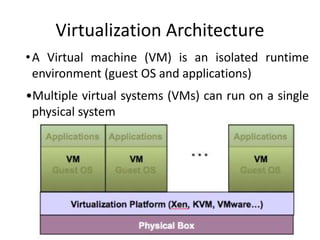
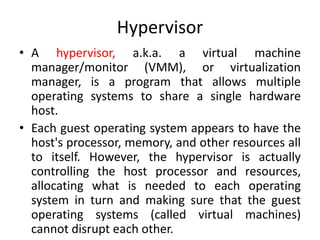
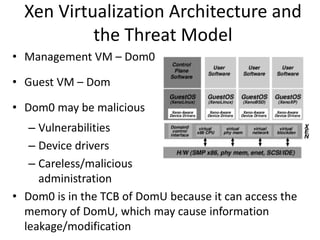
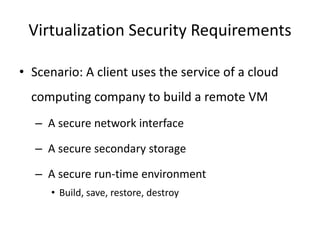
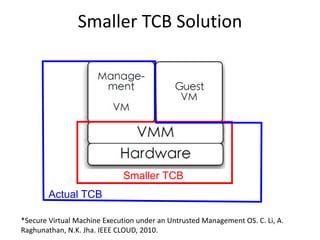
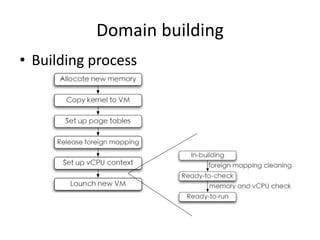
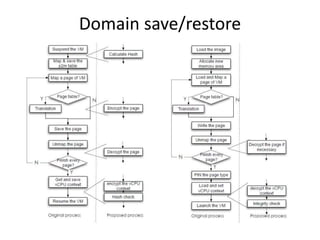
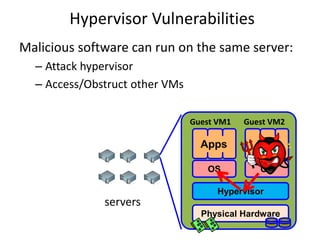
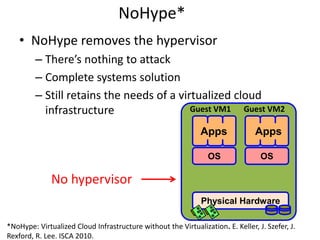
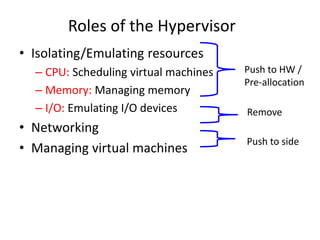
Virtualization allows multiple operating systems to run on a single physical system by sharing hardware resources. It is used to improve efficiency and reduce costs. A virtual machine (VM) isolates a guest operating system and applications. The hypervisor controls host resources and allocates them to VMs. Benefits include resource sharing, isolation, hardware independence, and portability. Cloud computing takes virtualization further by offering on-demand resources over the internet. Security challenges include the large trusted computing base of the hypervisor. Solutions aim to reduce the TCB by removing the hypervisor or isolating its functions in hardware and management software.