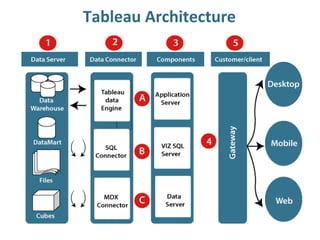
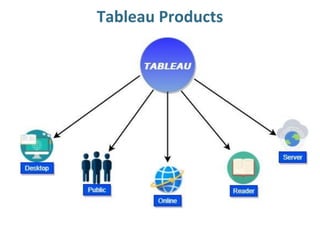
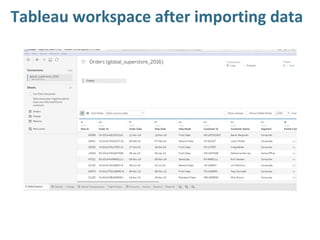
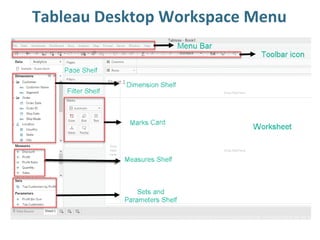
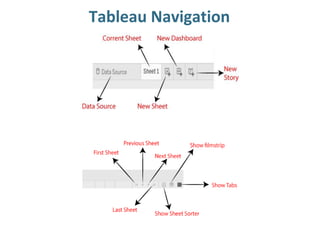
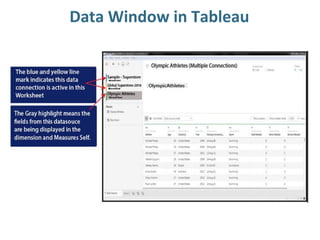
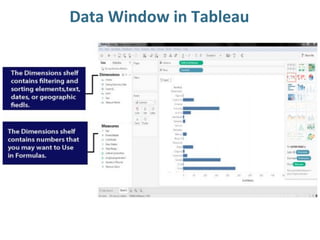
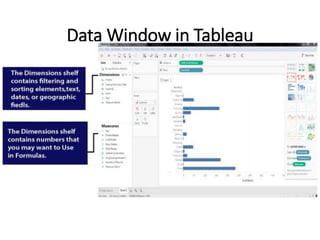
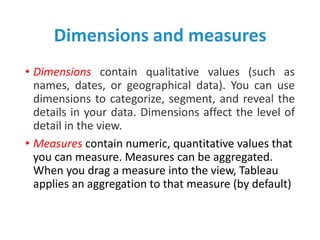
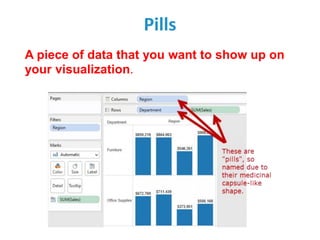
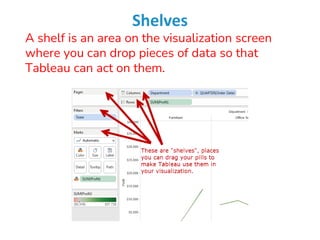
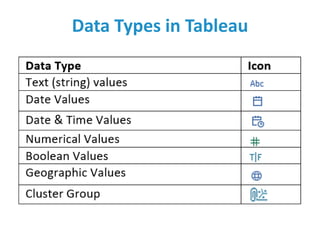
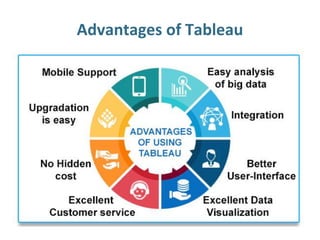
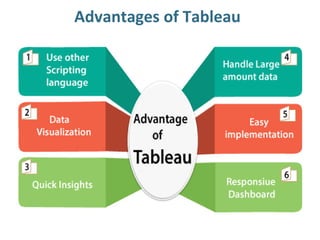
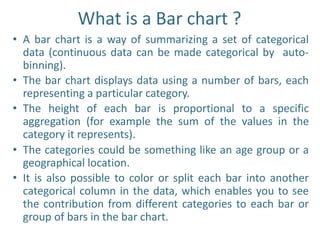
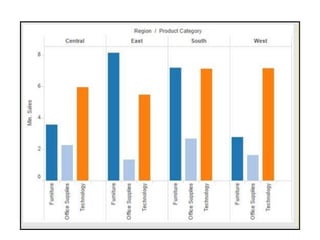
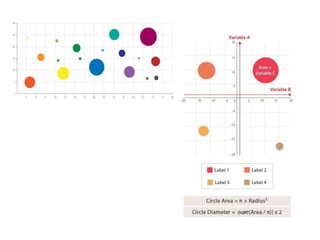
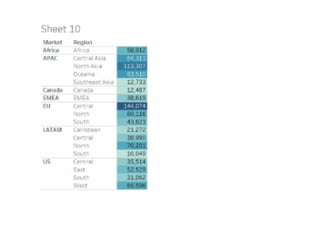
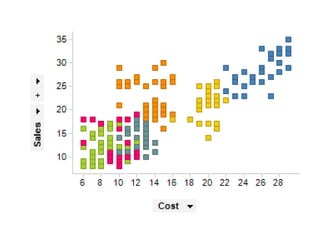
Tableau is a data visualization and business intelligence tool designed for analyzing large data sets, founded in January 2003 and currently owned by Salesforce Inc. The document provides an overview of various chart types, including bar charts, pie charts, and bubble charts, along with their advantages and disadvantages for data representation. It also covers Tableau's functionality, including dimensions and measures, and how different visualizations can be utilized to interpret and analyze data effectively.