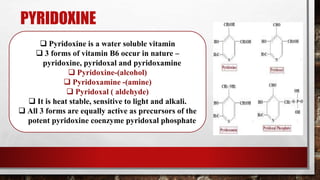
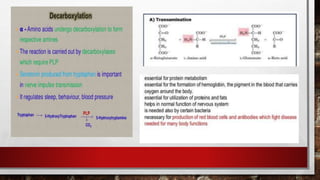
This document summarizes information about the vitamins niacin and pyridoxine. It states that niacin, also called vitamin B3, exists in tissues as nicotinamide and acts as a coenzyme in many metabolic reactions. Niacin is absorbed in the stomach and small intestine and is involved in over 200 oxidation-reduction reactions. Pyridoxine, also known as vitamin B6, exists in three forms - pyridoxine, pyridoxal, and pyridoxamine - and all three forms are converted to the active coenzyme pyridoxal phosphate. Pyridoxine is absorbed in the small intestine and transported bound to albumin, then stored in tissues.