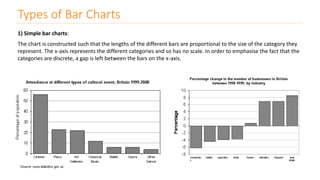
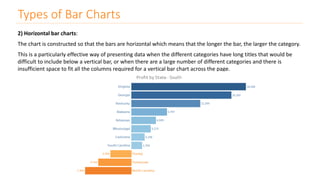
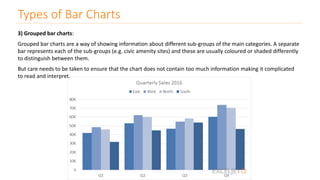
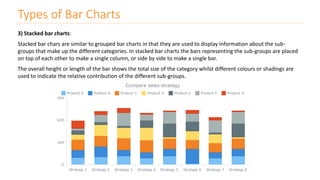
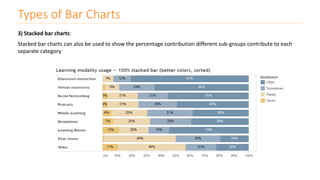
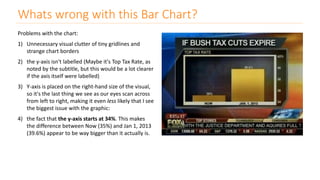
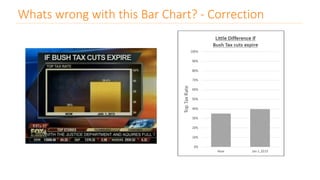
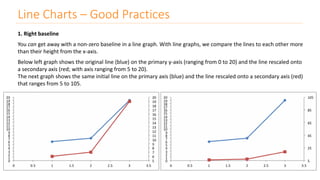
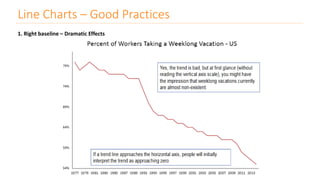
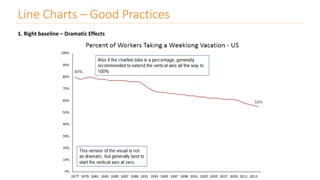
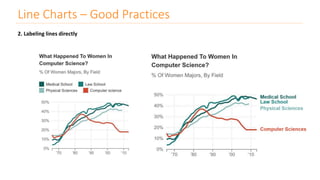
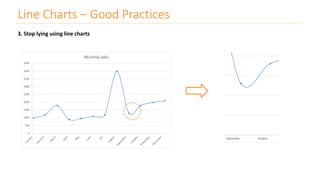
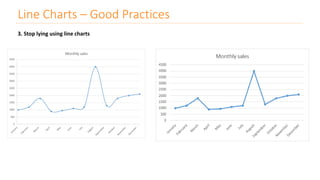
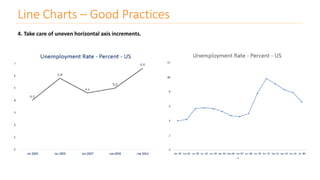
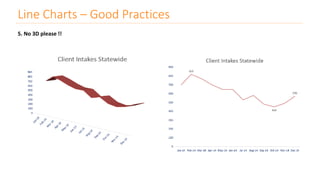
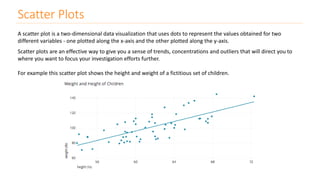
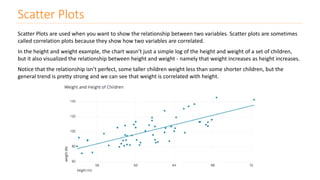
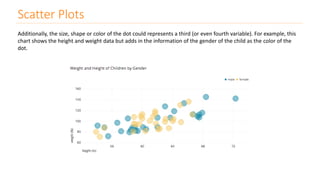
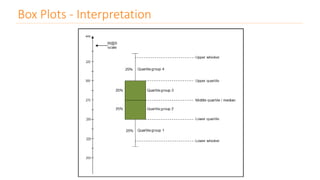
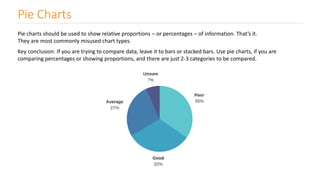
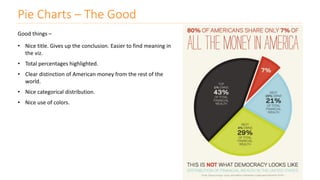
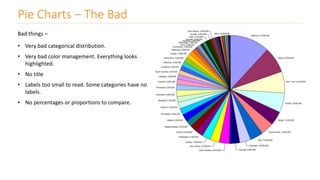
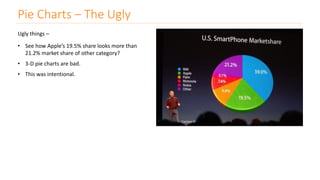
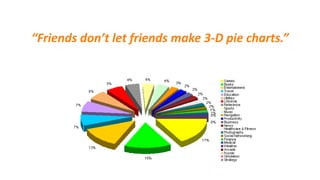
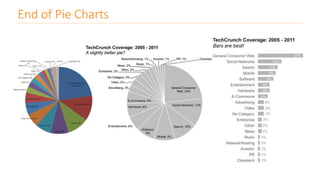
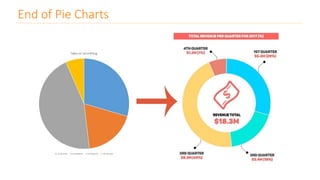
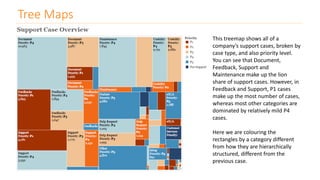
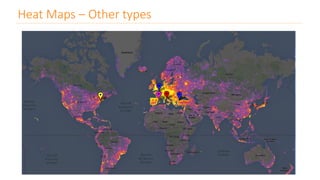
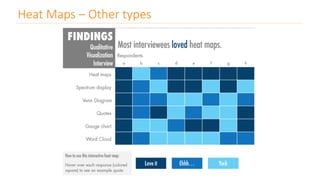
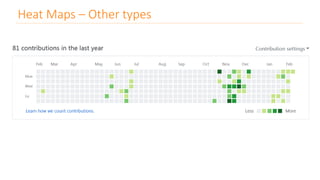
The document discusses various types of data visualizations, particularly focusing on bar charts, line charts, scatter plots, box plots, pie charts, tree maps, and heat maps, emphasizing their appropriate applications and best practices. It highlights the importance of clear, accurate visual representation of data, avoiding common pitfalls such as starting axes at non-zero values and misusing pie charts. Overall, the aim of data visualization is to enhance understanding and insight from complex datasets.