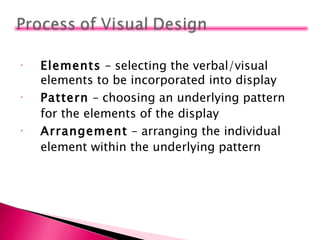
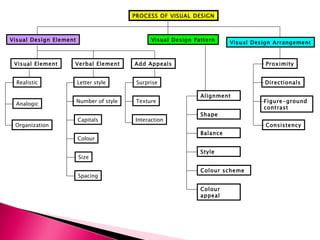
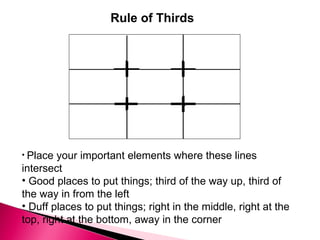
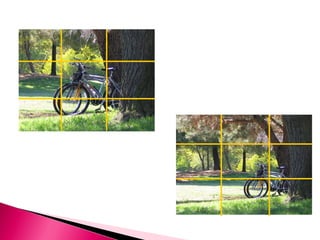
1) The document discusses various principles of visual design including visual elements, patterns, and arrangements. It addresses selecting appropriate elements, choosing underlying patterns, and arranging individual elements within the chosen pattern.
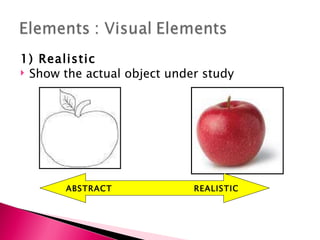
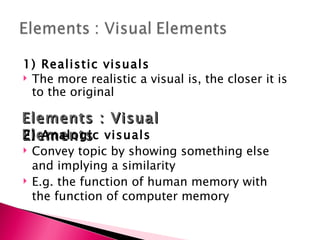
2) Key visual design elements discussed are realistic, analogic, and organizational visuals. Design patterns must consider principles like balance, proximity, and alignment. Effective arrangements focus attention on important messages and engage viewers.
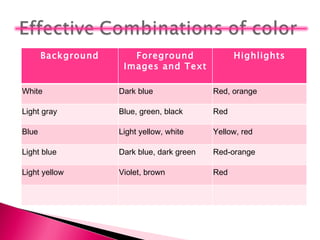
3) Cultural and audience factors like color preferences must also be considered. Visuals should be tailored based on whether the audience is children or adults.