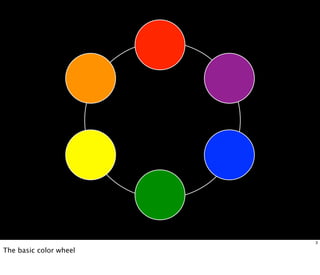
This document provides an overview of basic color theory concepts. It discusses the color wheel and primary, secondary, and tertiary colors. It explains that black absorbs all colors while white reflects all colors. Complementary colors are directly across from each other on the color wheel, while analogous colors are adjacent. Monochromatic color schemes use tints and shades of a single color. Warm colors tend to advance visually while cool colors recede. Color is influenced by its surroundings and can affect mood. The document also covers color systems for print versus screens, color meanings, and readability through color contrast.