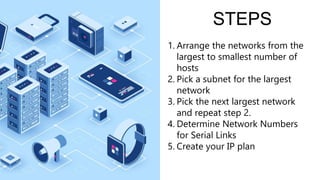
VLSM allows for more efficient use of IP addresses by using different subnet masks for different subnets. It involves "subnetting a subnet" so subnets of different sizes can exist on the same network. The key steps are:
1) Order networks from largest to smallest number of hosts needed
2) Assign the largest network a subnet using the smallest subnet mask that accommodates its host needs
3) Repeat for each smaller network using smaller subnet masks as needed
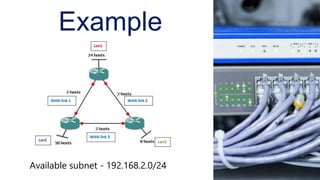
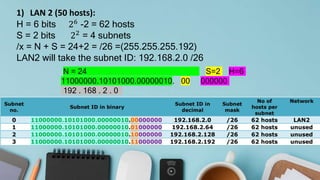
The example shows applying VLSM to a Class C network to create subnets of varying sizes for LANs and WAN links using different subnet masks.