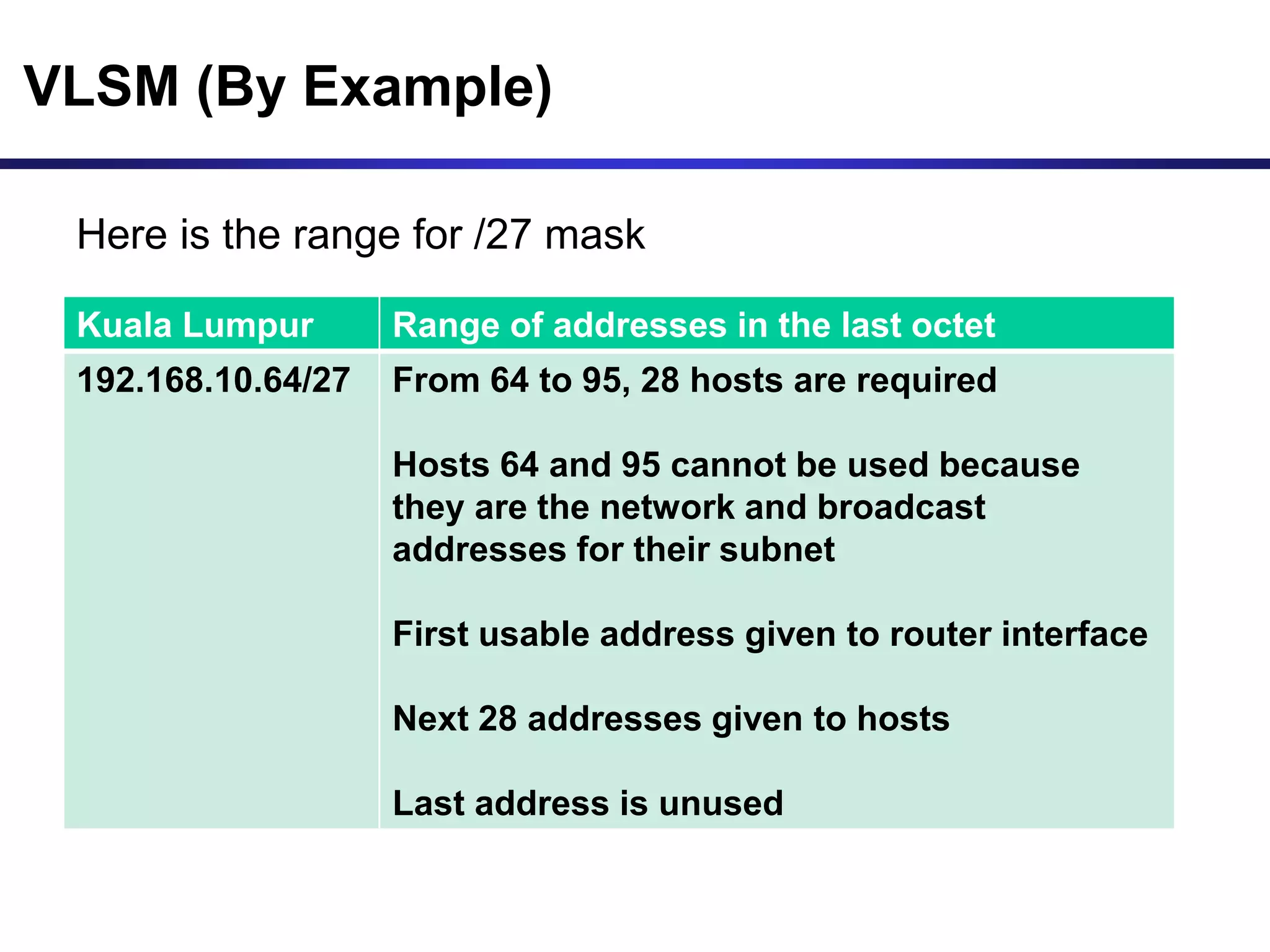
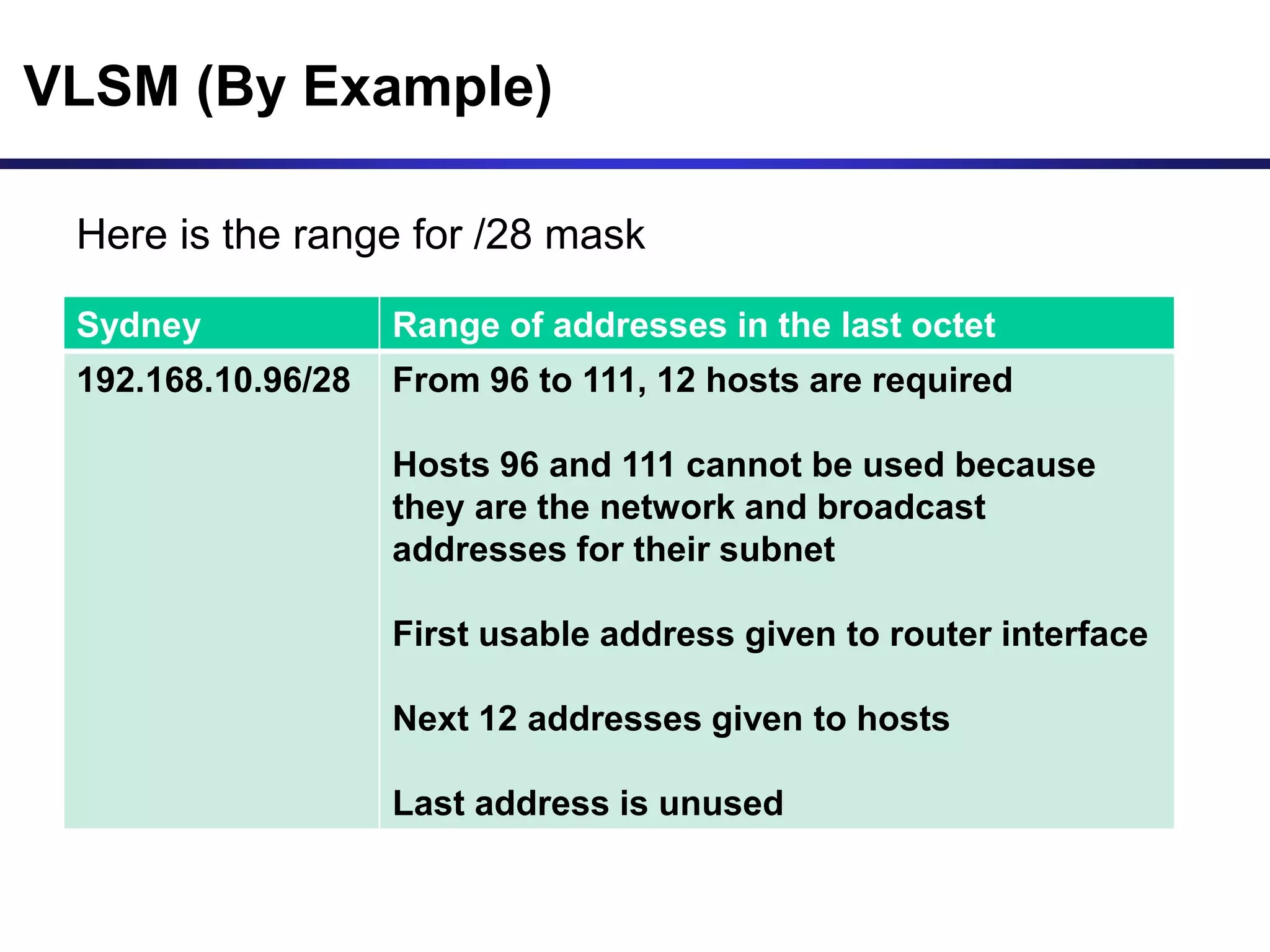
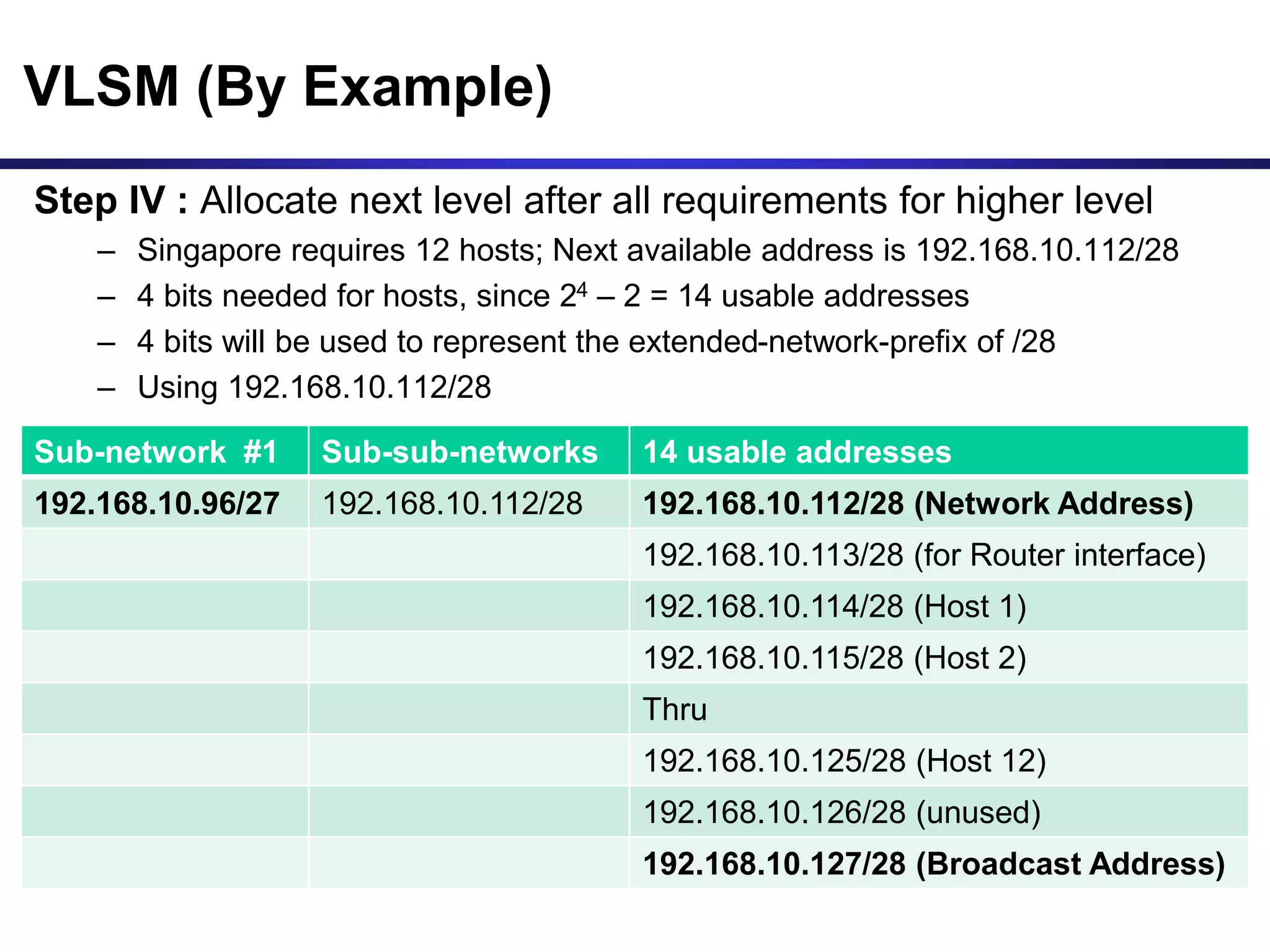
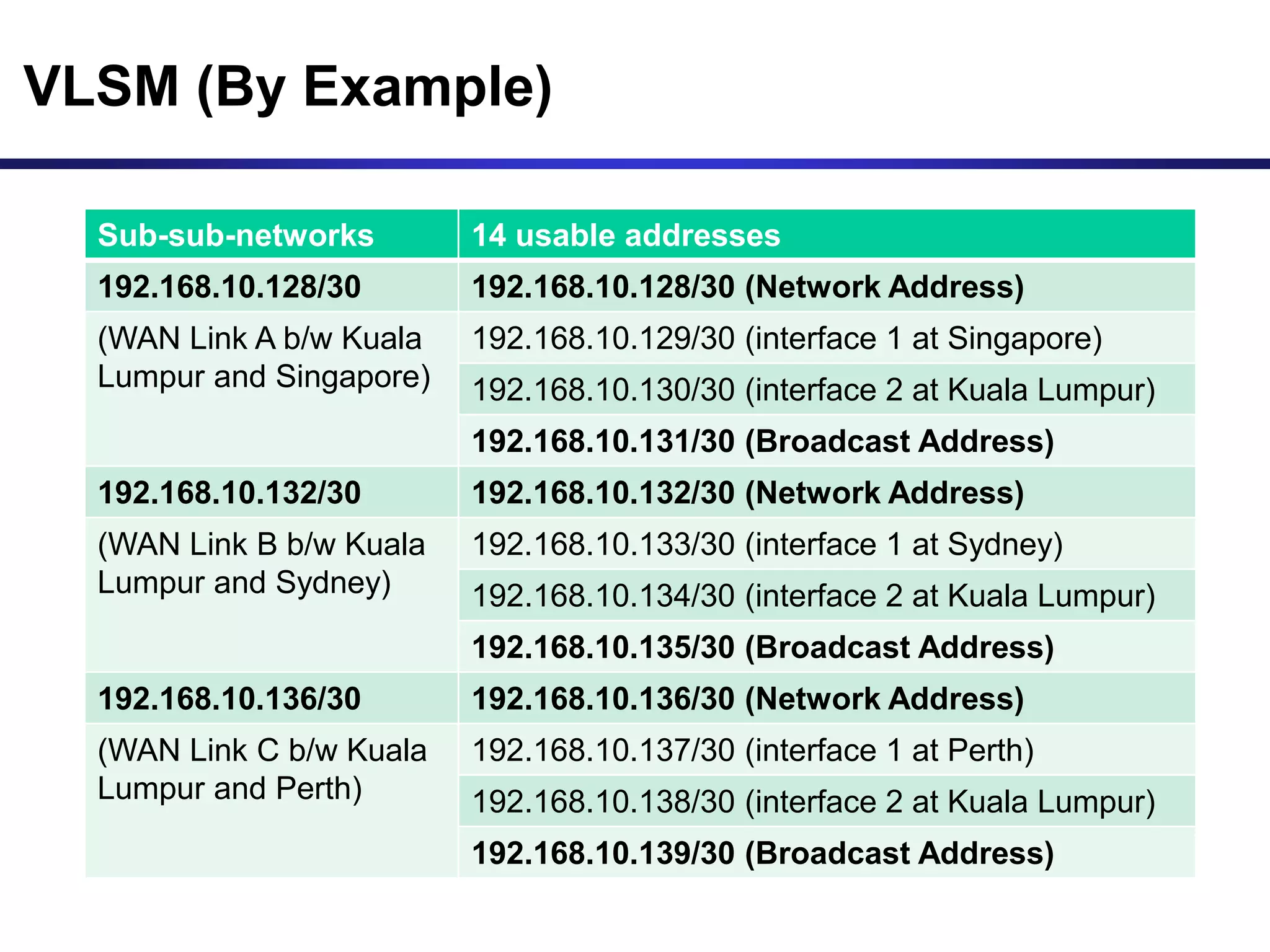
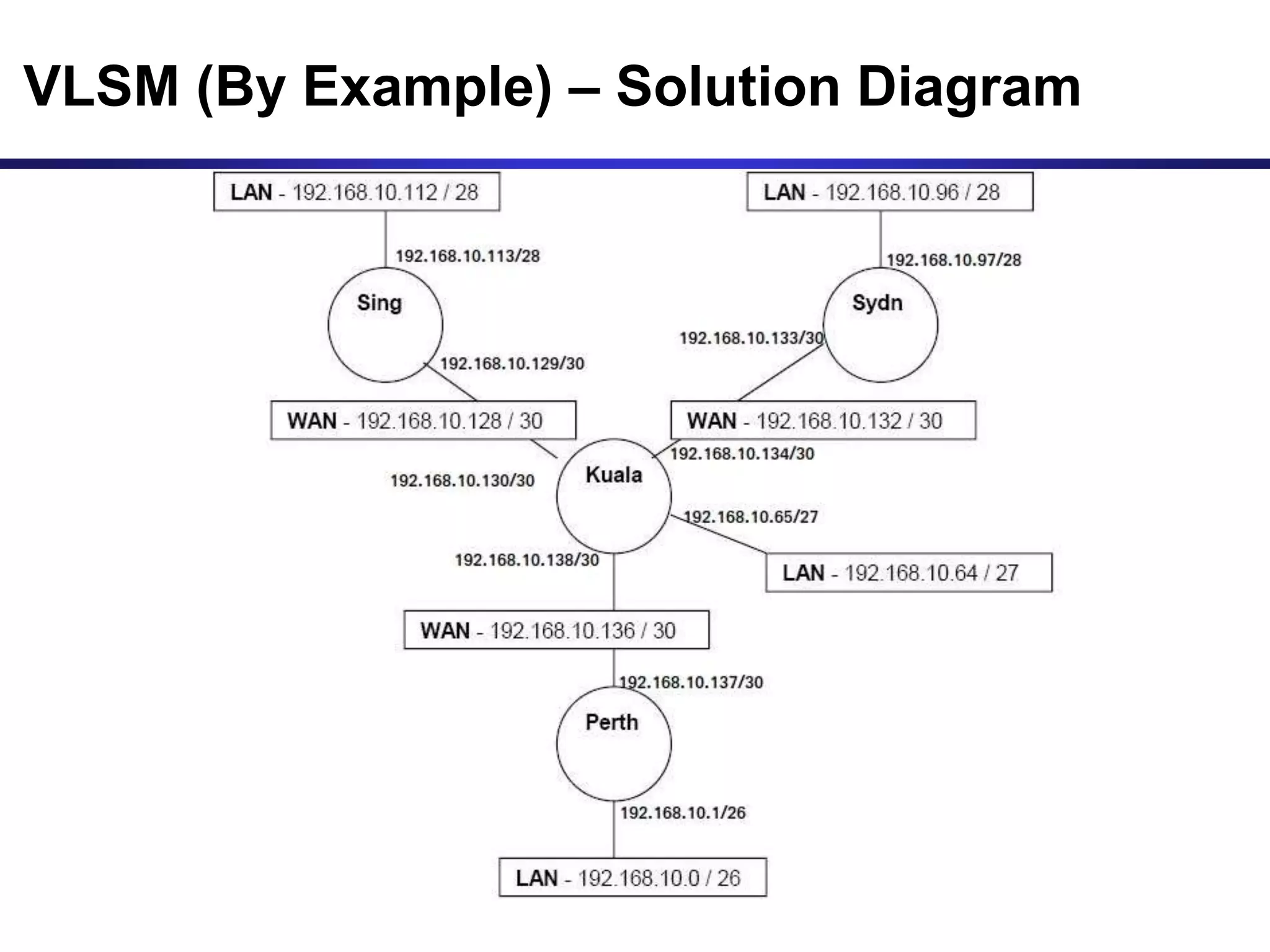
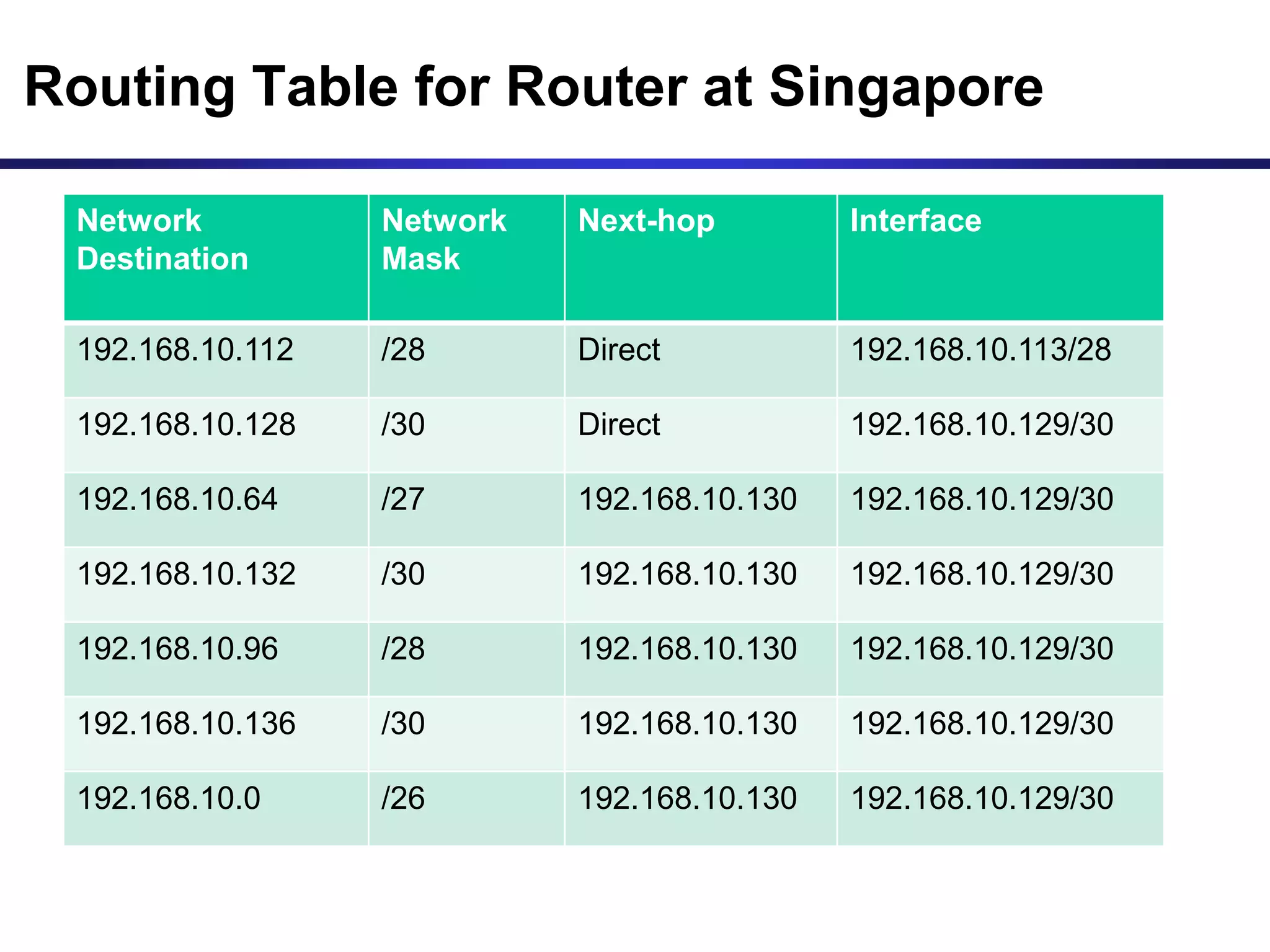
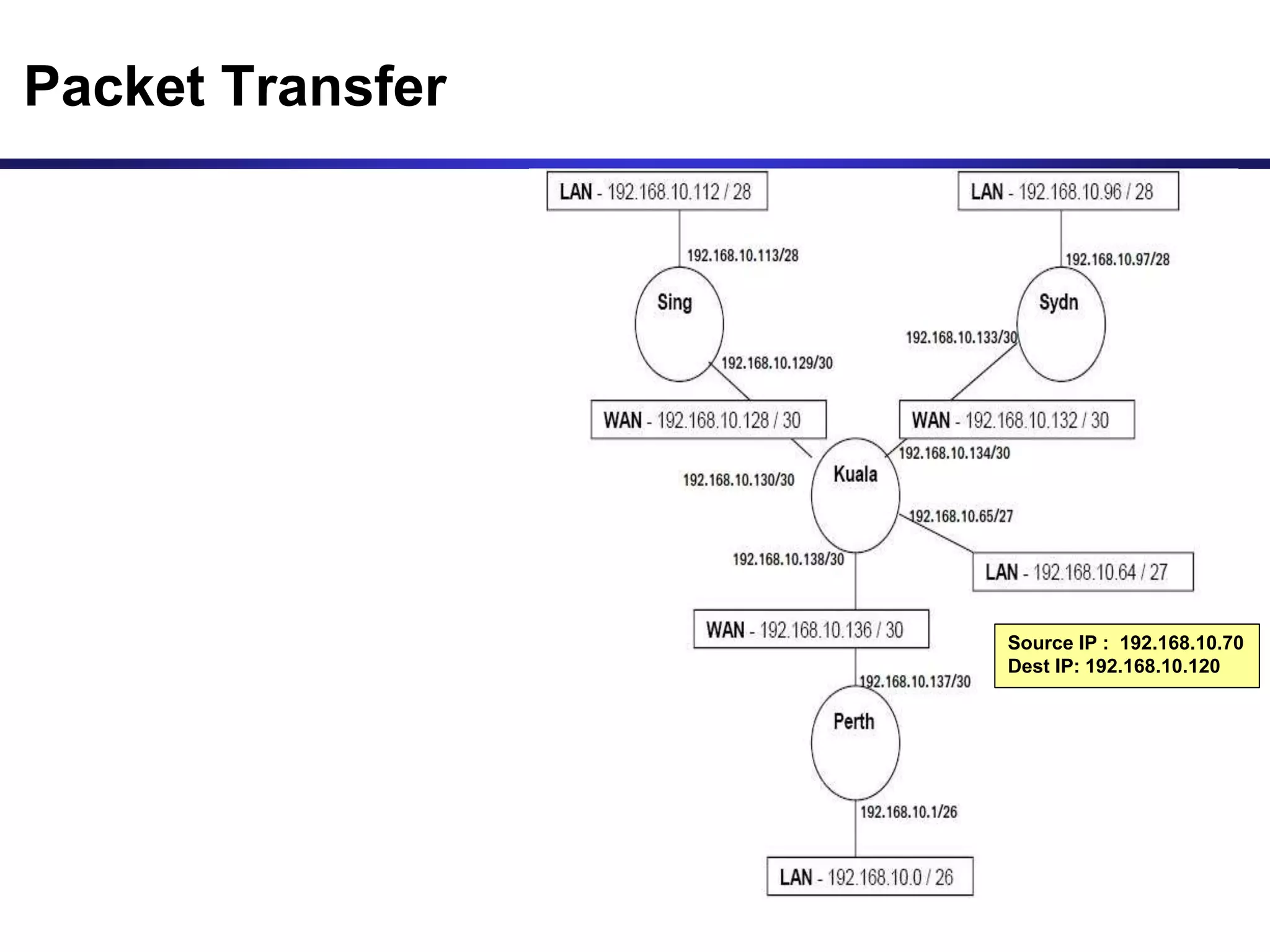
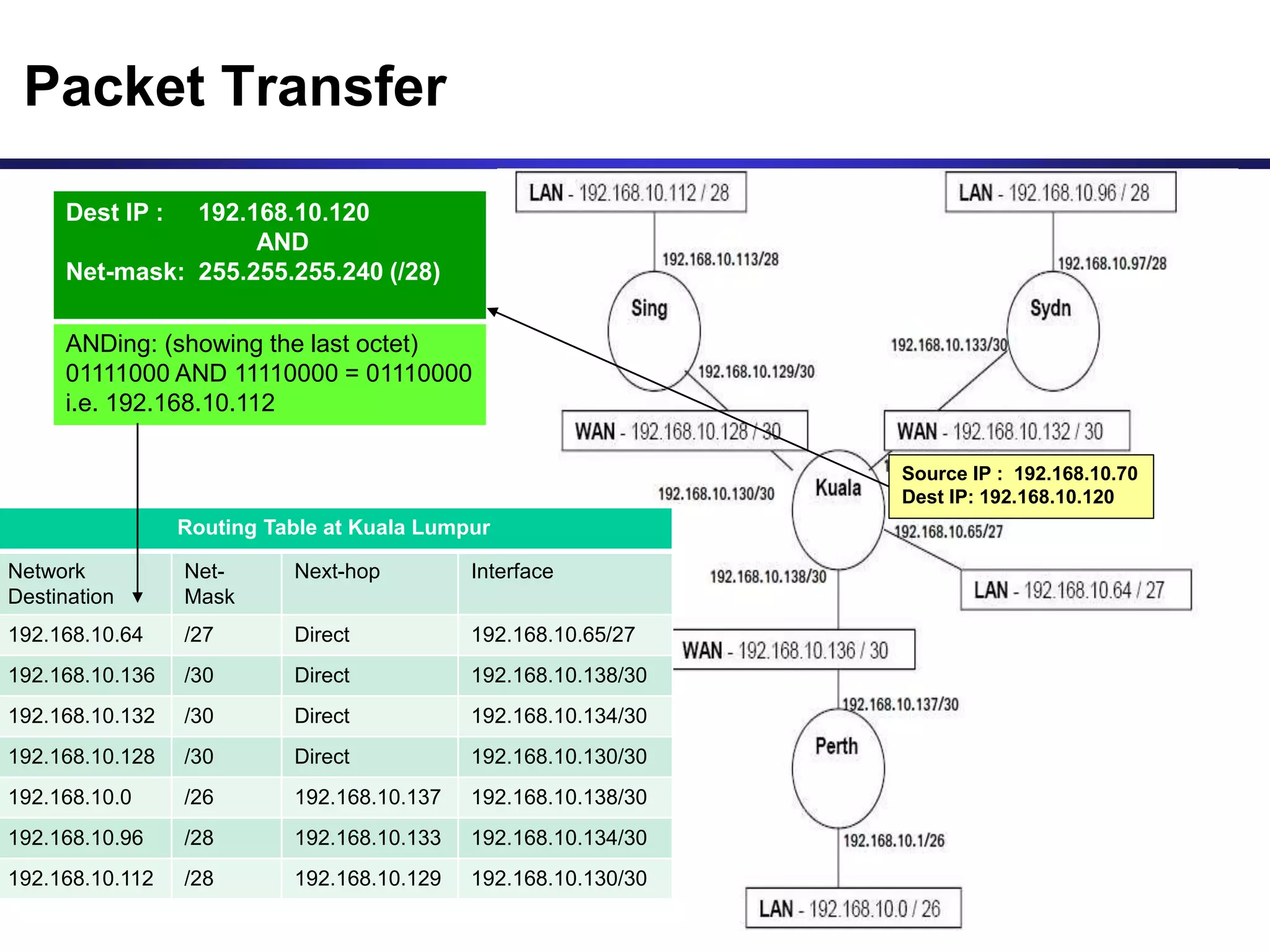
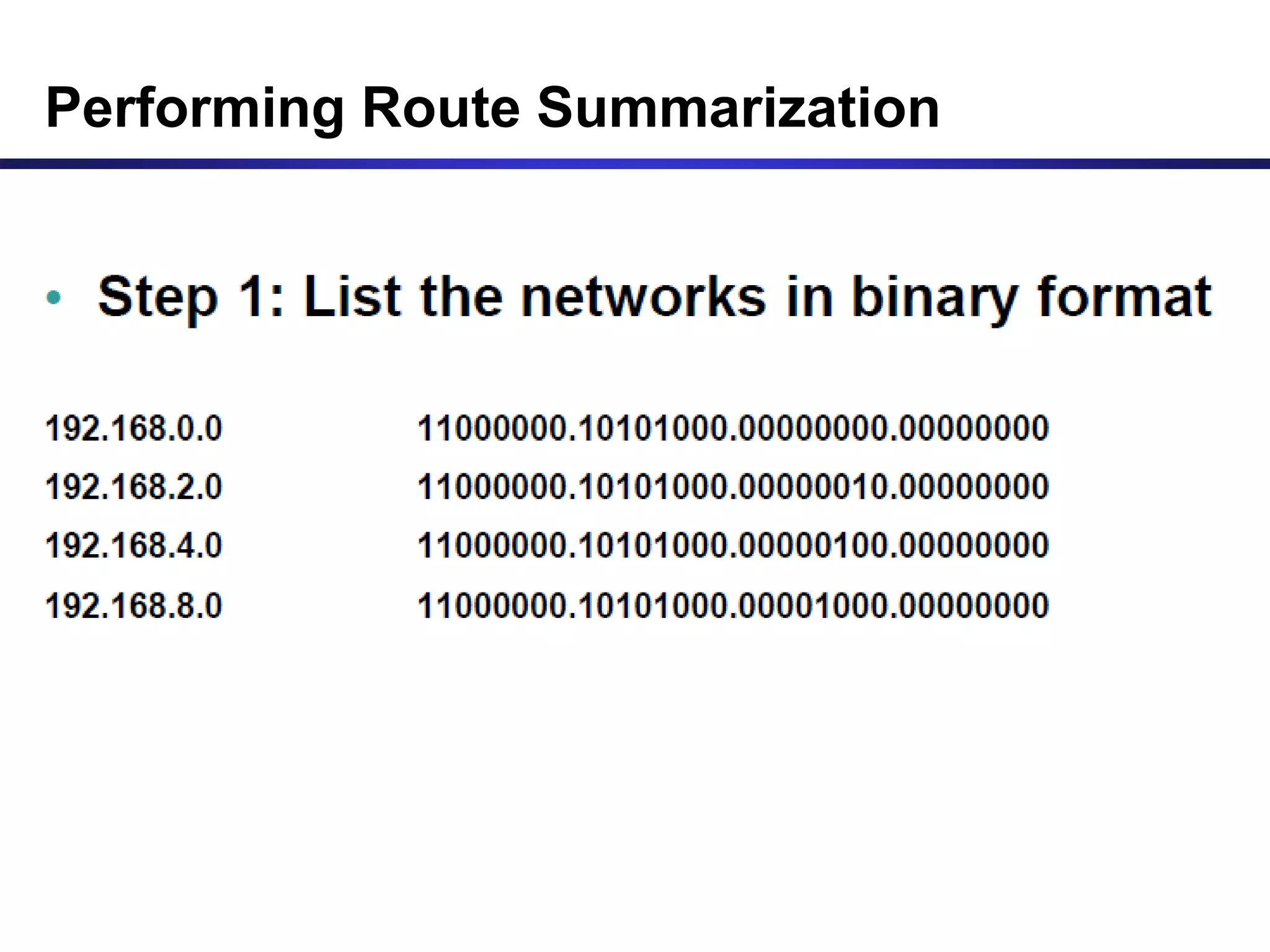
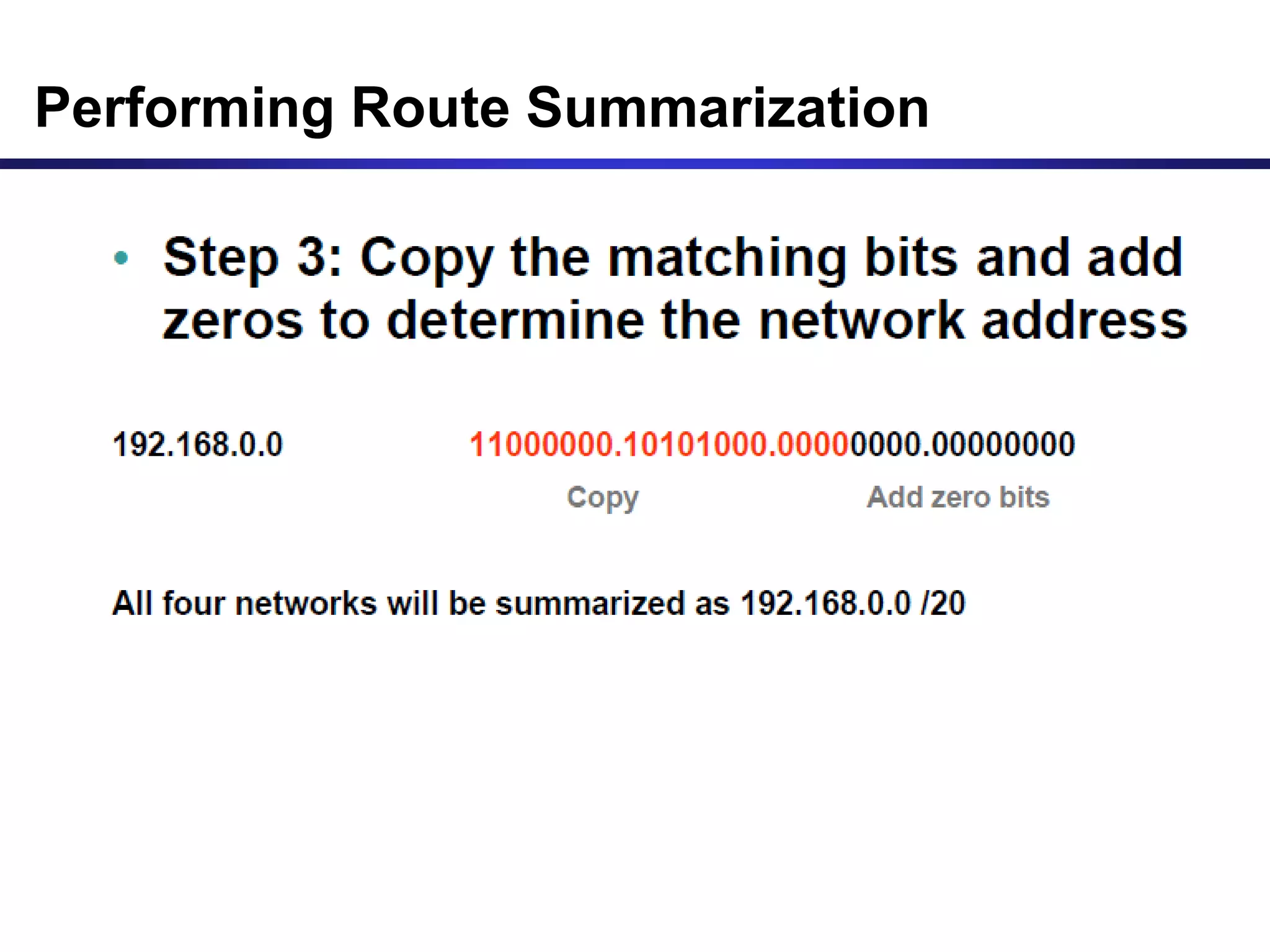
Variable Length Subnet Masking (VLSM) allows for more efficient use of IP addresses and reduces routing information. The document provides an example of how a Class C address of 192.168.10.0/24 is subnetted using VLSM to allocate IP addresses and subnets for locations in Perth, Kuala Lumpur, Sydney, and Singapore based on their host requirements. Detailed routing tables are shown for each location to route packets between the VLSM subnets.