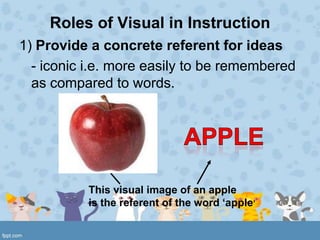
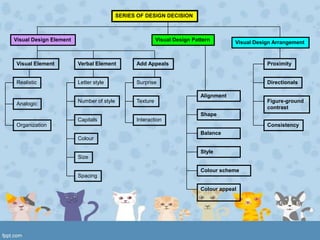
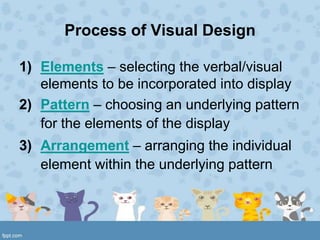
Visuals play important roles in instruction by providing concrete referents, motivating learners, and simplifying complex information. Effective visual design considers visual elements, patterns, and arrangement. Elements include realistic, analogic, and organizational visuals as well as consistent verbal elements like letter style and size. Effective patterns apply principles of alignment, shape, balance, style, and color scheme. Arrangement maximizes proximity of related items, uses directional cues, and employs figure-ground contrast and consistency. Proper visual planning and tools help create clear and impactful visual aids.